A Microscopic Imaging Method to Obtain Double Contrast of Light Absorption and Light Scattering Simultaneously
A microscopic imaging, dual-contrast technology, applied in scattering property measurement, color/spectral property measurement, material analysis by optical means, etc., can solve the problem that it is difficult to achieve clear imaging with optical microscope
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
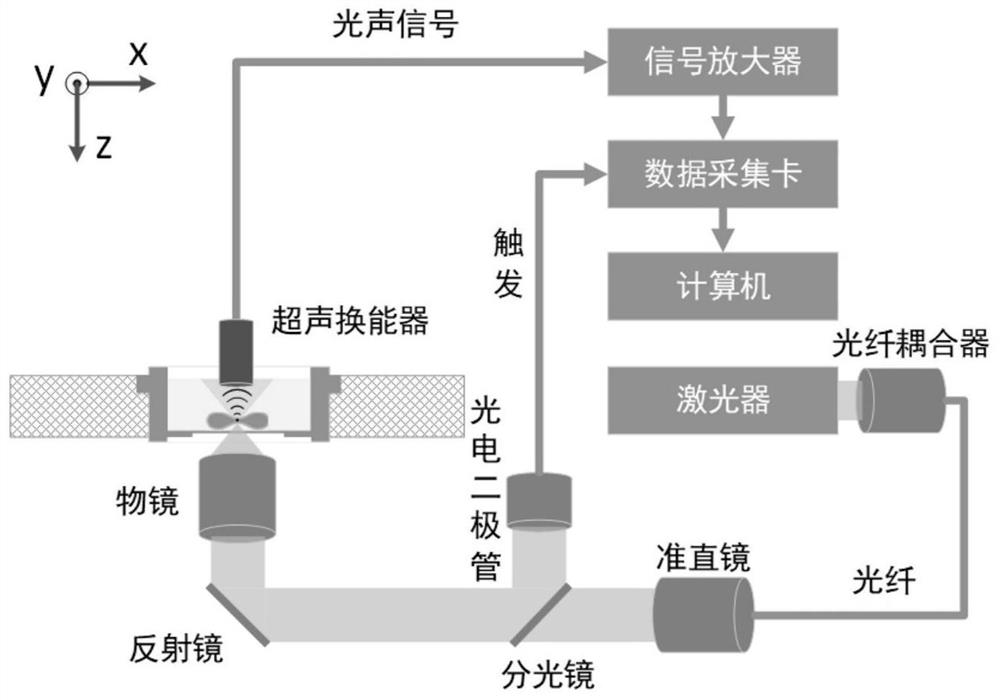
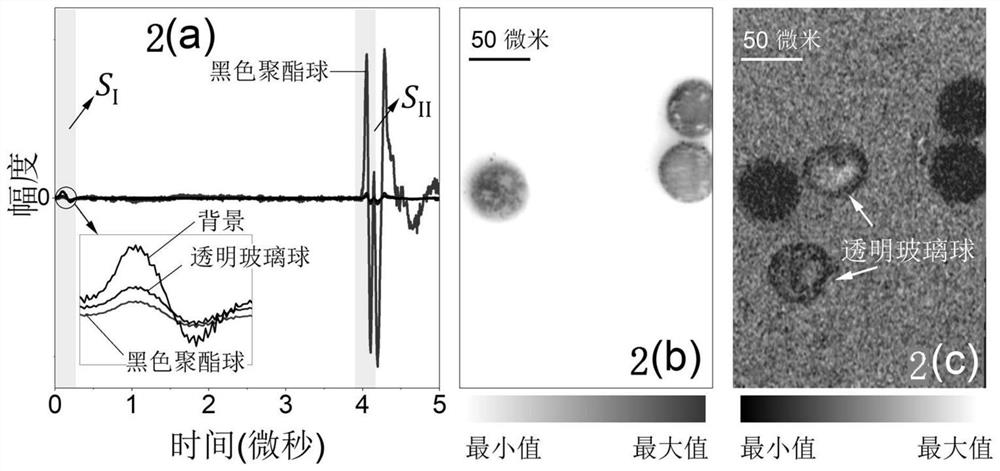
[0034] use figure 1 The system images binary mixed particles with different optical properties, including the following steps:
[0035] Step 1: The binary mixed particles composed of 50 micron diameter black polyester spheres and transparent glass spheres are spread on the bottom of the confocal dish, and distilled water is injected into the confocal dish to achieve ultrasonic coupling.
