Method for preparing magnetic refrigeration alloy using spark plasma sintering technology (SPS)
A magnetic refrigeration and magnetic alloy technology, applied in the field of magnetic refrigeration materials, to achieve the effects of fast sintering speed, easy storage, and controllable grain growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
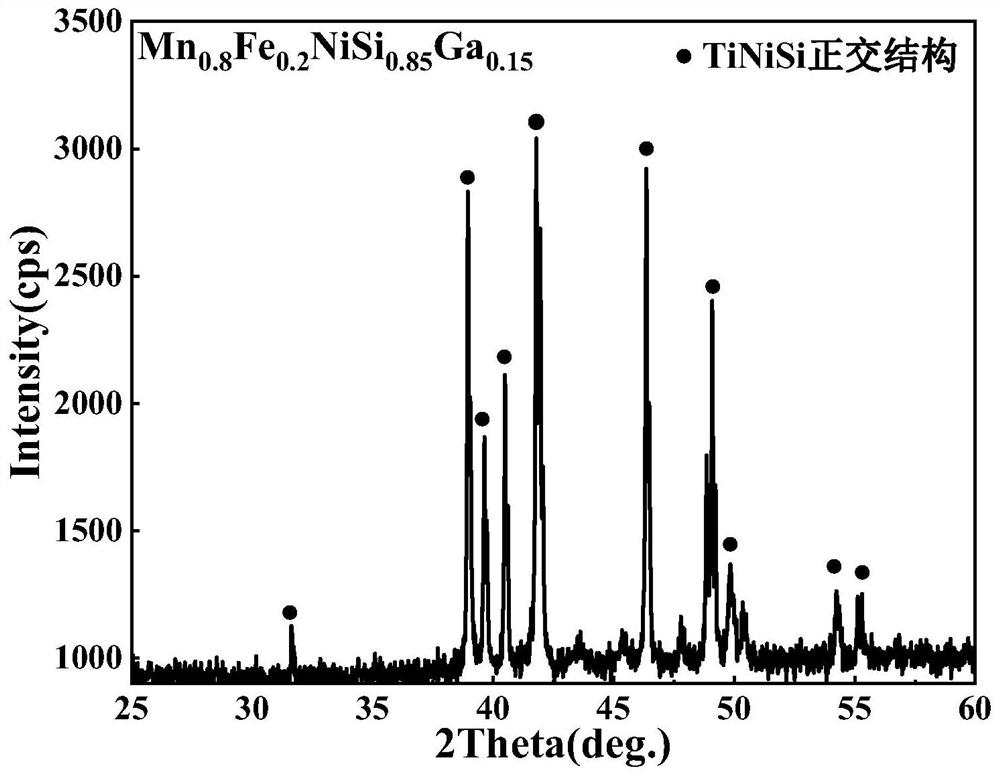
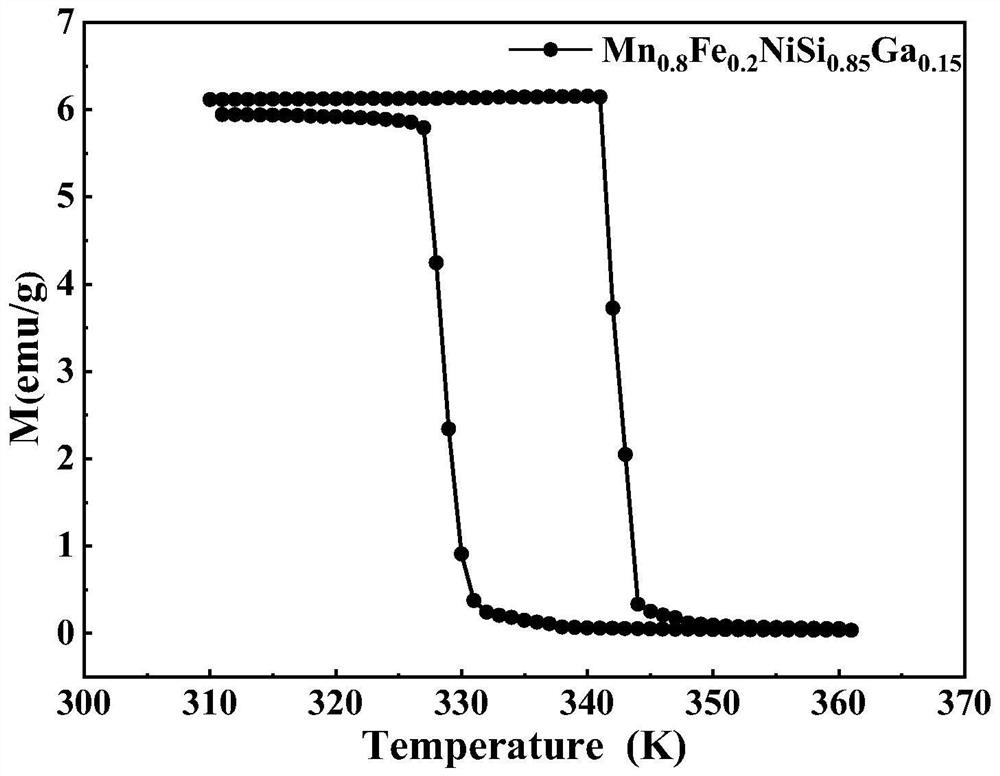
[0033]Example 1: The preparation chemical formula of this example is Mn0.8Fe0.2NiSi0.85Ga0.15Magnetic alloy block, where Mn0.8Fe0.2NiSi0.85Ga0.15The alloy refers to replacing 20% (molar ratio) of Mn with Fe and replacing 15% (molar ratio) of Si with Ga in the MnNiSi alloy. In other embodiments, the same explanation is also given. The preparation method is carried out according to the following specific steps:
[0034]Step 1, according to the molar ratio of Mn: Fe: Ni: Si: Ga = 0.8: 0.2: 1: 0.85: 0.15, weigh Mn, Fe, Ni, Si, Ga and other raw materials with a purity of 99.9%;
[0035]Step 2: Put the weighed raw materials into a water-cooled copper crucible, vacuum with a mechanical pump, and purge with argon gas. Repeat this 4 times. The suspension smelting method melts the polycrystalline sample ingot, and each sample is turned over 3 times. Co-melt 4 times to ensure uniform composition and prepare alloy ingots;
[0036]Step 3: Wrap the obtained ingots or fine particles with tantalum flakes,...
