Analysis method for determining high-content molybdenum element in metal material by potentiometric titration
A metal material, potentiometric titration technology, applied in chemical analysis by titration, electrochemical variables of materials, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of lack of rapid and accurate determination of high-content molybdenum in metal materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
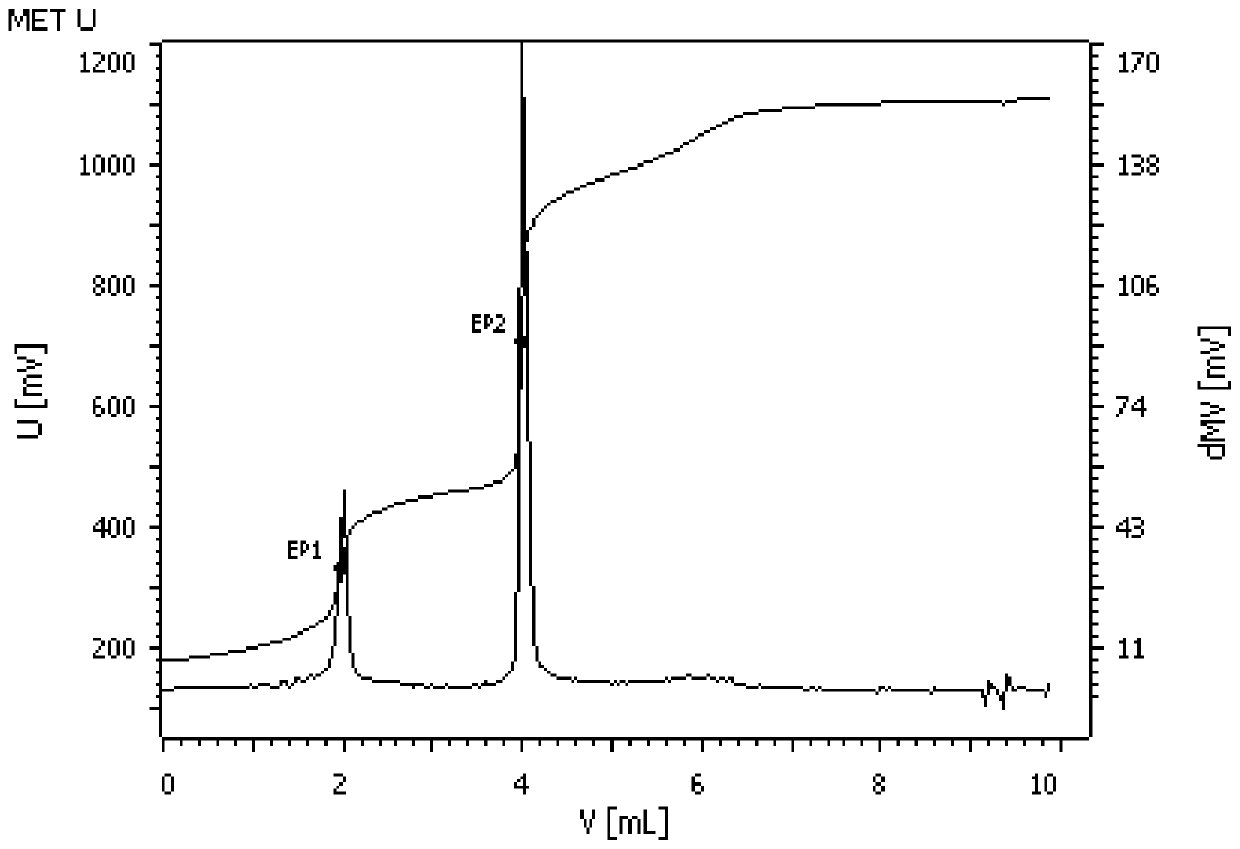
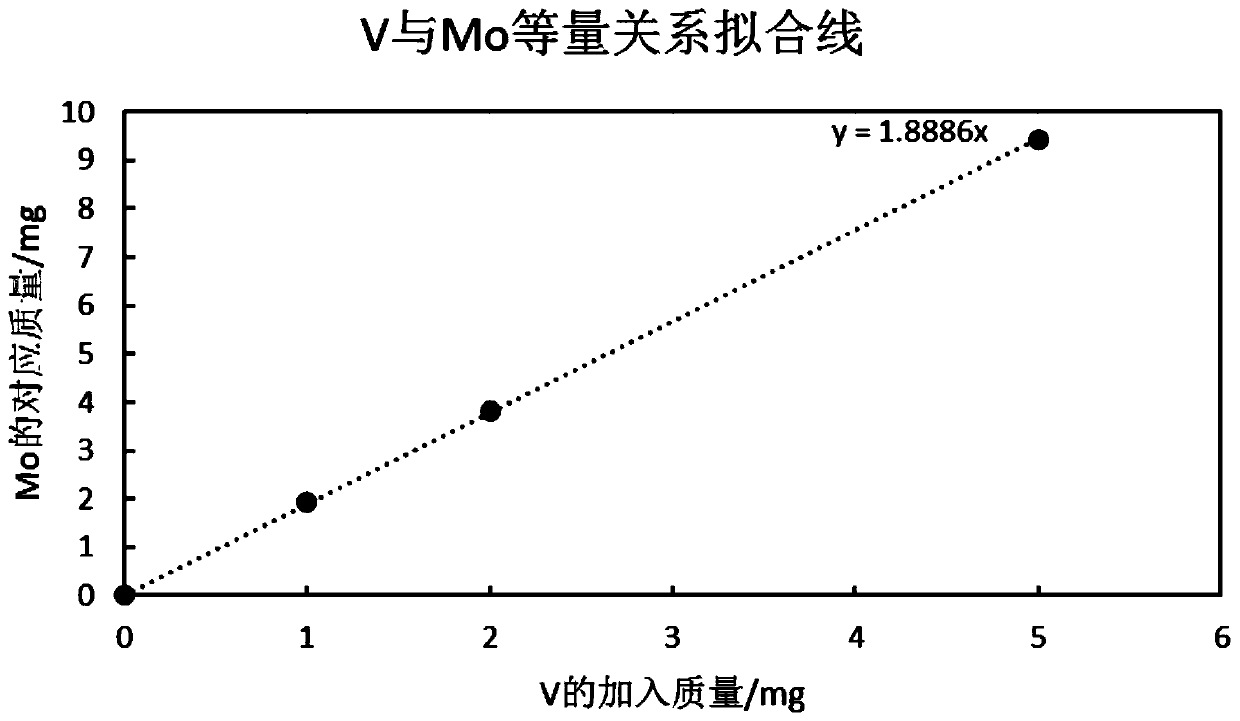
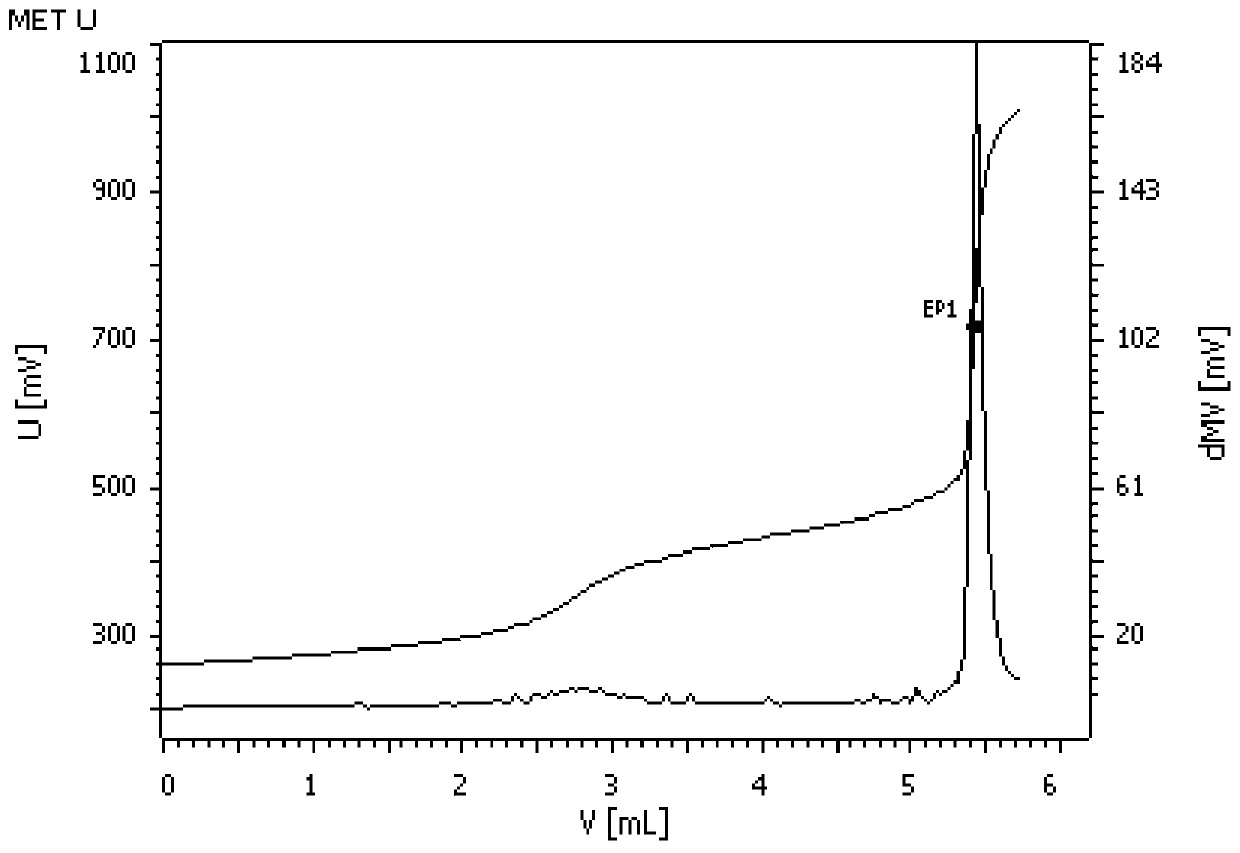
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Weigh 0.2g of metal material and place it in a 200mL beaker, add an appropriate amount of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid with a volume ratio of 6:1 to dissolve the mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid to form the first solution.
[0100] Add 15mL of the mixed acid aqueous solution of sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid to the first solution, heat to 550°C to emit phosphoric acid fumes for 60 seconds, then remove it quickly, stop heating, and let the phosphoric acid fumes evaporate completely to form the second