[0036] Step 2: The pulsed laser is coupled into the single-mode fiber through the fiber coupler. The output light of the single-mode fiber is collimated by the collimator and then enters the inverted microscope objective lens, and is focused on the sample through the bottom of the confocal dish. The numerical aperture of the inverted microscope objective lens is 0.6, the laser wavelength is 532nm, the pulse width is about 8ns, and the pulse repetition frequency is 10kHz. The photodiode is used to monitor the intensity of the laser and trigger the data acquisition card to collect the signal. ...
Embodiment 2
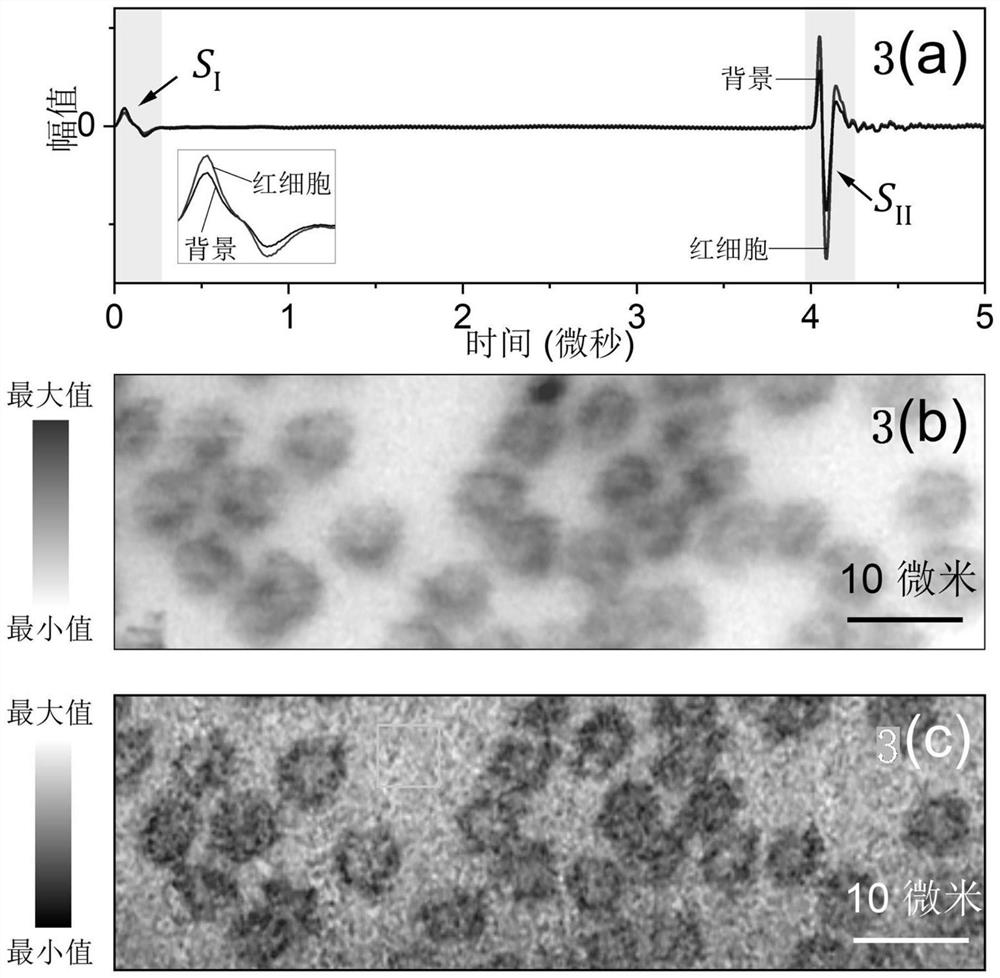
[0042] use figure 1 The system performs label-free imaging of red blood cells, including the following steps:
[0043] Step 1: Take fresh blood from a mouse (C57BL / 6JGpt, male, 10 weeks old, weighing about 25g), smear and fix it on the upper surface of the confocal dish, make a monolayer red blood cell smear, and inject it into the confocal dish Physiological saline for ultrasound coupling.
[0044] Step 2: The pulsed laser is coupled into the single-mode fiber through the fiber coupler. The output light of the single-mode fiber is collimated by the collimator and then enters the inverted microscope objective lens, and is focused on the sample through the bottom of the confocal dish. The numerical aperture of the inverted microscope objective lens is 0.6, the laser wavelength is 532nm, the pulse width is about 8ns, and the pulse repetition frequency is 10kHz. The photodiode is used to monitor the intensity of the laser and trigger the data acquisition card to collect the sig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com