Method for detecting accessibility of plant fibers
A plant fiber and detection method technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, color/spectral characteristic measurement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large error in results, high toxicity, high cost, etc., and achieve simple and clear results, simple operation, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
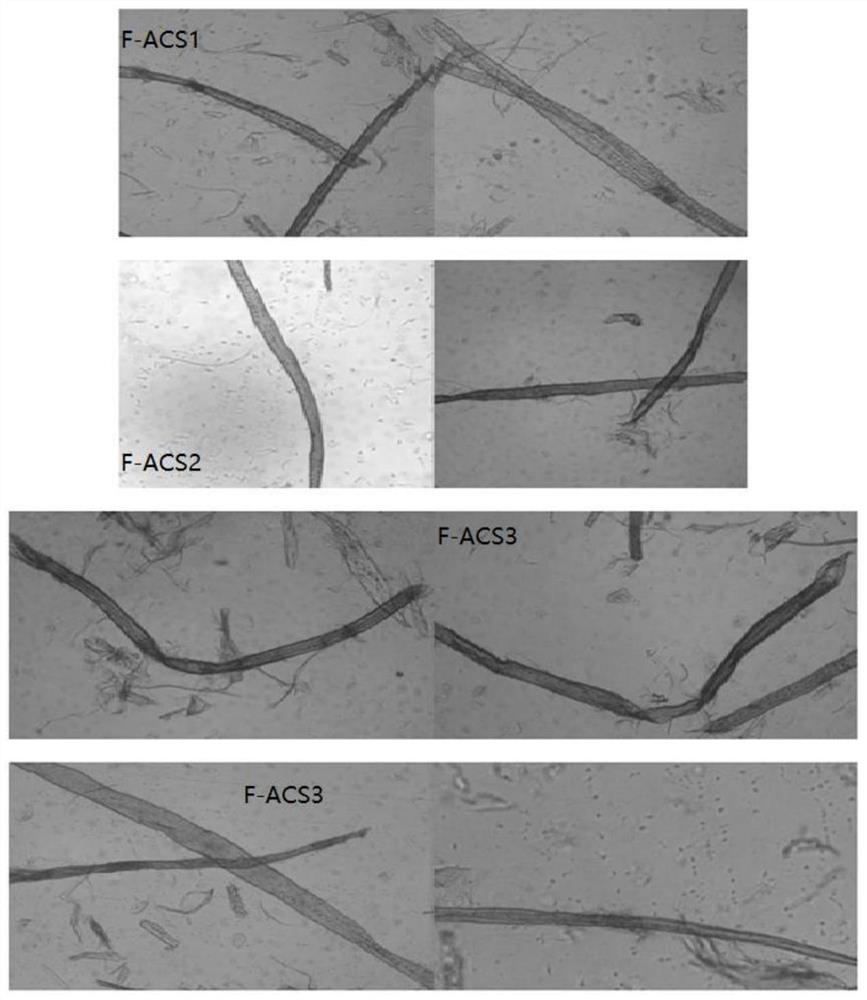
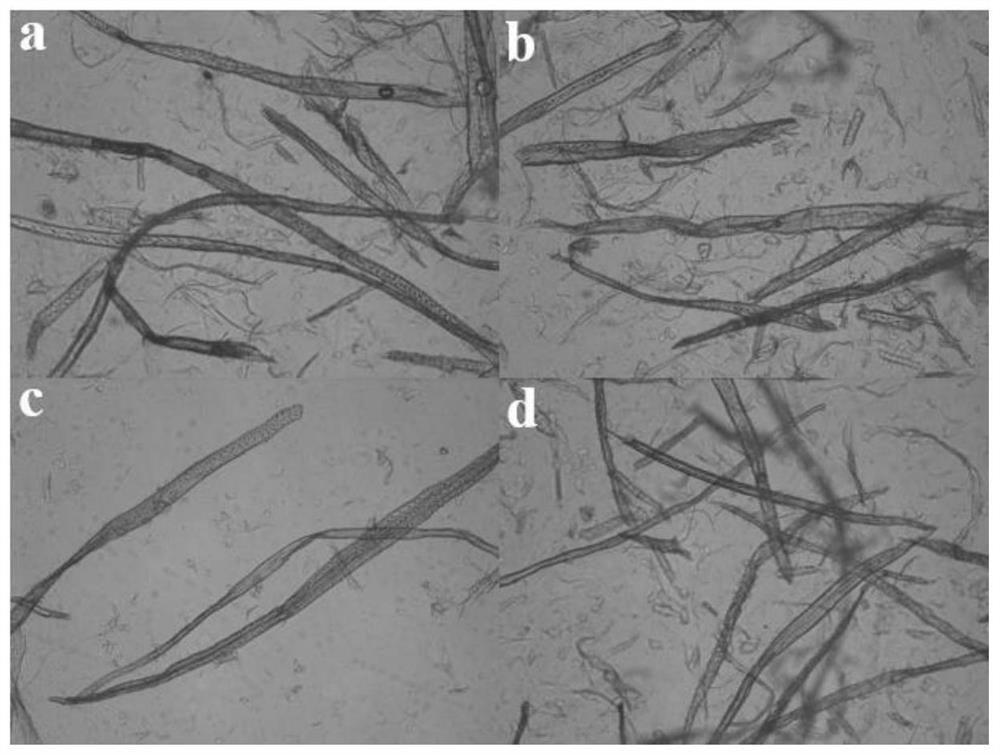
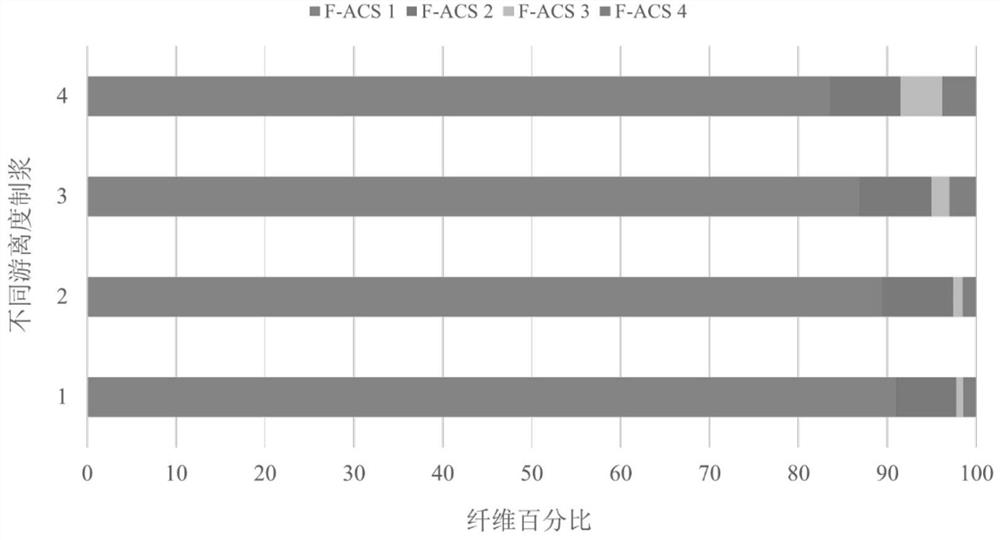
[0048] 0.5 to 8 m of Pondus fir was cut into 20 cm thick wood discs, the discs were pulverized through a shredder, and the pulverized wood samples were washed with distilled water and ground in a hammer mill until passing through a 2 cm sieve. Get the H of 1.5kg of the pond fir sawdust (dry weight 73.35%) that has been ground and 10% of the pond fir sample dry weight 2 o 2 solution, 8% NaOH solution by dry weight of plant samples, 1.5% NaOH by dry weight of plant samples 2 SiO 3 9H 2 O solution, 1.5% of the chelating agent diethyltriaminepentaacetic acid of the dry weight of the plant sample is mixed to form a plant sample with a mass ratio of 20%, and it is placed in an oven at 90°C for 1 hour. After the reaction, place it on a tray Refining in the mill and obtaining four different freeness samples of Pork cedar pulp, the resulting refined samples were depotentated with 100°C hot water, and screened in a sieving machine to finally obtain four different freeness The fiber ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] 0.5 to 8 m of Pondus fir was cut into 20 cm thick wood discs, the discs were pulverized through a shredder, and the pulverized wood samples were washed with distilled water and ground in a hammer mill until passing through a 2 cm