A vortex beam generation device, system and method with adjustable topological number
A vortex beam and generation device technology, applied in the field of laser applications, can solve the problems of difficult processing, low utilization rate of light energy, difficulty and high cost, and achieve continuous adjustable size, high energy conversion rate, and high edge energy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
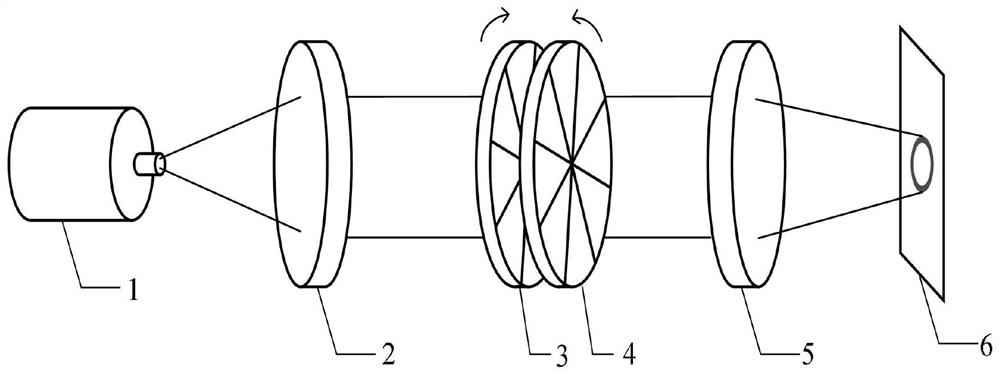
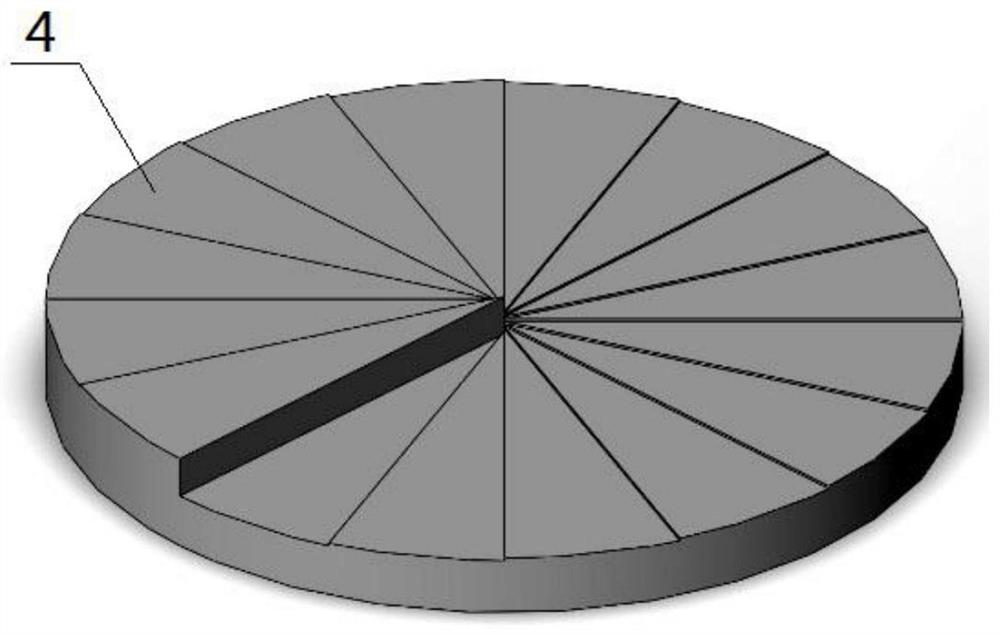
[0041] see figure 1 and figure 2 , this embodiment discloses a vortex beam generation device with adjustable topological number, including two helical-specific helical phase mirrors, and the phases of the two helical phase mirrors are respectively set to Aθ 2 and -Aθ 2 , A is a constant, which is used to control the variation range of the topological number of the obtained vortex beam. The topological number of the obtained vortex light takes all integers in the interval from 0 to 4Aπ, θ is the azimuth with the center of the spiral phase mirror as the origin, and two Two helical phase mirrors are arranged on the optical path in turn, and the laser beam is attached with a helical phase factor with a set topological number after passing through two helical phase mirrors in turn, turning into an annular vortex beam, which is controlled by rotating one or two helical phase mirrors. The angle difference between the two spiral phase mirrors is used to adjust the topological numbe...
