Process for producing sodium carbonate, aluminum oxide and blended cement from red mud
A technology of alumina and red mud, applied in the fields of alumina, production of soda ash, and cement mixing, can solve problems such as high risk, damage to cement and concrete structures, and restrictions, and achieve the effect of saving process water consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
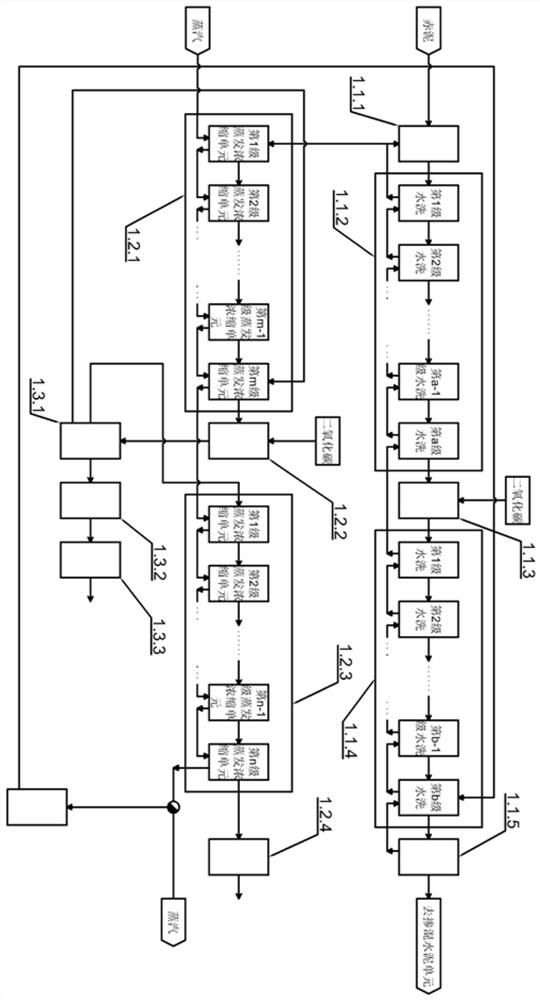
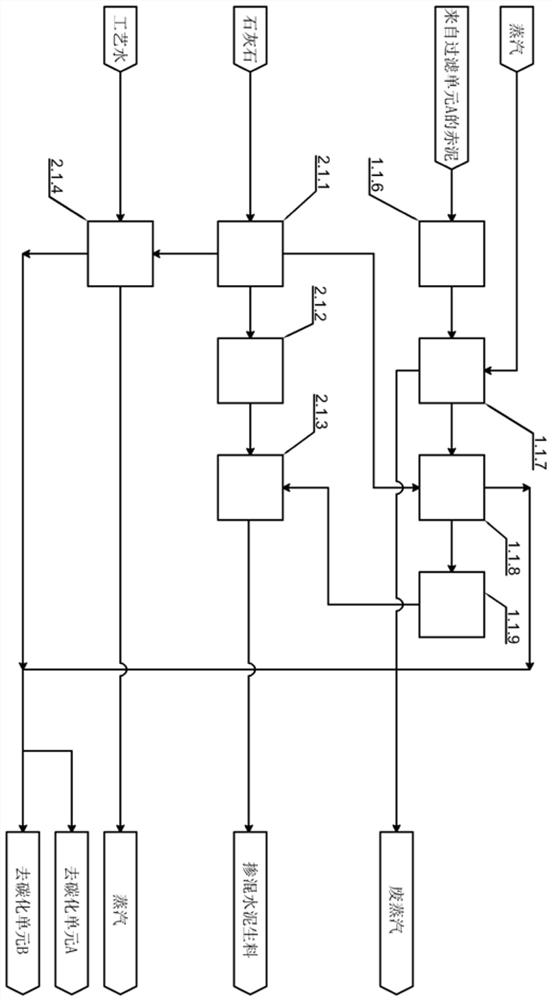
[0027] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, a process of using red mud to produce soda ash, alumina, and blended cement: the untreated red mud is diluted with water in the mixing and dilution unit 1.1.1 to obtain a thin red mud with a liquid-solid ratio of 2.7 to ensure It has good fluidity. In this embodiment, the mixing and dilution unit 1.1.1 is a mixing tank, and the thin red mud is pumped through the diaphragm into the a-level washing unit 1.1.2 for washing. Here, a=4, the main purpose is The free sodium aluminate (NaAlO 2 ), each level of washing unit will wash part of the sodium aluminate in the thin red mud into the washing water, and then send the thin red mud to the next level of washing unit, and finally, the thin red mud will be sent to the carbonization unit A1.1.3, At this time, the relatively insoluble sodium silicate in the thin red mud will react to form silicic acid colloid or precipitate and sodium carbonate that is easily soluble in water, that is, at t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com