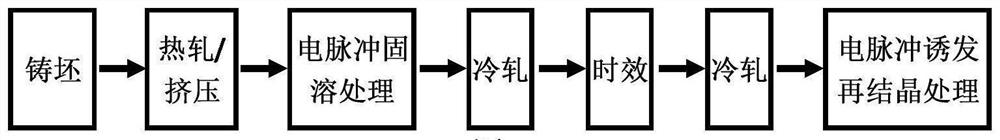
A method for strengthening and toughening magnesium alloy strips
A magnesium alloy and strip technology, applied in the field of metal materials, can solve problems such as local overburning, coarse alloy grains, and demanding processing technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
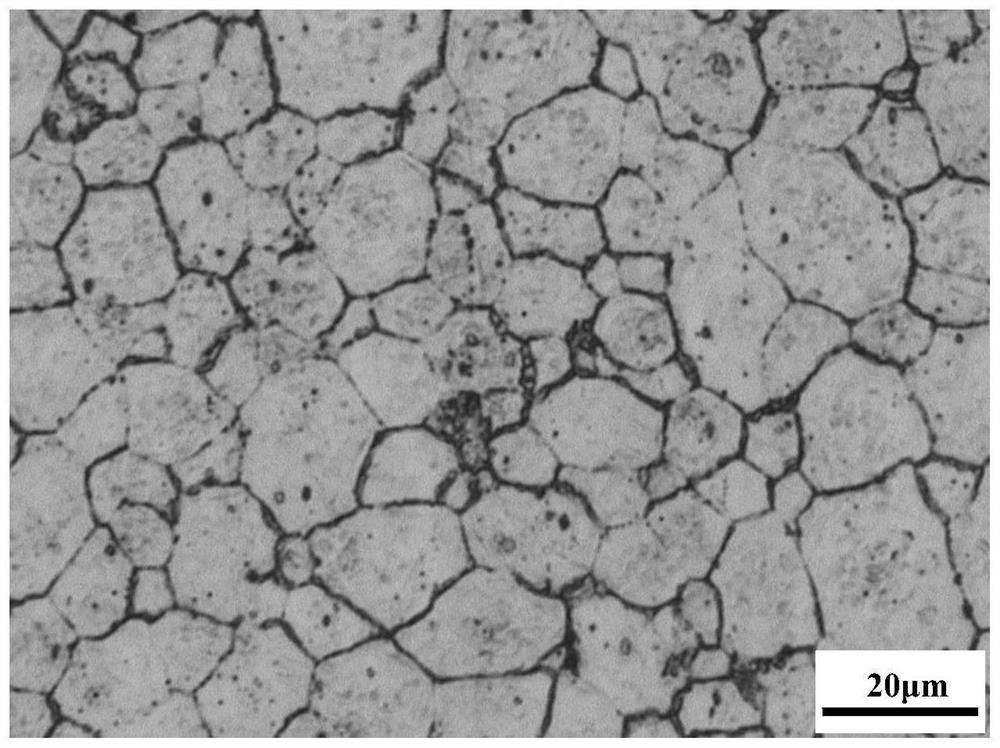
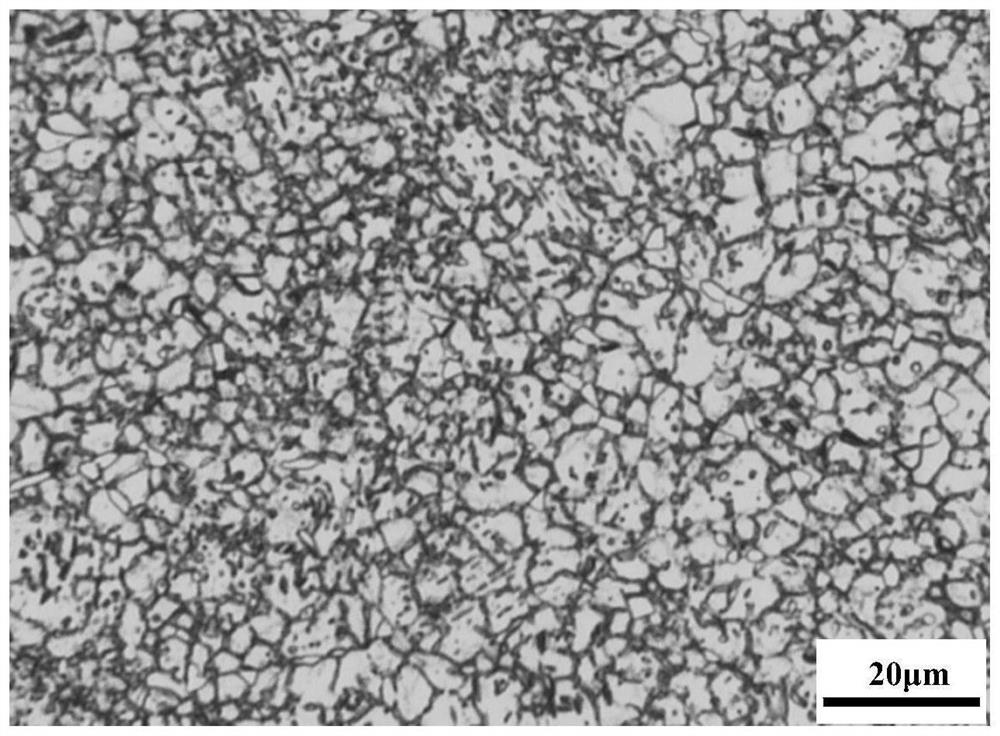
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1: Preparation of AZ61 magnesium alloy strip
[0046] (1) Rapid solid solution and water spray cooling and quenching are carried out on the extruded AZ61 magnesium alloy (Cu-6wt%Al-1wt%Zn) billet by electric pulse, so that the precipitated phase in the alloy is solid-dissolved in the magnesium matrix . The parameters of the electric pulse input to the energized region of the magnesium alloy strip blank are: frequency 1200Hz, pulse width 100μs, current density amplitude 2200A / mm 2 , effective current density 250A / mm 2 , the maximum heating temperature is 340°C, the heating time is 10s; the cooling water flow rate of spray water is 12L / min.
[0047] (2) Carry out a cold rolling to the magnesium alloy strip material of the electric pulse solution treatment in the step (1), the pass reduction rate is 25%, the total reduction rate is 50%, and the rolling speed is 5m / min;
[0048] (3) Aging treatment is carried out to the primary cold-rolled magnesium alloy stri...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Embodiment 2: Preparation of AZ91 magnesium alloy strip
