Method for separating single cells in animals and plants
A separation method and single-cell technology, applied in the field of single-cell separation in animals and plants, can solve the problems of low cell purity, impurity separation, small diameter, etc., to improve cell yield and purity, promote cell activity, and high cell purity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
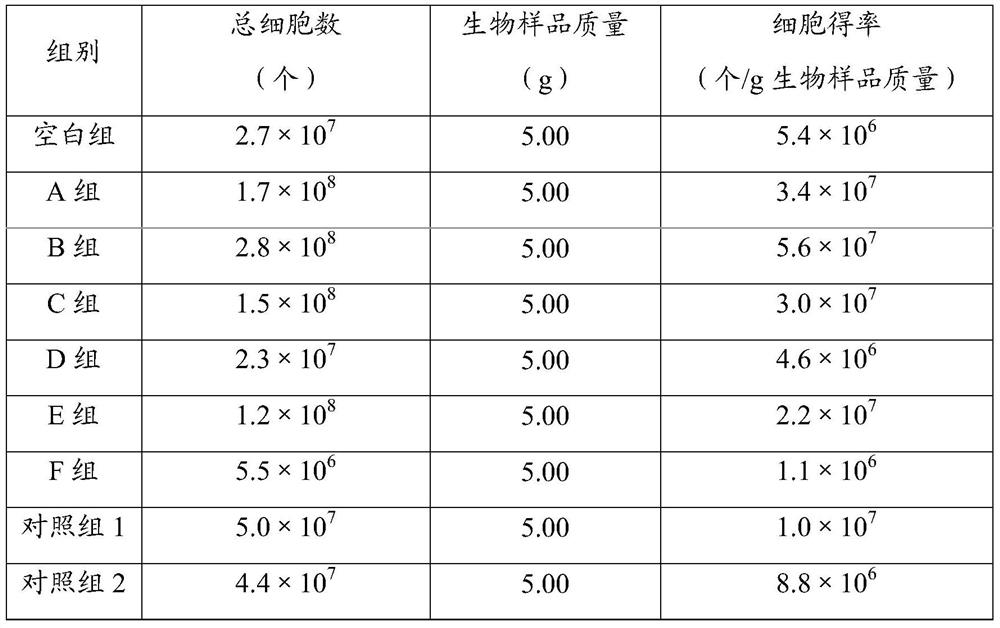
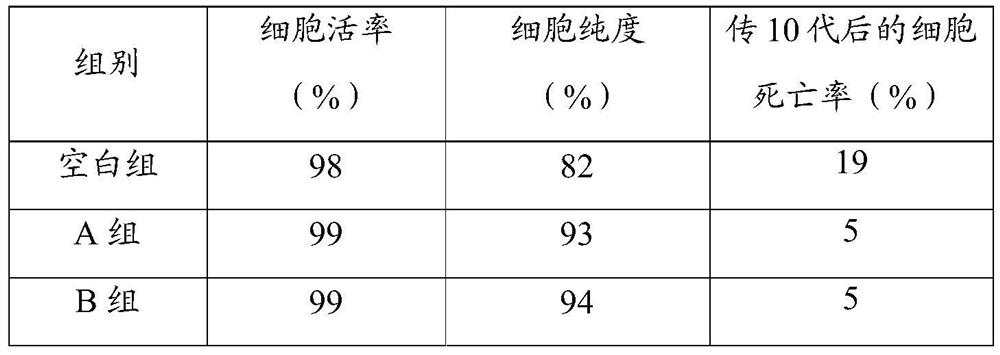
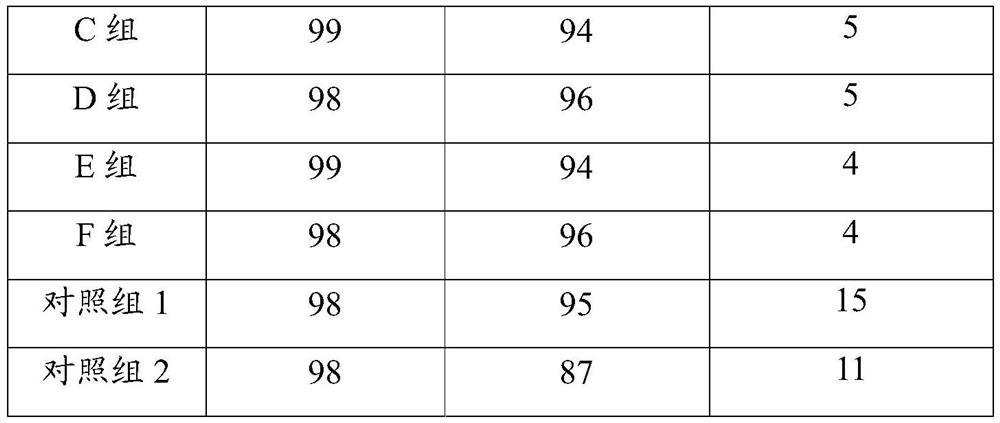
[0025] A method for isolating single cells in animals and plants, comprising:
[0026] Step 1, biological sample pretreatment: add active liquid and separation enzyme to the biological sample, soak for 1 hour, and obtain the soaking mixture;
[0027] The active liquid was prepared according to the following method: sodium chloride 9g, potassium chloride 0.5mg, lanthanum nitrate 0.01mg, 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid 2.4g, distilled water to 1L, pH 7.2;
[0028] The solid-liquid ratio of the biological sample and the active liquid is 10g:100mL;
[0029] The isolated enzyme is a mixture of pectinase and collagenase, and 0.5 g of pectinase and 0.5 g of collagenase are added to every liter of active liquid;
[0030] Step 2, small molecule filtration: filter the soaking mixture with a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm;
[0031] Step 3, large particle filtration: soak and stir the filter membrane and the sediment above it in the active solution, resuspend si...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method for isolating single cells in animals and plants, comprising:
[0035] Step 1, biological sample pretreatment: add active liquid and separation enzyme to the biological sample, soak for 1.5h, and obtain the soaking mixture;
[0036] The active liquid was prepared according to the following method: 8.5g of sodium chloride, 0.7mg of potassium chloride, 0.05mg of lanthanum nitrate, 2.4g of 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid, distilled water to 1L, pH 7.4;
[0037] The solid-liquid ratio of the biological sample and the active liquid is 15g:100mL;
[0038] The isolated enzyme is a mixture of pectinase and collagenase, and 0.75 g of pectinase and 0.75 g of collagenase are added per liter of active liquid;
[0039] Step 2, small molecule filtration: filter the soaking mixture with a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.45 μm;
[0040] Step 3, large particle filtration: soak and stir the filter membrane and the sediment above it in the active solution, res...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A method for isolating single cells in animals and plants, comprising:
[0044] Step 1, biological sample pretreatment: add active liquid and separation enzyme to the biological sample, soak for 2 hours, and obtain the soaking mixture;
[0045] The active solution was prepared according to the following method: sodium chloride 9g, potassium chloride 0.5mg, lanthanum chloride 0.03mg, 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid 2.4g, distilled water to 1L, pH 7.2;
[0046] The solid-liquid ratio of the biological sample and the active liquid is 20g:100mL;
[0047] The isolated enzyme is a mixture of pectinase and collagenase, and 1 g of pectinase and 1 g of collagenase are added in every liter of active liquid;
[0048] Step 2, small molecule filtration: filter the soaking mixture with a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm;
[0049] Step 3, large particle filtration: soak and stir the filter membrane and the sediment above it in the active solution, resuspend si...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com