Sulfur and phosphorus deep removal method of slagless steelmaking
A deep, removal technology, applied in the field of steel slag dephosphorization and desulfurization, can solve problems such as iron loss, and achieve the effects of reducing iron loss in slag phase, reducing flue gas volume, and improving preparation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
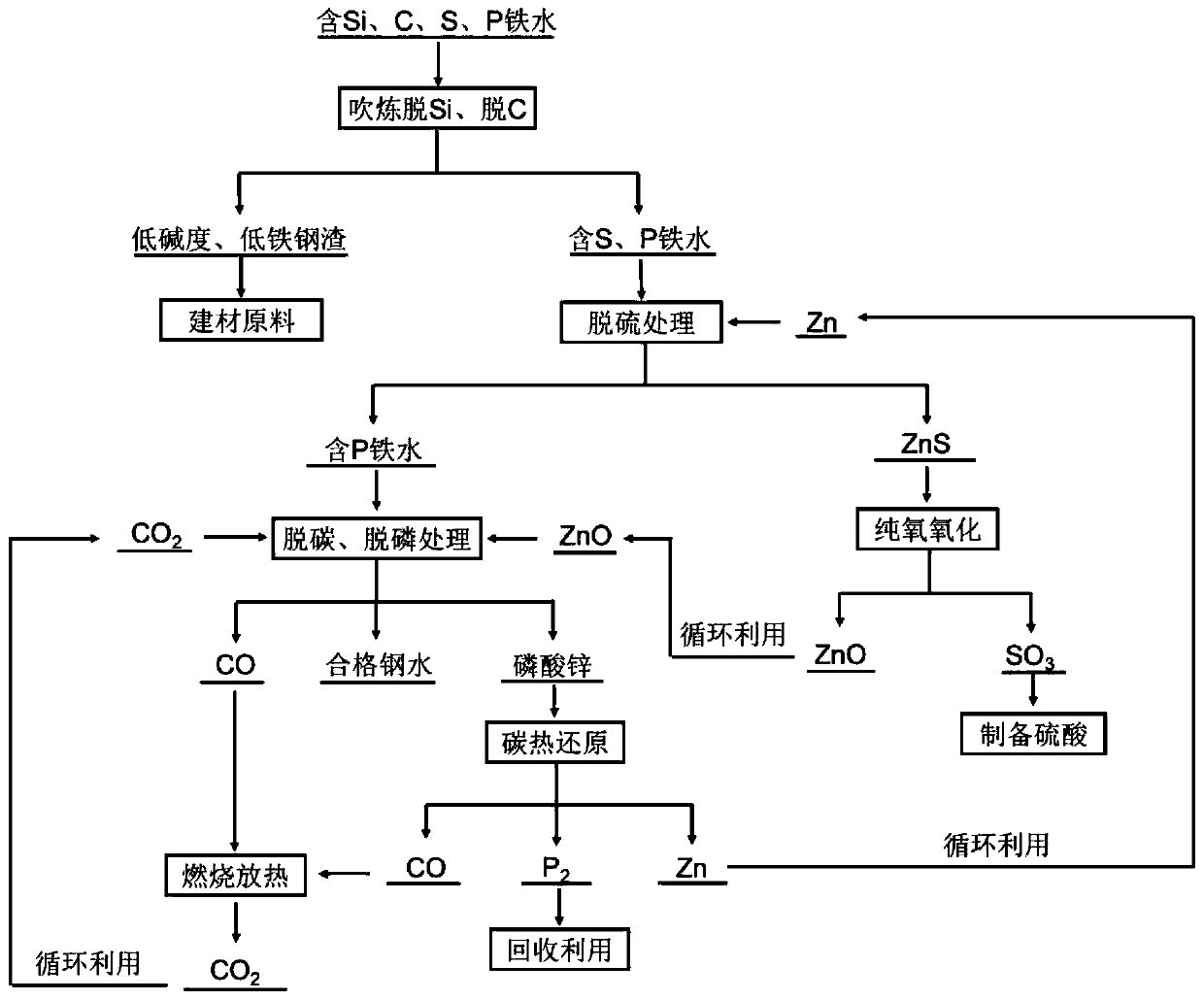
[0061] Using pure iron, ferrosilicon and graphite powder as raw materials, they are completely melted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace to prepare molten iron with a silicon content of 0.15% and a carbon content of 3.5%, which is used for desiliconization and decarburization at a temperature of 1650°C. The mass of molten iron per furnace is 20kg.
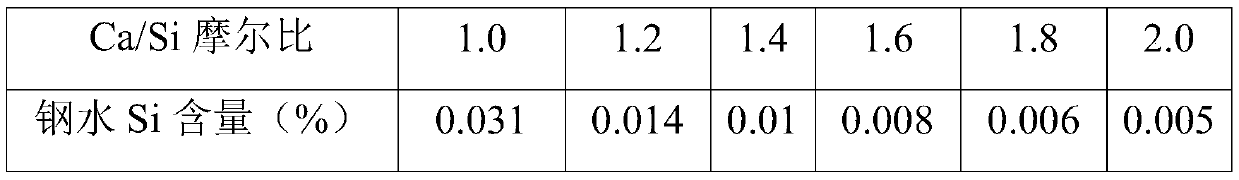
[0062] After the molten iron is completely melted, the flux quicklime (pure chemical reagent) is added as a desiliconization agent, and O is sprayed to the bottom of the molten iron through a corundum tube. 2 , O 2 The gas flow rate is 20L / min, and the oxygen blowing is stopped after the injection time reaches 35 minutes. After standing still for 10 minutes, a small amount of molten steel and molten slag are extracted respectively through the sampler, which are broken into small steel particles and slag particles after cooling, and the steel particles are determined by chemical analysis. Particle silicon content and sl...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Using pure iron and FeS pure chemical reagents as raw materials, they are completely melted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace to prepare molten steel with a S content of 0.05% for desulfurization experiments. The experimental temperature is 1650 ° C, and the mass of molten steel per furnace is 20kg.
[0069] Add zinc particles to the molten steel through the corundum tube, the addition amount is 0.05-0.2% of the mass of the molten steel, and the addition amount is 0.05% each time. The corundum tube is inserted into the bottom of the molten steel to prevent zinc from quickly escaping from the molten steel after vaporization, and increase the relationship between zinc and molten steel. Reaction time. Wait for 10 minutes after each addition of zinc particles. After the composition of molten steel is completely uniform, a small amount of molten steel is extracted through a sampler. After cooling, it is broken into small steel particles, and the sulfur content of...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Using pure iron and iron phosphide pure chemical reagents as raw materials, they are completely melted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace to prepare molten steel with a P content of 0.15% for dephosphorization experiments. The experimental temperature is 1650 ° C, and the mass of molten steel per furnace is 20kg.
[0073] Add ZnO powder reagent to the molten steel through a corundum tube and stir to disperse the ZnO in the molten steel. The amount of ZnO added is 0.5-0.8% of the mass of the molten steel. The first addition is 5%, and then 1% each time. After each addition of ZnO, CO was injected to the bottom of the molten steel through a corundum tube 2 gas, CO 2 The gas flow rate is 2L / min, the injection time is 30min after the first addition of ZnO, and the injection time is 6min after each addition of ZnO. Stand still for 10 minutes after each injection to ensure that the formed FeO fully reacts with ZnO and P to form zinc phosphate. A small amount of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com