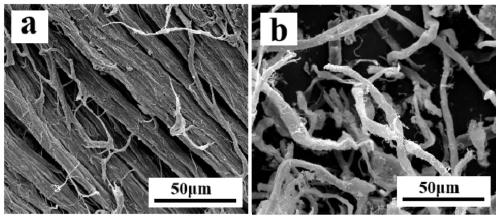
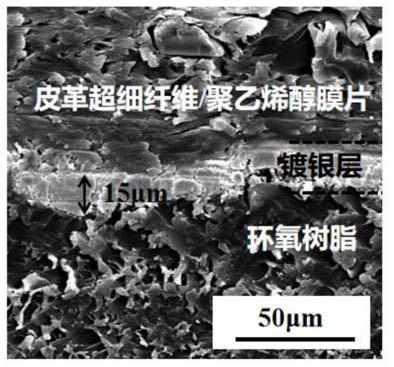
Discarded leather superfine fiber, high electromagnetic shielding material combined with discarded leather superfine fiber and polyvinyl alcohol and preparation methods of discarded leather superfine fiber and high electromagnetic shielding material
A technology of ultra-fine fiber and polyvinyl alcohol, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, magnetic field/electric field shielding, fiber treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high degree of protein fiber bundles, compound modification, and inability to melt, and achieve low cost , good flexibility, and the effect of inhibiting foaming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1) Put the tanning solid waste into the disc-shaped mechanochemical reactor, and feed circulating cooling water at the same time, control the temperature of the disc surface to 35°C, control the pressure to 20kN, control the speed to 400 rpm, control vacuum feeding, and circulate grinding 9 times to get waste leather microfibers, the average fiber diameter of the ultrafine fibers is 2 μm, and the average length is 100 μm;
[0040] 2) 100 parts of polyvinyl alcohol 1799 (that is, the degree of polymerization is 1700, and the degree of alcoholysis is 99%) is heated and dissolved in hot water at 95 ° C to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a concentration of 20 wt%, and then mixed with 5 parts of glycerin and 200 parts Mix waste leather microfibers, then drop 0.3wt% polyvinyl alcohol defoamer BK-802 into the mixed suspension, and use a high-speed stirrer to mix and stir for 20 minutes;
[0041] 3) Put the obtained mixed liquid into an ultrasonic device with a power o...
Embodiment 2
[0046] 1) Put the tanning solid waste into the disc-shaped mechanochemical reactor, and feed circulating cooling water at the same time, control the temperature of the disc surface to 20°C, control the pressure to 17kN, control the speed to 300 rpm, control the vacuum feeding, and circulate the grinding 8 times to get the waste leather superfine fiber, the average fiber diameter of the superfine fiber is 5 μm, and the average length is 500 μm;
[0047] 2) Heat and dissolve 100 parts of polyvinyl alcohol 2597 in hot water at 80°C to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a concentration of 10 wt%, then mix it with 10 parts of urea and 400 parts of waste leather microfiber, and then mix it in the mixed suspension Add 0.1wt% polyvinyl alcohol defoamer DF-898 dropwise, and use a high-speed stirrer to mix and stir for 10 minutes;
[0048] 3) Put the obtained mixed liquid into an ultrasonic device with a power of 800W for 10 minutes at room temperature, and then stir and defoam at...
Embodiment 3
[0053] 1) Put the tanning solid waste into the disc-shaped mechanochemical reactor, and feed circulating cooling water at the same time, control the temperature of the disc surface to 5°C, control the pressure to 15kN, control the speed to 100 rpm, control the vacuum feeding, and circulate the grinding 7 times to get the waste leather superfine fiber, the average fiber diameter of the superfine fiber is 8 μm, and the average length is 800 μm;
[0054] 2) Heat and dissolve 100 parts of polyvinyl alcohol 1799 in hot water at 90°C to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a concentration of 10 wt%, then mix it with 10 parts of caprolactam and 200 parts of waste leather microfiber, and then mix it in the mixed suspension Add 0.1wt% polyvinyl alcohol defoamer GPE-3000 dropwise, and mix with a high-speed stirrer for 10 minutes;
[0055] 3) Put the obtained mixed liquid into an ultrasonic device with a power of 700W at room temperature for ultrasonic treatment for 20 minutes, and t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electromagnetic shielding performance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com