Melon and fruit antiseptic and fresh-keeping agent, preparation method thereof and melon and fruit storage method
A preservative, melon and fruit technology, applied in the direction of protecting fruits/vegetables with a protective layer, preserving fruits/vegetables and food ingredients by freezing/refrigeration, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
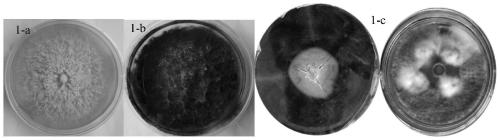
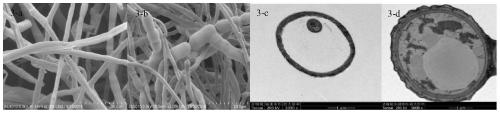
[0039] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the preparation method of the kiwi fruit antiseptic and fresh-keeping agent of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0040] 1. Target the pathogens that affect the rot of kiwifruit.
[0041] a. Take Hongyang kiwi as the test fruit, the same below. High-throughput sequencing (Illumina HiSeq) was used to understand the main dominant pathogen species of kiwi fruit soft rot.
[0042] b. Isolation of major dominant pathogens. Take the kiwi fruit pulp (0.2cm away from the lesion), rinse with sterile water 3 times, soak in 70% ethanol for 8 seconds, then rinse with plenty of sterile water, and blot the sterile water with sterile paper Afterwards, a small amount of tissue was inoculated on a PDA plate, cultured in a 27°C incubator in the dark, 4 days after culture.
[0043] b. Purification of pathogenic bacteria. Pick the dominant colonies in the above-mentioned plate and inoculate them on another new plate. Cultivate for 4 days in a 27°C...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the preparation method of the kiwi fruit antiseptic and fresh-keeping agent of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0080] 1. Target the pathogens that affect the rot of kiwifruit.
[0081] a. Take the jade kiwi fruit as the test fruit, the same below. High-throughput sequencing (Illumina HiSeq) was used to understand the main dominant pathogen species of kiwi fruit soft rot.
[0082] b. Isolation of major dominant pathogens. Take the kiwi fruit pulp (0.25cm away from the diseased spot), rinse with sterile water 3 times, soak in 75% ethanol for 8 seconds, rinse with plenty of sterile water, and blot the sterile water with sterile paper Afterwards, a small amount of tissue was inoculated on a PDA plate, cultured in a 27°C incubator in the dark, 4 days after culture.
[0083] b. Purification of pathogenic bacteria. Pick the dominant colonies in the above-mentioned plate and inoculate them on another new plate. Incubate for 4 days i...
Embodiment 3
[0110] The preparation method of melon and fruit antiseptic and fresh-keeping agent includes the following steps:
[0111] 1. Configuration of antiseptic and fresh-keeping agent
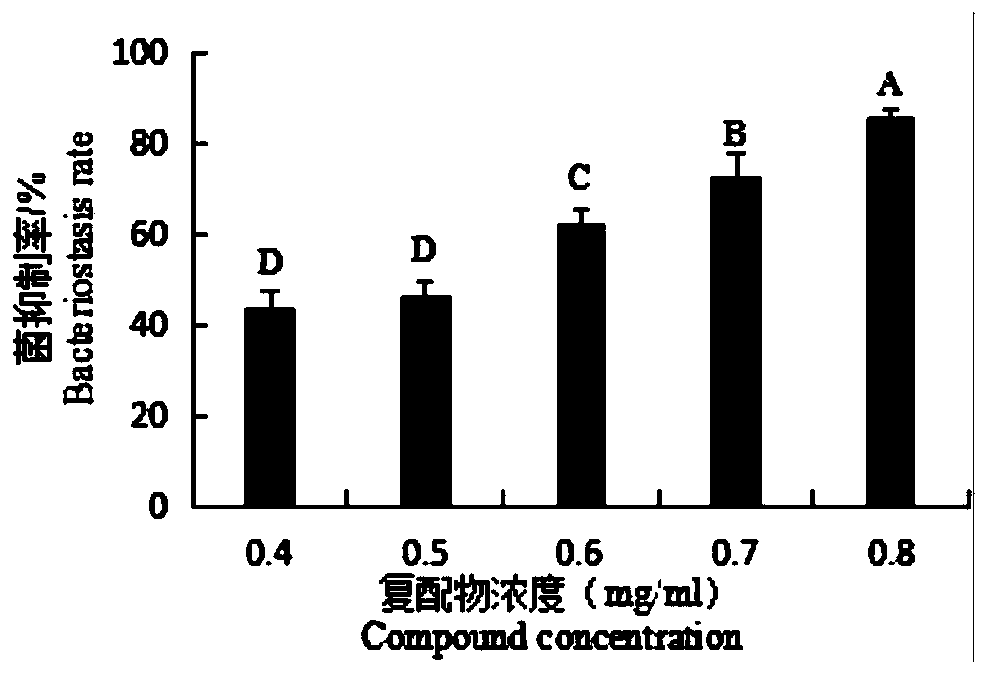
[0112] a. According to the results of the previous collaborative antibacterial test, and further optimization. Weigh the above-mentioned reagents according to the formula. Among them, the oil-tea meal extract is both a sterilization and a mixed solvent. The emulsifying thickener is a mixture of chitosan and sodium alginate. Scutellaria baicalensis extract 0.05%, clove oil 0.15%, cinnamon oil 0.05%, saponin thorn extract 0.06%, patchouli oil 0.17%, calamus oil 0.17%, camellia meal extract 0.5%, chitosan 0.30%, chlorinated Calcium 1.5%, sodium alginate 7%, carrageenan 2.5%, citric acid 0.3%; the balance is water, and the total amount of raw materials is 100%.
[0113] b. First, mix the extract of scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, clove oil, cinnamon oil, saponaria saponaria extract, patchouli oil, and calamus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com