Embodiment 2
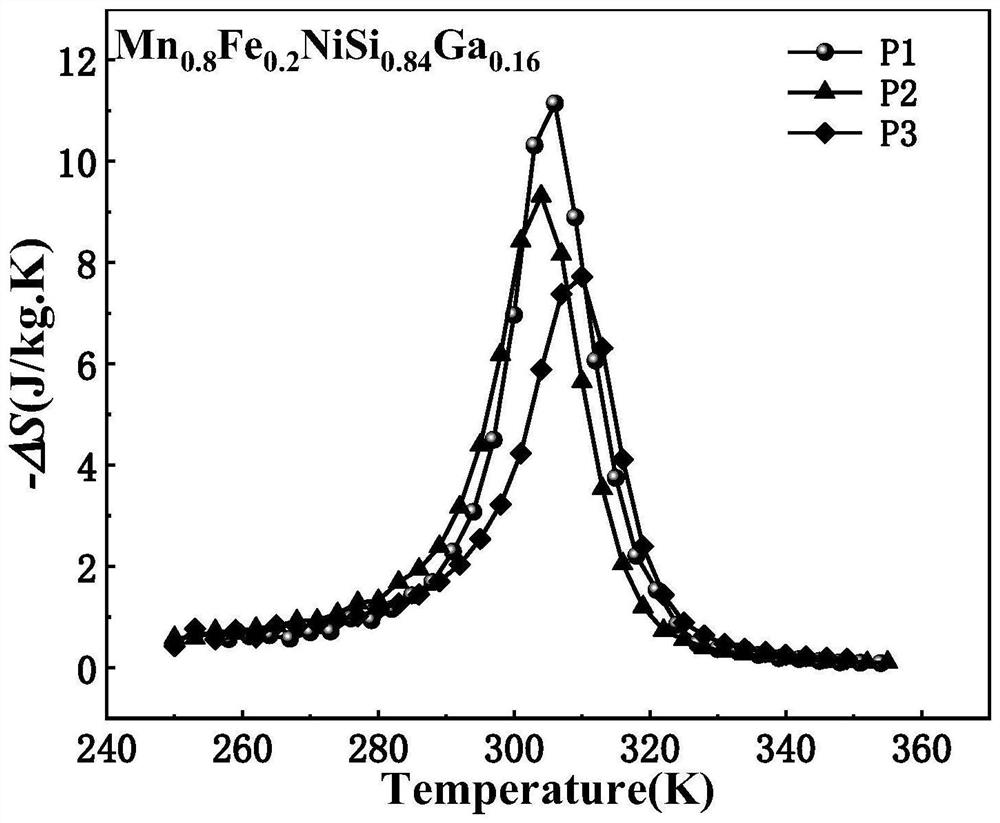
[0040]Example 2: The preparation chemical formula of this example is Mn0.8Fe0.2NiSi0.84Ga0.16The preparation method of the magnetic alloy block is similar to the method in Example 1, except that the step four screening uses three particle size ranges, namely P1 (74~150μm), P2 (50~74μm), P3(37~ 50μm) sample; Step 5 is sintered at 900°C and 50Mpa.
[0041]Mn prepared in this example0.8Fe0.2NiSi0.84Ga0.16The alloy has the same crystal structure and similar change laws as in Example 1.image 3 Mn0.8Fe0.2NiSi0.84Ga0.16The magnetic entropy change and temperature dependence curve of the alloy, as the particle size decreases, the magnetic entropy change decreases, and the maximum magnetic entropy change is as high as 11.14J / kg·K.
Embodiment 3
[0042]Example 3: The preparation chemical formula of this example is Mn0.8Fe0.2NiSi0.83Ga0.17The preparation method of the magnetic alloy block is similar to that of Example 1, except that in step four, samples with a particle size range of P3 (37-50μm) will be screened; step five will be sintered at 800°C and 80Mpa.
[0043]Mn prepared in this example0.8Fe0.2NiSi0.83Ga0.17The alloy has a different crystal structure from Example 1 and Example 2.Figure 4Mn0.8Fe0.2NiSi0.83Ga0.17The backscattered electron image of the alloy. It can be seen from the image that there are a large number of micro-cracks inside a single particle. This indicates that the destruction of the particles during the hot pressing process further reduces the size of the particles and introduces particle defects, thereby reducing the alloy The phase transition temperature.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com