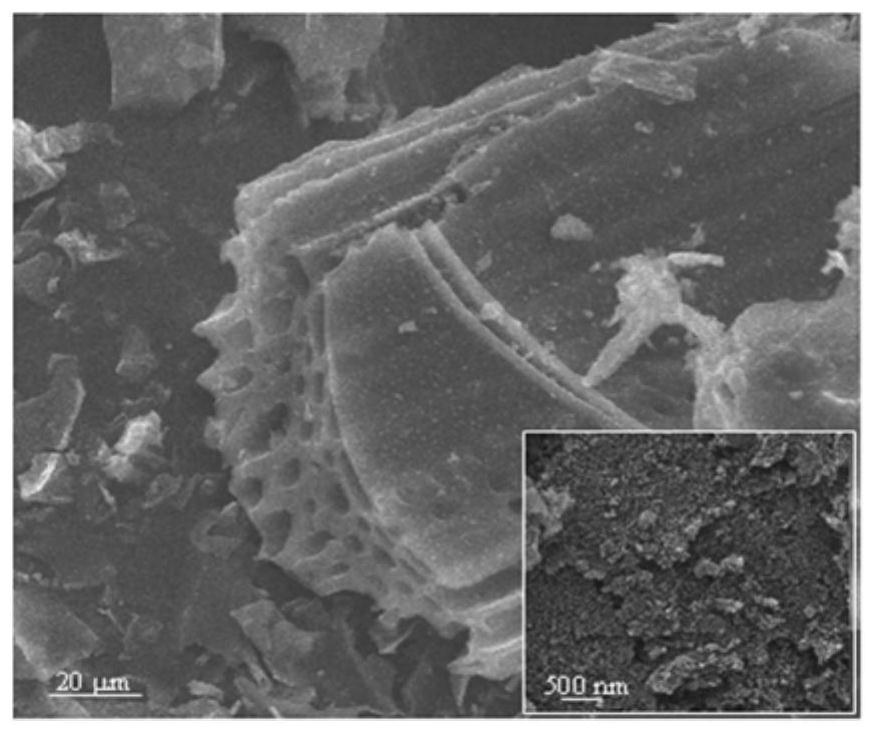
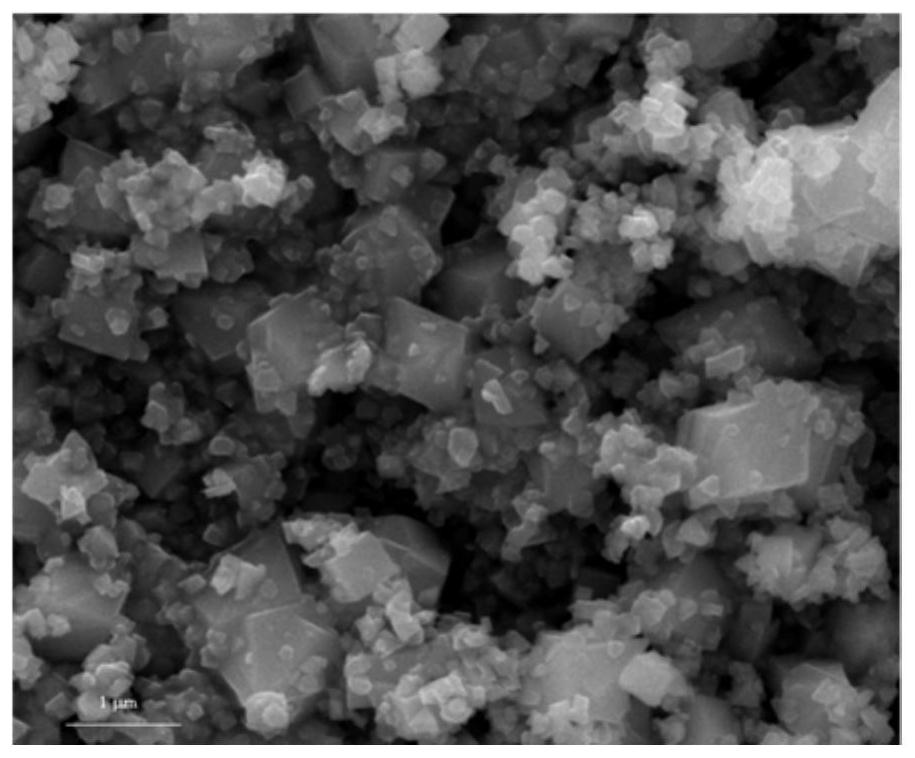
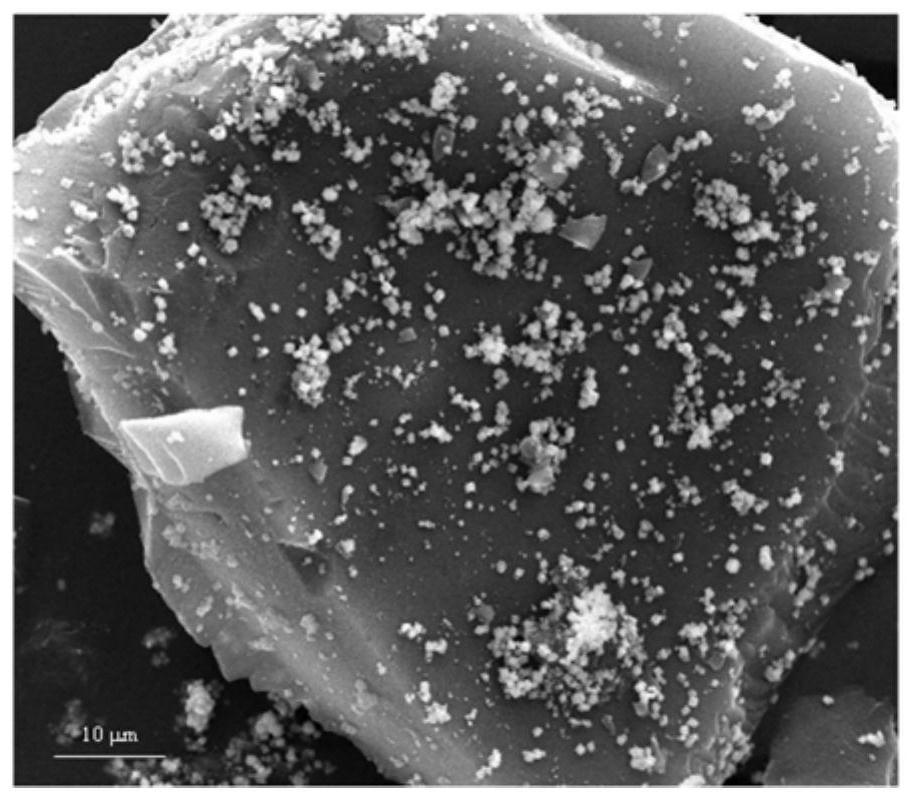
Porous biochar/zinc ferrite composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and biochar technology, applied in the field of environmental functional materials and water treatment, can solve problems such as preparation process optimization, and achieve the effects of increasing the number of adsorption sites, reducing preparation costs, and high product recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Abandoned corn stalks were collected as biochar precursors in rural areas around Baotou City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Take it back, wash it, air-dry it, and then crush it. After sieving, the obtained powder is bagged for later use. First, take 20g corn stalk powder, choose it and ZnCl 2 The mass ratio is 1.5:1, put it in a beaker, add a small amount of deionized water, then perform magnetic stirring for 30 minutes, soak for 20 hours, and dry at 80°C for 24 hours. Subsequently, the mixture was pyrolyzed in a tube furnace at 600 °C for 1 h, and the heating rate during the pyrolysis was 10 °C min -1 , N 2 The purge rate is 200mL min -1 , and finally wash the pyrolysis product with deionized water to neutrality, and dry it to obtain porous biochar.
[0041] Take 1.36g (0.01mol) ZnCl 2 (AR) and 5.41g (0.02mol) FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O(AR), were dissolved in 15.0ml ultrapure water, and magnetically stirred for 10 minutes to make it evenly mixed. Then add 4g (0.02mol) ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Utilizing the magnetic porous biochar zinc ferrite composite material of Example 1 of the present invention to adsorb radioactive thorium in the aqueous solution comprises the following steps:
