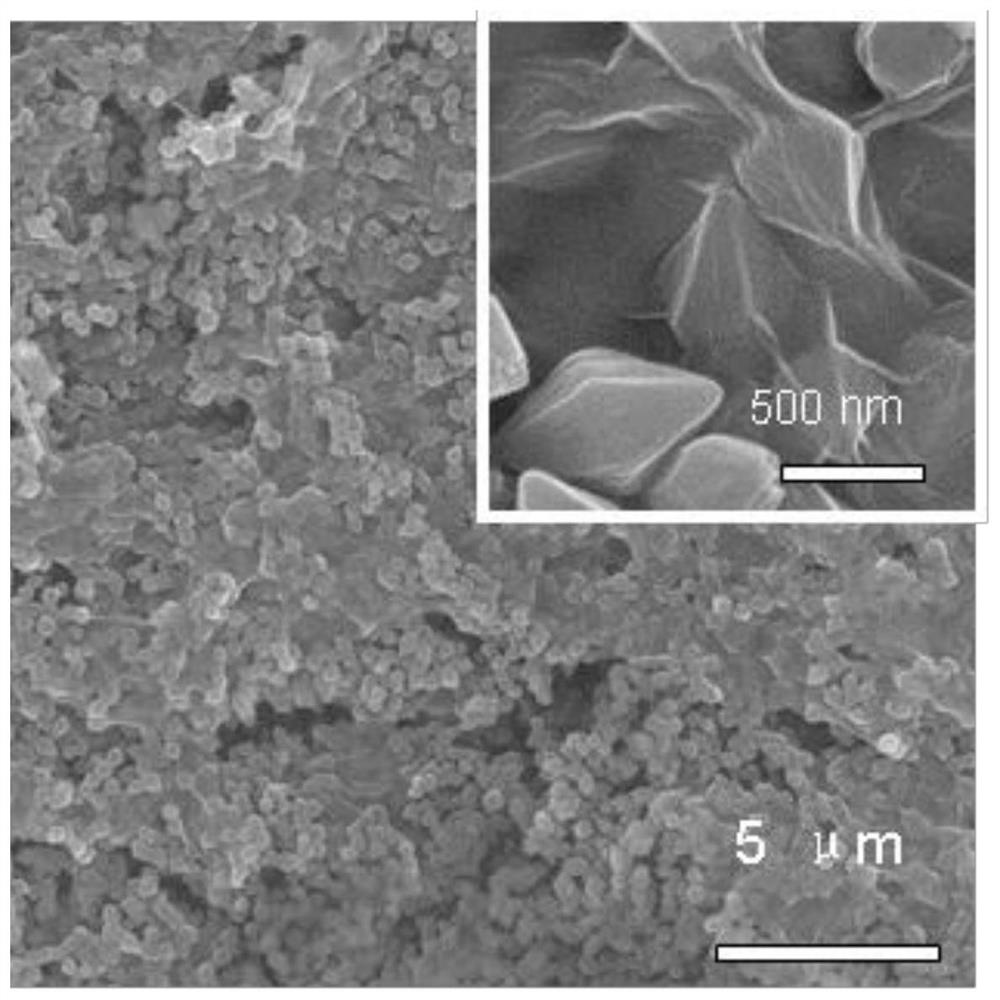
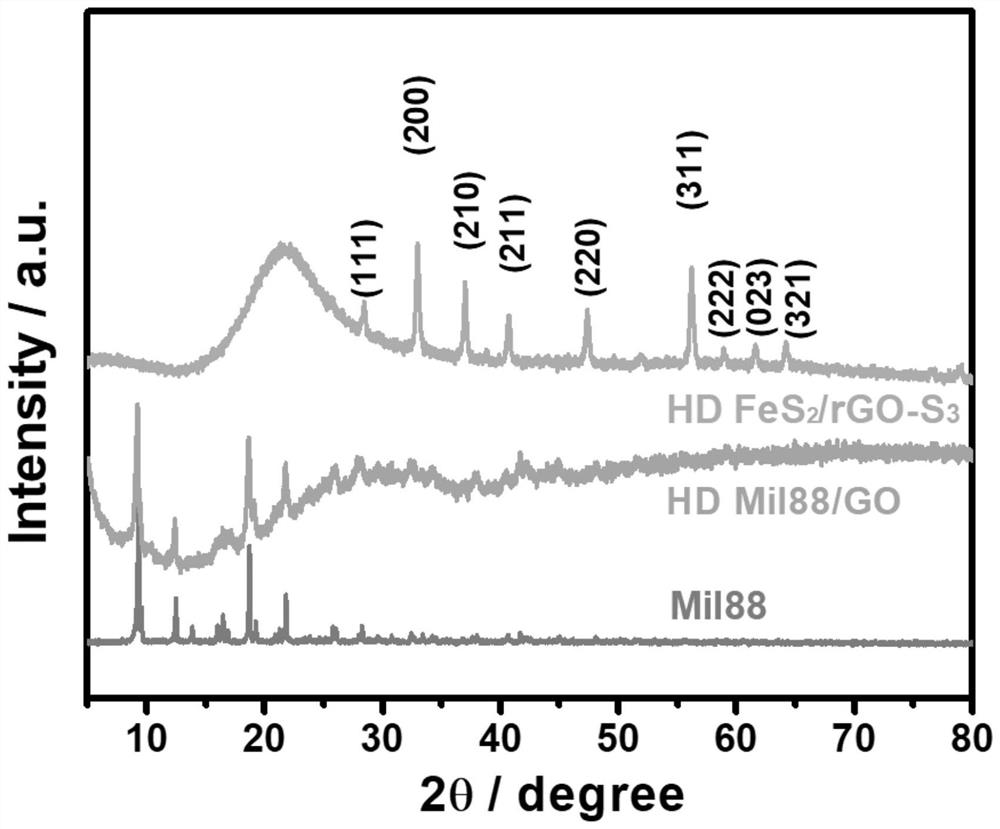
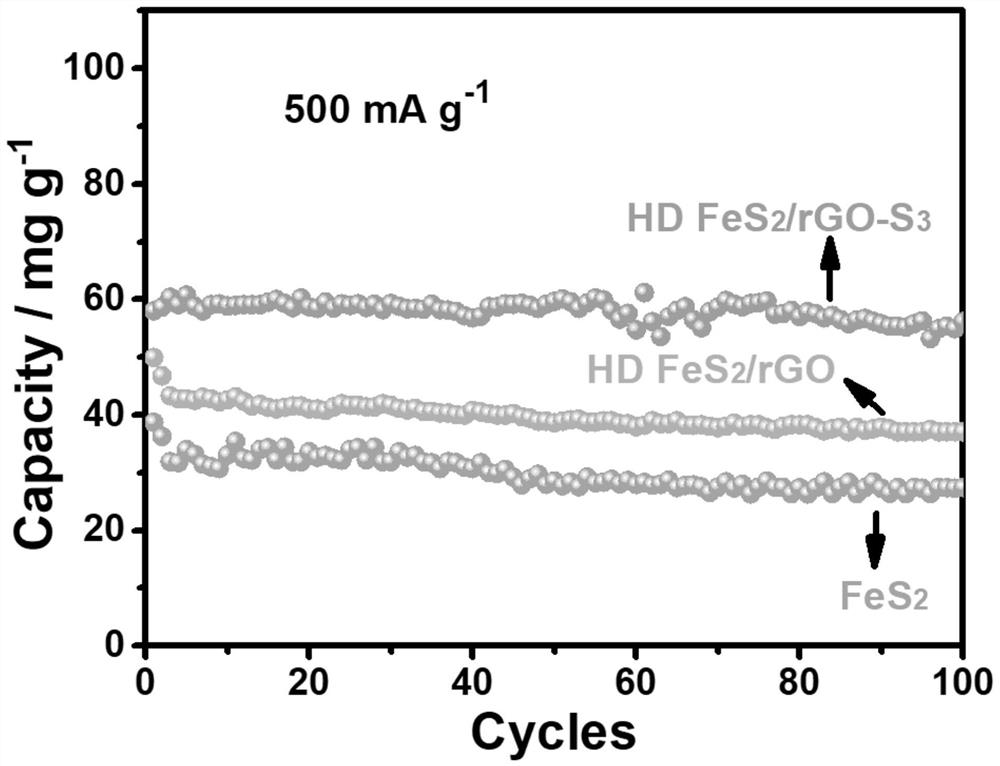
Method for regulating and controlling FeS2/reduced graphene oxide compact assembly structure
An assembly structure, graphene technology, applied in graphene, chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, etc., can solve the problem of limiting ion rapid transmission, and achieve the effect of adjustable shape, controllable structure, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A regulatory FeS 2 A method for reducing graphene oxide dense assembly structure, comprising the following steps:
[0026] (1) Preparation of Mil88 powder: Add 100 ml DMF to a 250 ml beaker, dissolve 2.43 g anhydrous ferric chloride and 1.66 g terephthalic acid in DMF, stir until completely dissolved, and place in a 100 °C In an oil bath, let stand at constant temperature for 12 hours. After the reaction, wash with ethanol for 3 times, and dry the product in a vacuum oven at 60°C for 24 hours to obtain Mil88 powder;
[0027] (2) Preparation of Mil88 / GO / S powder: Add 500 mg of Mil88 powder and 1500 mg of sulfur powder prepared in step (1) into a 20 ml glass bottle, and then add 10 ml of graphene oxide GO (the mass of GO powder is 100 mg) dispersion liquid, stirred well, and then dried in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h to obtain Mil88 / GO / S powder;
