Regeneration and resource utilization method of thallium poisoning SCR denitration catalyst
A denitrification catalyst and catalyst technology, applied in the direction of catalyst regeneration/reactivation, chemical instruments and methods, catalyst activation/preparation, etc., to achieve the effect of avoiding secondary pollution of catalysts, simple and efficient methods, and less loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0050]The spent catalyst after one year of use in a cement plant will be physically cleaned to remove the dust on the surface of the catalyst and dredge the pores.
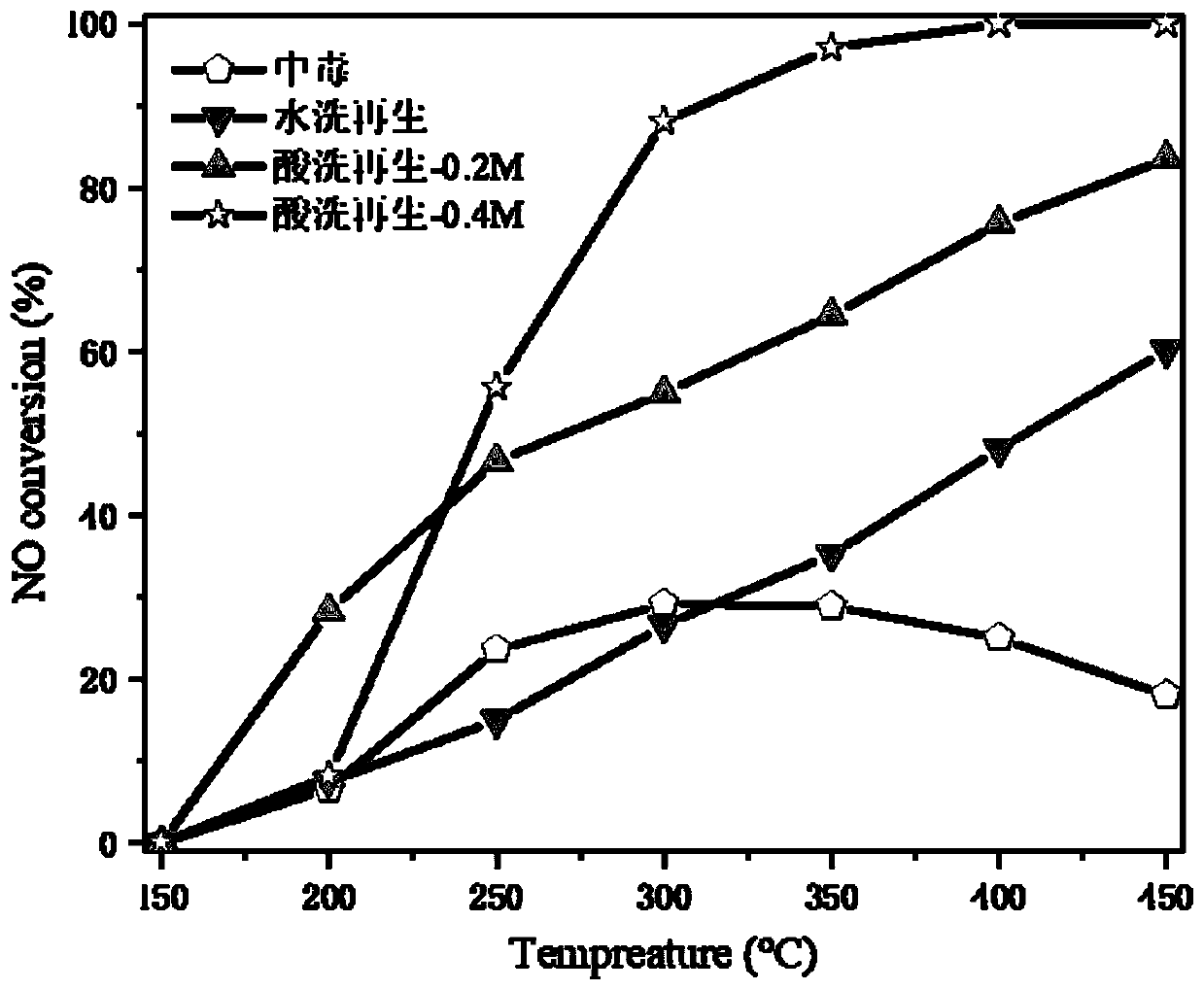
[0051] Step 2: Soak the catalyst in deionized water at 80°C with 50KHz ultrasonic treatment for 60 minutes to completely wash away the poisoned thallium sulfate and other soluble impurities on the surface of the catalyst, exposing the thallium trioxide tightly wrapped on the surface of the catalyst (Tl 2 o 3 )Floor.
[0052] Step 3: Soak the washed catalyst in 0.2M dilute sulfuric acid washing solution and treat it with 50KHz ultrasonic for 60min. The layer of thallium trioxide is dissolved to recover the active sites of the catalyst.
[0053] Step 4: Use a high-pressure water gun to clean the surface of the pickled catalyst to remove residual dilute sulfuric acid and thallium sulfate.
[0054] Step five: drying the catalyst at 60°C for 12 hours.
[0055] Step 6: using the waste heat co-processing solid waste...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Step 1: Physically clean up the spent catalyst after one year of use in a cement plant, remove the ash on the surface of the catalyst and dredge the pores.
[0059] Step 2: Soak the catalyst in deionized water at 80°C with 50KHz ultrasonic treatment for 60 minutes to completely wash away the poisoned thallium sulfate and other soluble impurities on the surface of the catalyst, exposing the thallium trioxide tightly wrapped on the surface of the catalyst (Tl 2 o 3 )Floor.
[0060] Step 3: Soak the washed catalyst in 0.4M dilute sulfuric acid washing solution and treat it with 50KHz ultrasonic for 60min. The layer of thallium trioxide is dissolved to recover the active sites of the catalyst.
[0061] Step 4: Use a high-pressure water gun to clean the surface of the pickled catalyst to remove residual dilute sulfuric acid and thallium sulfate.
[0062] Step five: drying the catalyst at 60°C for 12 hours.
[0063] Step 6: using the waste heat co-processing solid waste ...
Embodiment 4
[0066] Step 1: Physically clean up the spent catalyst after one year of use in a cement plant, remove the ash on the surface of the catalyst and dredge the pores.
[0067] Step 2: Treat the catalyst at 510°C for 30 minutes in a mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen with a hydrogen content of 1%, and the space velocity of the mixed gas is 60000h -1 . The Tl in the thallium trioxide layer is replaced by hydrogen 3+ reduced to Tl + . At the same time at this temperature, because of the thiophilic nature of thallium, Tl + It will react with the residual ammonium bisulfate (ABS) on the surface of the catalyst to convert the thallium trioxide on the surface of the catalyst into thallium sulfate.
[0068] Step 3: Soak the catalyst treated with hydrogen gas mixture in deionized water at 80°C and accompany it with 50KHz ultrasonic treatment for 60 minutes to completely wash away the poisoning substance thallium sulfate and other soluble impurities on the surface of the catalyst, so that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com