[0048] Using the magnetic porous biochar zinc ferrite composite material obtained in Example 1 of the present invention to adsorb radioactive thorium in the aqueous solution comprises the following steps:
[0049] Get 25ml of thorium-containing solution whose initial concentration is 20~300mg / L, add the magnetic porous biochar / zinc ferrite composite material adsorbent that embodiment 1 makes, the consumption of this adsorbent is 1.2g / L, in constant temperature shaker After 4 hours, use a magnet to separate the adsorbent from the waste water, and use a UV spectrophotometer to measure the content of thorium in the solution that is not adsorbed by the magnetic composite material at 660nm. The calculated adsorption results are shown in Table 1. shown.
[0050] Table 1: Adsorption d...
Embodiment 3
[0055] In order to evaluate the reusability of the magnetic porous biochar zinc ferrite composite material, the present invention uses 25mL 0.05mol L -1 Citric acid desorbed 0.05g of thorium-adsorbed composite material for 6h, and carried out 5 cycles of adsorption-desorption cycle research under the same conditions, and the initial concentration of thorium in the adsorption experiment process was 50mg / L.
[0056] Table 2: Adsorption data of thorium by adsorbent in 5 desorption cycles
[0057]
[0058] It can be seen from Table 2 that under certain conditions, the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent still reaches 39.98 mg / g after 3 desorption cycles, and its adsorption capacity can reach 35.14 mg / g after 5 cycles. It shows that the magnetic porous biochar zinc ferrite composite material of the present invention has a good recycling effect.
[0059] Figure 7 It is the FT-IR diagram before and after 5 times analysis of the composite material in the embodiment of the prese...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com