[0063] (1) Rapid solid solution and water spray cooling and quenching are carried out on the extruded AZ91 magnesium alloy (Cu-9wt%Al-1wt%Zn) billet by electric pulse, so that the precipitated phase in the alloy is solid-dissolved in the magnesium matrix . The parameters of the electric pulse input to the energized region of the magnesium alloy strip blank are: frequency 1500Hz, pulse width 120μs, current density amplitude 2500A / mm 2 , effective current density 400A / mm 2 , the maximum heating temperature is 350°C, the heating time is 10s; the flow rate of water spray cooling water is 20L / min
[0064] (2) Carry out one-time cold rolling to the magnesium alloy strip material of electric pulse solution treatment in step (1), pass reduction ratio 18%, total reduction ratio 50%, rolling speed 3m / min;
[0065] (3) aging treatment is carried out to the primary cold-rolled magnesium alloy strip in step (2), the aging ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3: the preparation of ZK60 magnesium alloy strip
[0077](1) Rapid solid solution and water spray cooling and quenching treatment of the hot-rolled ZK60 magnesium alloy (Cu-5.8wt%Zn-0.7wt%Zr) strip blank by electric pulse, so that the precipitated phase in the alloy is solid-dissolved in the magnesium matrix middle. The parameters of the electric pulse input to the energized region of the magnesium alloy strip blank are: frequency 1800Hz, pulse width 150μs, current density amplitude 2700A / mm 2 , effective current density 450A / mm 2 , the maximum heating temperature is 370°C, the heating time is 15s; the flow rate of water spray cooling water is 25L / min
[0078] (2) Carry out a cold rolling to the magnesium alloy strip material of the electric pulse solution treatment in the step (1), the pass reduction rate is 20%, the total reduction rate is 50%, and the rolling speed is 4m / min;
[0079] (3) aging treatment is carried out to the primary cold-rolled magnesi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com