A 3D printing device and method for compounding continuous fiber and granular matrix material
A continuous fiber and matrix material technology, which is applied in the field of 3D printing devices combining continuous fiber and granular matrix materials, can solve the problems of short impregnation time, difficult polymer materials, and improved mechanical strength, so as to reduce equipment and operating costs, The effect of reducing void defects and simplifying the manufacturing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] In this embodiment, the continuous fiber is continuous carbon fiber (T300B-1000-50C, 1000 pieces, fiber bundle diameter 0.5 mm, single carbon fiber diameter 8 μm); particle matrix material is polylactic acid (PLA, melting point 170 ° C, particle size is 15 mesh).
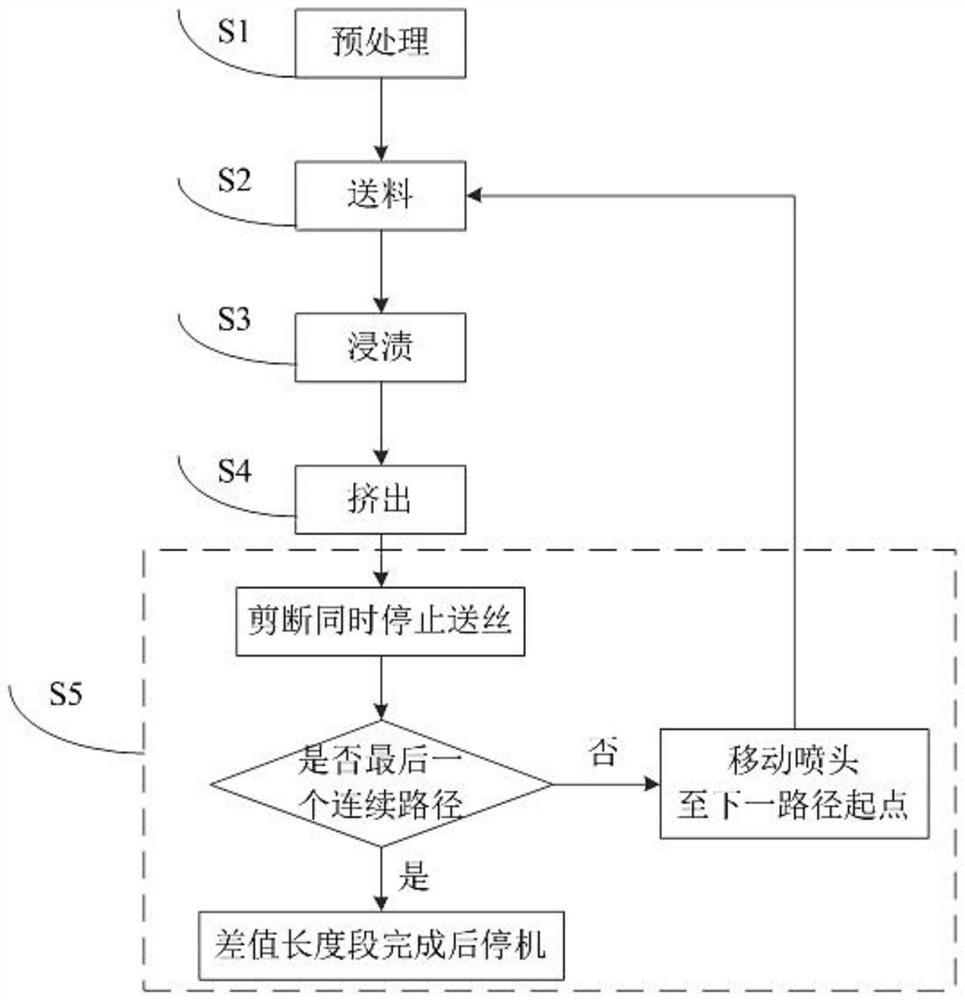
[0066] The 3D printing method of continuous fiber and particle matrix material composite of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
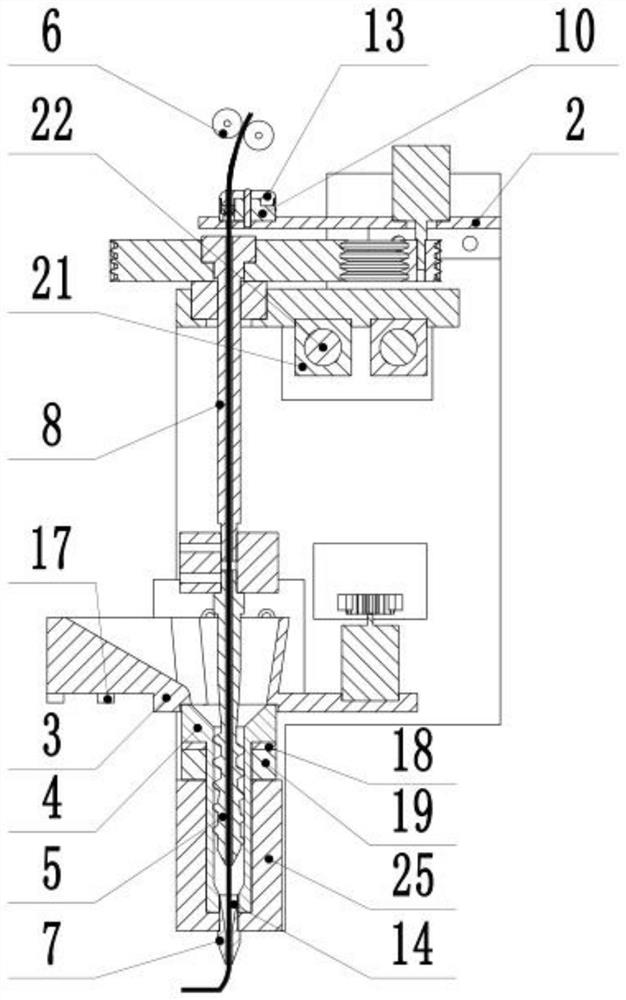
[0067] S1 pretreatment: heat the heating block 25 to 210°C, turn on the water pump switch at the same time, the water circulation fluid is provided by the external water tank and circulates through the spiral channel provided inside the heat dissipation sleeve 19 to take away the heat and realize the cooling and heat dissipation function ;
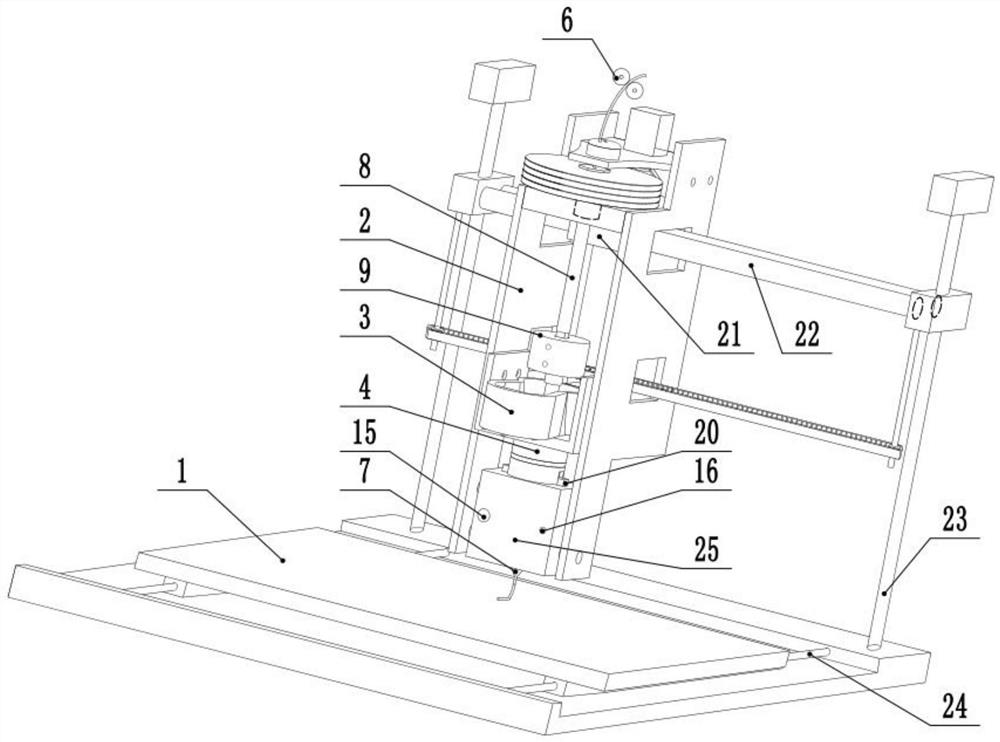
[0068] S2 Feeding: Start the wire feeding element 6 (fiber delivery speed is 10mm / s) to feed the continuous carbon fiber from the fiber delivery pipe 8, and reach the nozzle 7 through the screw 5. When the top of ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] In this embodiment, the continuous fiber is continuous flax fiber (200tex, fiber bundle diameter 0.5mm, single fiber diameter 15μm); matrix material is epoxy resin, powdery, particle size is 125 mesh, melting point is 65 ℃, doped 2.5% carbon nanotubes (CNTs, model XFM-18) are used as reinforcing fillers (carbon nanotubes ensure the stress transmission of the matrix material due to their high specific surface area and aspect ratio, and further improve the strength and toughness of the composite material) , the molten state of the matrix material is a high-viscosity fluid. Compared with thermoplastic materials, thermosetting materials need to be post-cured after printing, so a curing agent needs to be added to the epoxy resin. This embodiment uses a high-temperature curing agent. The high-temperature curing agent has excellent properties, fast curing speed, and strong operability. The curing process is divided into two stages. The first stage is pre-cured at a lower tempe...
Embodiment 3
[0084] In this example, the continuous fiber is continuous carbon fiber (T300B-1000-50C, 1000 pieces, fiber bundle diameter 0.5 mm, single carbon fiber diameter 8 μm), and the particle matrix material is polyether ether ketone (PEEK, melting point 343 ° C, particle size The number is 15 mesh)
[0085] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 mainly lies in:
[0086] (1) In the S1 pretreatment step, the heating block 25 is heated to 370°C.
[0087] (2) Since the fluidity of molten PEEK is worse than that of PLA used in Example 1, it is more difficult to extrude under the conveying action of screw 5. At the same fiber delivery speed as in Example 1, S4 extrusion step The fiber content of the composite silk obtained in is 60wt%;
[0088] All the other are with embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com