solution. Wherein, in the mixed acid aqueous solution of sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid, the volume ratio of sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid and water is 1:2:3. When the metal material is selected from one of nickel-based alloys, cobalt-based alloys, or metal materials containing tungsten and vanadium, 10 mL of phosphoric acid is additionally added to the first solution.
[0101] In the second solution, add 80mL phosphoric acid (if Fe in the seco...
Embodiment 2
[0105] This example is to compare the effect of phosphoric acid concentration.
[0106] Accurately pipette 25 mL of 1000 mg / mL molybdenum standard solution and place it in a 200 mL beaker, and follow the preparation process in Example 1 above to obtain the second solution sample to be tested. According to Table 2, different volumes of phosphoric acid were added to the 7 parts of the above-mentioned solution to be tested, and the subsequent measurement conditions were the same as in the above-mentioned Example 1. The specific test results are shown in Table 2.
[0107] The influence of table 2 phosphoric acid concentration on titration result
[0108]
[0109] It can be seen from Table 2 that when the concentration of phosphoric acid in the solution is less than 11.5mol / L, the first equivalence point disappears, and the measured result is low due to incomplete reduction of molybdenum. However, if the concentration of phosphoric acid is too high, the viscosity of the soluti...
Embodiment 3
[0111] This embodiment is to compare the influence of sulfuric acid concentration.
[0112] According to the preparation process in the above-mentioned Example 1, the second solution sample to be tested was obtained. According to Table 3, 0, 1, 2, 2.5, and 3 mL of sulfuric acid were added to 7 parts of the above-mentioned second solution samples, and the subsequent measurement conditions were the same as in the above-mentioned Example 1. The specific test results are shown in Table 3.
[0113] The influence of table 3 sulfuric acid concentration on titration result
[0114]
[0115] It can be seen from Table 3 that with the increase of sulfuric acid addition, the first equivalent point jump potential dropped from 325mV to 281mV. Adding more than 1mL of sulfuric acid can increase the potential jump, and adding 2mL of sulfuric acid can be used.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com