Rice PAL1 gene as well as encoding protein and application thereof
A rice and protein technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of unknown specific models and insufficient number of genes, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 pal1 Mutant acquisition and phenotypic analysis
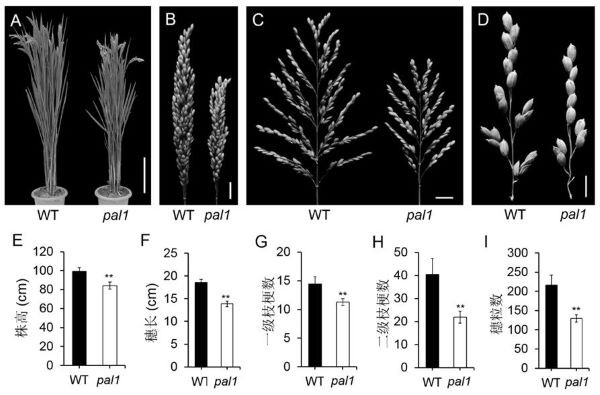
[0040] Mutagenesis of Japonica Rice Variety Huaidao 5 by 60Co-γ Radiation , to obtain a mutant with reduced plant height and shorter panicle length pal1 ( panic length 1 ). 20 wild-type and pal1 For the samples of mutants, statistical analysis was carried out on the plant height, panicle length, primary branch number, secondary branch number and panicle grain number. The results of the analysis showed that rice pal1 The mutant plant height was significantly reduced by 15.2% compared with the wild type ( figure 1 A, E). Compared with wild type, pal1 The panicle length of the mutant was significantly reduced by 25.6%, and the number of primary branches and secondary branches were also significantly reduced by 22.0% and 45.9%, respectively ( figure 1 B, C, D, F, G, H), which finally led to a significant decrease of 40.2% in the number of grains per panicle ( figure 1 I).
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2 Rice PAL1 Gene acquisition
[0042] Will pal1 F 1 , F 1 F 2 To separate groups, use F 2 Populations for genetic analysis and gene mapping. to F 2 The analysis of the strains segregating generation traits showed that the segregation ratio of normal and mutant plants was 3:1, which indicated that the mutant traits were controlled by a pair of recessive genes.
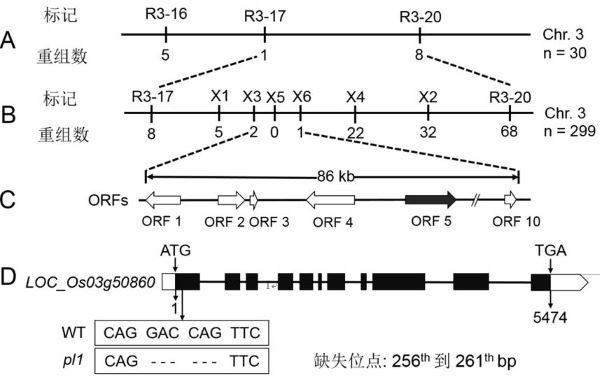
[0043] with F 2 30 mutants of the japonica rice variety Nipponbare provided by NCBI (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) were developed by comparing the whole genome sequence of the indica rice variety Dular sequenced in this experiment with the genome sequence of the japonica rice variety Nipponbare. A large number of Indel markers evenly distributed on the 12 chromosomes of rice were initially mapped, and the candidate gene was located between the R3-17 and R3-20 markers on chromosome 3 ( figure 2 A). In order to further fine-tune the candidate genes, continue to expand the F 2 Generation mapp...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 pCAMBIA1305.1::PAL1 vector transformed rice pal1 mutant
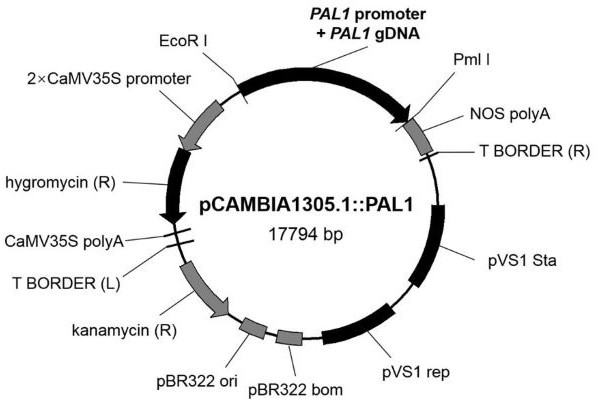
[0051] In order to conduct functional complementarity experiments, a PAL1 Functional complementation vector driven by the gene's own promoter. The 2525 bp before the translation initiation site ATG was selected as the promoter of the gene, and the promoter region and genomic DNA (excluding 3'UTR) were simultaneously amplified. The 5' end of the amplified fragment was introduced into the EcoRI site, and the 3' end was introduced into the PmlI site. The length of the PCR product was 8836 bp (including the homologous sequence on the vector). will eventually PAL1 A total of 8802 bp (shown in SEQ ID NO.2) of the self-promoter and the entire genome were connected together between the EcoRI and PmlI sites of the pCAMBIA1305.1 vector to form a reversion vector driven by the self-promoter ( image 3 ).
[0052] Transform the constructed complementary vector into Agrobacterium EHA105, and infect pal1 Mu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com