sieve. Get the H of 1.5kg of the pond fir sawdust (dry weight 73.35%) that has been ground and 10% of the pond fir sample dry weight 2 o 2 solution, 13% NaOH solution by dry weight of plant samples, 1.5% NaOH by dry weight of plant samples 2 SiO 3 9H 2 O solution, 1.5% of the chelating agent diethyltriaminepentaacetic acid of the dry weight of the plant sample is mixed to form a plant sample with a mass ratio of 20%, and it is placed in an oven at 90°C for 1 hour. After the reaction, place it on a tray Refining in the mill and obtaining four different freeness samples of Pork cedar pulp, the resulting refined samples were depotentated with 100°C hot water, and screened in a sieving machine to finally obtain four different freeness The fiber...
Embodiment 3
[0052] 0.5 to 8 m of Pondus fir was cut into 20 cm thick wood discs, the discs were pulverized through a shredder, and the pulverized wood samples were washed with distilled water and ground in a hammer mill until passing through a 2 cm sieve. Get the ground pond fir sawdust (dry weight 73.35%) 1.5kg and 15% H of the pond fir sample dry weight 2 o 2 solution, 18% NaOH solution by dry weight of plant samples, 1.5% NaOH by dry weight of plant samples 2 SiO 3 9H 2 O solution, 1.5% of the chelating agent diethyltriaminepentaacetic acid of the dry weight of the plant sample is mixed to form a plant sample with a mass ratio of 20%, and it is placed in an oven at 90°C for 1 hour. After the reaction, place it on a tray Refining in the mill and obtaining four different freeness samples of pond cedar pulp, depotting the obtained refined samples with hot water at 100°C, and screening in a sieving machine to finally obtain four different freeness The fiber samples of pond cedar with h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com