Bionic tissue engineering scaffold and preparation method thereof
A technology for tissue engineering scaffolds and corneas, which can be used in tissue regeneration, non-woven fabrics, and pharmaceutical formulations. It can solve problems such as inability to effectively guide repair and regeneration, large differences in ECM structures, and poor mechanical strength of scaffolds. It achieves excellent results. Biocompatibility and degradability, enhanced in vivo safety, favorable adhesion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0051] The invention provides a biomimetic tissue engineering scaffold, which comprises more than one kind of ECM extraction material with a weight of more than 90%, and the ECM extraction material is extracted from biological tissue.
[0052] The bionic engineering scaffold in this embodiment includes more than one kind of ECM extraction material extracted from biological tissues with a weight of more than 90%, which reduces the by-products generated during the degradation process of artificially synthesized polymer materials, and effectively improves the efficiency of the bionic engineering scaffold. Human biocompatibility.
[0053] ECM extraction materials are extracted from biological tissues, which can be but not limited to bone, skeletal muscle, cornea, liver and skin.
[0054]In a bionic engineering scaffold, a combination of more than two ECM extraction materials can be used, specifically, it can be a combination of ECM extraction materials extracted from decalcified b...
Embodiment approach 2
[0059] The invention provides a method for preparing a bionic tissue engineering scaffold, which comprises the following steps: adding a cross-linking agent to more than one ECM extraction material before electrospinning to generate a cross-linked material through an in-situ cross-linking reaction, and making the cross-linked material Made bionic tissue engineering scaffold.
[0060] Wherein, the cross-linking agent is but not limited to one or a combination of two or more of formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde and transglutaminase.
[0061] Wherein, the addition amount of each component in the cross-linking agent is the following percentage by weight of the ECM extraction material: 0.2%-4% of formaldehyde, 1%-3% of glutaraldehyde or 2%-6% of transglutaminase.
[0062] In order to improve the performance of the material, especially the mechanical performance, its ECM extraction material is also blended with one or more than two of the following components: polylactic acid, chitosan, ...
Embodiment approach 3
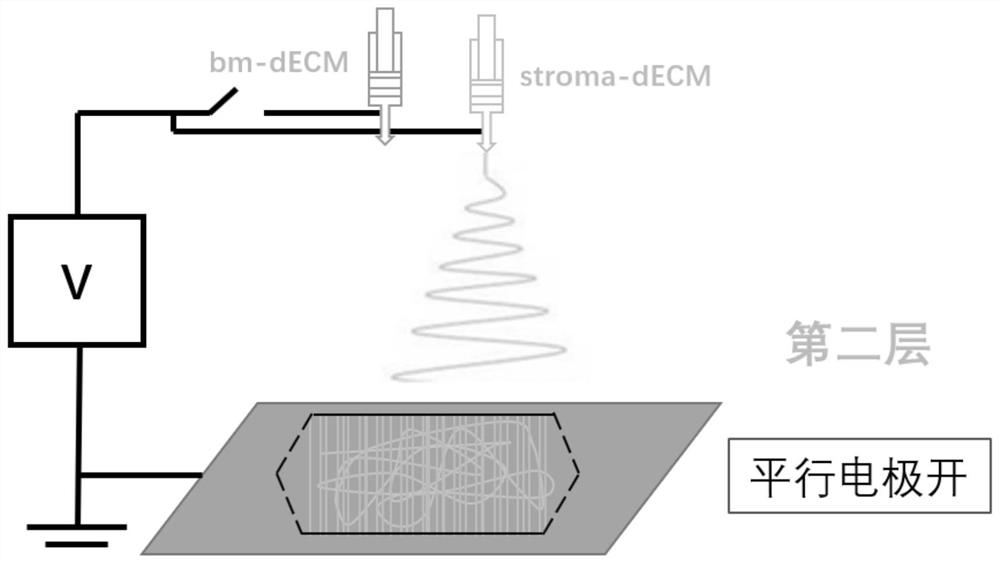
[0068] The following embodiments lie in successfully spinning two or more ECM extraction materials through electrospinning to obtain biomimetic tissue engineering scaffolds. It includes the following steps:
[0069] S1 Adding two or more ECM extraction materials to cross-linking agents respectively to obtain cross-linked materials after in-situ cross-linking reaction;
[0070] S2 Set the parameters of electrospinning and adjust the corresponding spinning orientation. According to the structure designed by the bionic tissue engineering scaffold, one or more cross-linked materials obtained are spun sequentially in sequence to obtain the bionic tissue engineering scaffold.
[0071] The electrospinning machine used may be a computer-controlled multi-nozzle electrospinning machine whose parameters can be set. It can also be a computer-controlled single-nozzle electrospinning machine with parameters that can be set. When it is necessary to spin a variety of ECM extraction materials...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com