DNA nano-molecule machine for exosome and surface protein analysis and application
A surface protein and nanomolecule technology, applied in analytical materials, biological material analysis, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome analysis steps, low sensitivity, and expensive instruments and equipment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
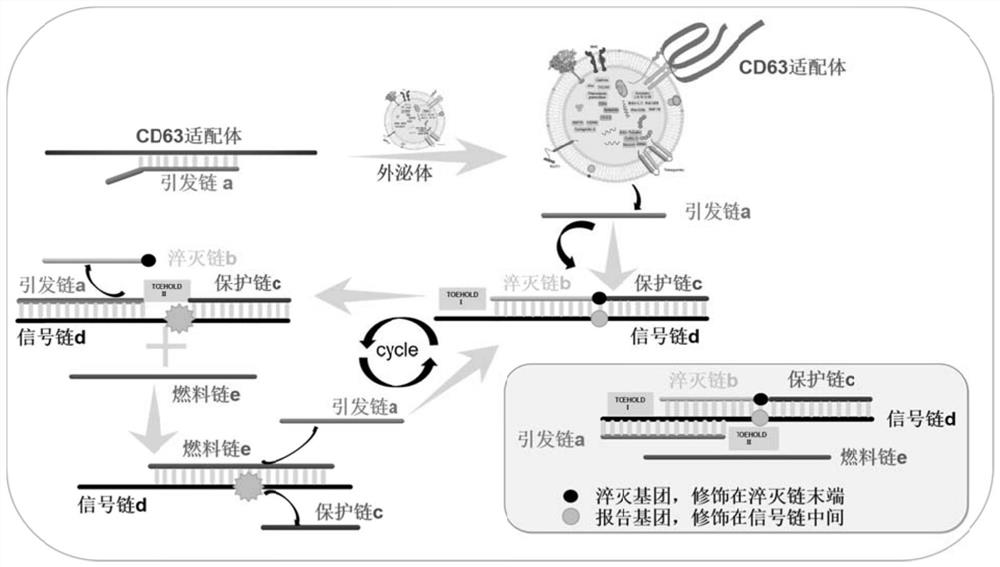
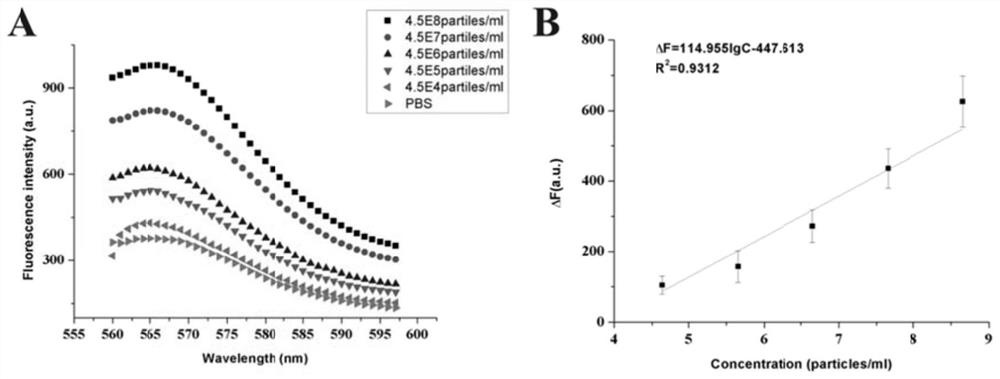
[0062] DNA molecular nanomachines for the quantification of exosomes in tumor cell culture supernatants, including:
[0063] The recognition probe is a double-stranded DNA structure formed by hybridizing the priming strand a with the nucleic acid aptamer (Apt-CD63) sequence of CD63. Preparation of the recognition probe: Add the nucleic acid aptamer and priming strand a to a certain volume of ligation reaction buffer at a final concentration ratio of 1:1, denature at 95°C for 5 minutes to open the local secondary structure of the DNA strand, and quickly Cool down to room temperature, so that the two oligonucleotide chains hybridize into a recognition probe, and store at 4°C for future use.
[0064] The signal probe is a double-stranded DNA structure formed by the hybridization of two short DNA strands (quencher strand b and protection strand c modified at the end of BHQ2) and a long DNA strand (reporter strand modified in the middle of Cy3). After the signal probe self-assembl...
Embodiment 2
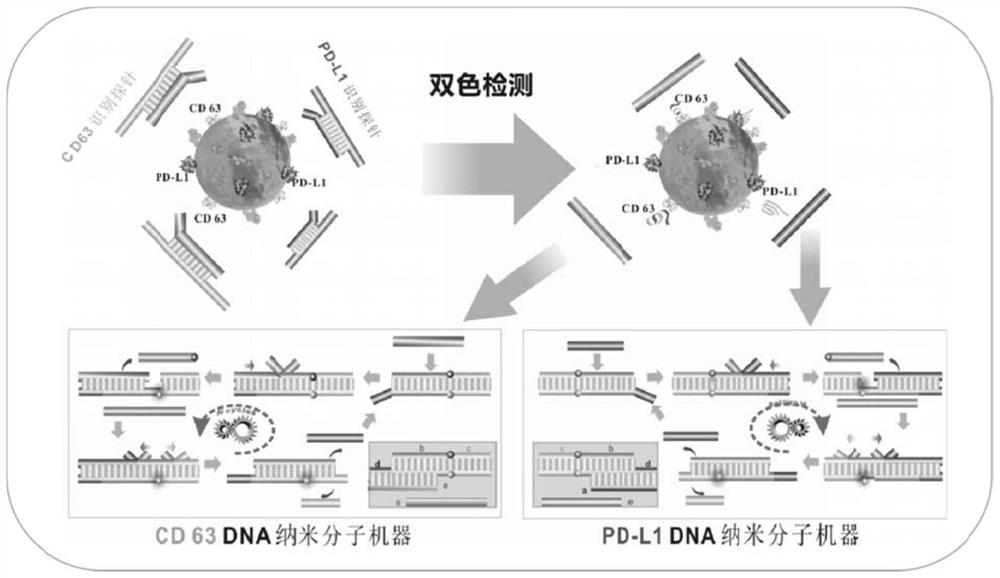
[0073] DNA nanomolecular machines for two-color phenotyping of exosomes (CD63 and PD-L1) in tumor cell culture supernatants, including:
[0074] Recognition probe: CD63 recognition probe is initiated by strand a CD63 Aptamers to CD63 (Apt CD63 ) double-stranded DNA structure formed by partial hybridization of sequences. The PD-L1 recognition probe is initiated by a PD-L1 In the nucleic acid aptamer (Apt PD-L1 ) double-stranded DNA structure formed by partial hybridization of sequences. The preparation method of the recognition probe is the same as that in Example 1.
[0075] Signal probe: The CD63 signal probe is a quenched chain b modified by two short DNA strands (BHQ2 ends) CD63 and protection chain c CD63 ) and a long DNA strand (reporter strand modified in the middle of Cy3) to form a double-stranded DNA structure. After the signal probe self-assembled successfully, the Cy3 and BHQ2 groups modified internally caused the fluorescence of Cy3 to be quenched by BHQ2 du...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com