[0028] (3) Dense FeS 2 / Preparation of reduced graphene oxide: add 100 mg of Mil88 / GO / S powder to the downstream porcel...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A regulatory FeS 2 A method for reducing graphene oxide dense assembly structure, comprising the following steps:
[0033] (1) Preparation of Mil88 powder: Add 100 ml DMF to a 250 ml beaker, dissolve 0.2 g anhydrous ferric chloride and 0.8 g terephthalic acid in DMF, stir well until completely dissolved, and place in a 60 °C In an oil bath, stand at constant temperature for 13 h. After the reaction, wash with ethanol for 3 times, and dry the product in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h to obtain Mil88 powder;
[0034] (2) Preparation of Mil88 / GO / S powder: Add 400 mg of Mil88 powder and 1000 mg of sulfur powder prepared in step (1) into a 20 ml glass bottle, and then add 25 ml of graphene oxide GO (the mass of GO powder is 200 mg) dispersion liquid, stirred well, and then dried in a vacuum oven at 50 °C for 24 h to obtain Mil88 / GO / S powder;
[0035] (3) Dense FeS 2 / Preparation of reduced graphene oxide: add 100 mg of Mil88 / GO / S powder to the downstream porcelain boat,...
Embodiment 3
[0037] A regulatory FeS 2 A method for reducing graphene oxide dense assembly structure, comprising the following steps:
[0038] (1) Preparation of Mil88 powder: Add 100 ml DMF to a 250 ml beaker, dissolve 3.5 g anhydrous ferric chloride and 0.7 g terephthalic acid in DMF, stir until completely dissolved, and place in a 120 °C In an oil bath, stand at constant temperature for 11 h. After the reaction, wash with ethanol for 3 times, and dry the product in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 24 h to obtain Mil88 powder;
[0039] (2) Preparation of Mil88 / GO / S powder: Add 2000 mg of Mil88 powder and 5000 mg of sulfur powder prepared in step (1) into a 20 ml glass bottle, and then add 20 ml of graphene oxide GO (the mass of GO powder is 300 mg) dispersion liquid, stirred well, and then dried in a vacuum oven at 70 °C for 24 h to obtain Mil88 / GO / S powder;
[0040] (3) Dense FeS 2 / Preparation of reduced graphene oxide: add 100 mg of Mil88 / GO / S powder to the downstream porcelain boat, ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com