Application of azithromycin in reversing antibiotic resistance of food animal-derived pathogenic bacteria
A technology of antibiotic resistance and azithromycin, applied in the direction of antibacterial drugs, pharmaceutical formulations, organic active ingredients, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing sensitivity, enhancing antibacterial activity, and reducing the dosage used
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
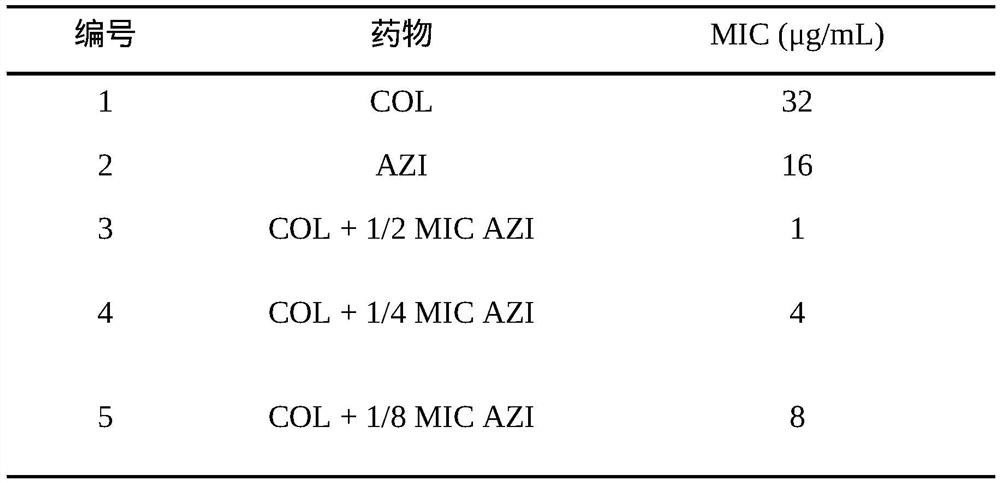
[0020] Observation on the effect of azithromycin in reversing the colistin resistance of clinical isolate Escherichia coli E57
[0021] (1) Test drugs
[0022] Azithromycin: content 97%, purchased from Sichuan Hengrui Tongda Co., Ltd.
[0023] Colistin sulfate: potency ≥ 23000u / mg, purchased from Hebei Shengxue Dacheng Tangshan Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
[0024] Azithromycin was prepared with 30% absolute ethanol and deionized water to make a stock solution with an initial concentration of 1280 μg / mL; colistin sulfate was prepared with deionized water to make a stock solution with an initial concentration of 1280 μg / mL, and stored at -20 °C.
[0025] (2) Strains
[0026] The clinically isolated colistin-resistant strain E. coli E57 was positive for mcr-1, and it was verified by cloning and sequencing that the drug resistance of the strain was mediated by the mcr-1 gene, provided by the Pharmacology Laboratory of Henan Agricultural University.
[0027] (3) culture medium
[...
Embodiment 2
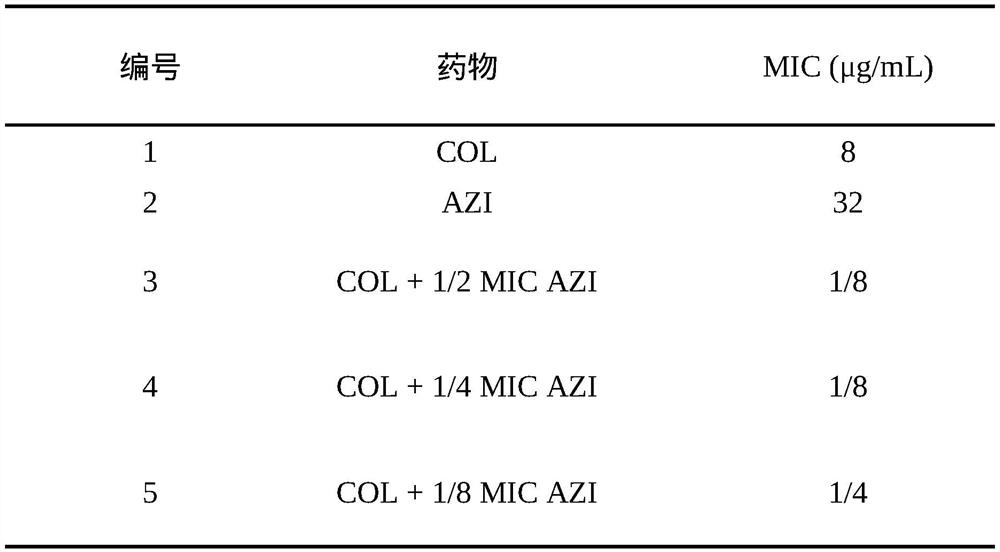
[0050] Effect of azithromycin on reversing colistin resistance of clinical isolate Escherichia coli ED16
[0051] Experimental drugs, culture medium, instruments, bacterial solution preparation and MIC determination and determination methods are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is:
[0052] The strain used was Escherichia coli isolate ED16, negative for mcr-1, which was proved to be a colistin-resistant strain mediated by chromosomal mutation or increased expression by next-generation sequencing of the whole genome, provided by the Pharmacology Laboratory of Henan Agricultural University.
[0053] Embodiment 2 experimental result is as follows:
[0054] Table 2 Effect of azithromycin on drug resistance of Escherichia coli isolate ED16
[0055]
[0056] Note: COL: colistin; AZI: azithromycin; 1 / 2MIC AZI: the amount of azithromycin added is 16 μg / mL; 1 / 4MICAZI: the amount of azithromycin added is 8 μg / mL; 1 / 8MIC AZI: the amount of azithromycin added is 4 μg / m...
Embodiment 3
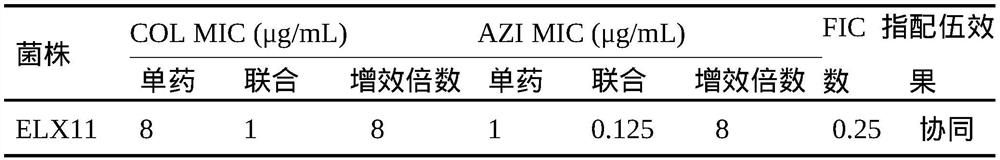
[0059] Colistin and Azithromycin Combined Drug Test in Vitro
[0060] Test medicine, culture medium, instrument and bacterial liquid preparation are identical with embodiment 1, difference is:
[0061] The experimental strain was Escherichia coli isolate ELX11, which was positive for mcr-1. It was verified by cloning and sequencing that the drug resistance of the strain was mediated by the mcr-1 gene, provided by the Pharmacology Laboratory of Henan Agricultural University.
[0062] MIC and FIC index determination:
[0063] The determination and interpretation of MIC were the same as in Example 1. The FIC (Fractionalinhibitory concentration, partial inhibitory concentration index) index of the combination of colistin and azithromycin against Escherichia coli was determined, and the in vitro antibacterial activity of the combination of the two drugs was determined by the 8×8 checkerboard method. FIC = MIC of colistin combination / MIC of colistin alone + MIC of azithromycin comb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com