Embodiment 2
[0051] see Figure 1 to Figure 7 , this embodiment discloses a vortex beam generation system with adjustable topological number, including a collimation unit 2, a focusing unit 5, and the vortex beam generation device described in Embodiment 1, and the vortex beam generation device is set at The optical path between the collimating unit 2 and the focusing unit 5;
[0052] The collimation unit 2 is used to collimate the input laser to obtain a collimated laser beam;
[0053] The vortex beam generating device is used to add a helical phase factor of the corresponding topological charge to the collimated laser beam emitted by the collimation unit to become an annular beam, and its topological charge is determined by the angle difference between the two helical phase mirrors ;
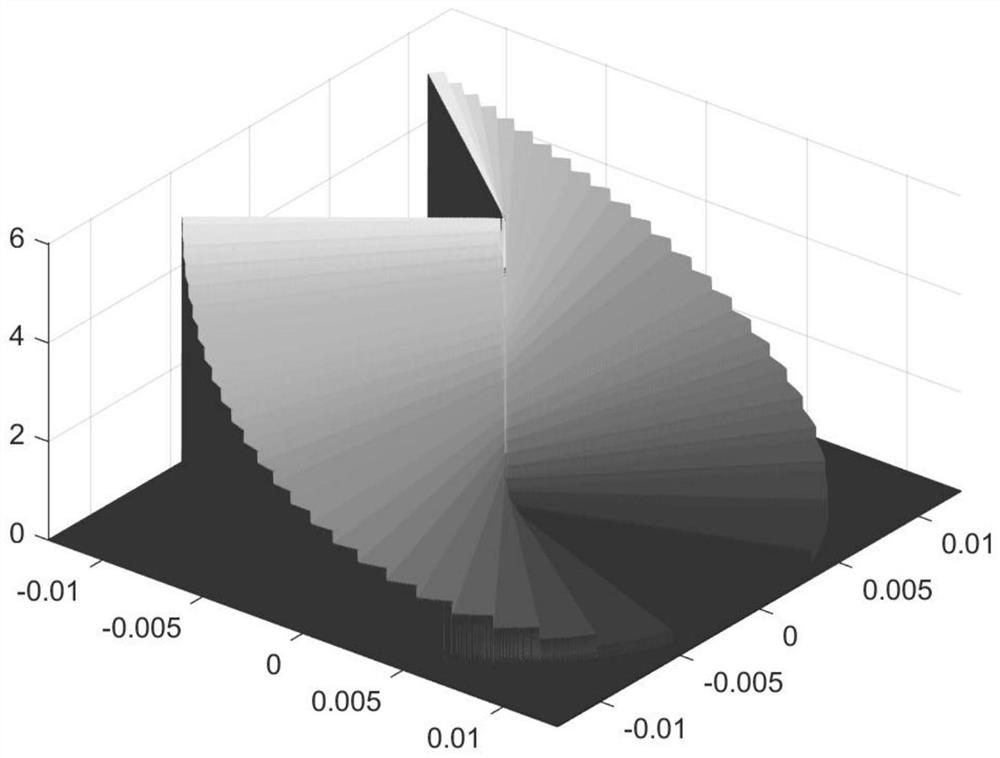
[0054] The focusing unit 5 is used to focus the ring-shaped beam emitted by the vortex beam generating device to obtain a light spot with ring-shaped energy distribution.
[0055] Further, before the co...
Embodiment 3
[0064] see Figure 8 , The vortex beam generation system of this embodiment also includes two scanning galvanometers, the two scanning galvanometers are arranged on the optical path between the vortex beam generating device and the focusing unit 5, and the optical path is carried out by two scanning galvanometers. Toggle to change the focus position of the focus plane. Other technical features of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 2.
[0065] After the laser beam passes through the collimation unit 2 and the vortex beam generating device, it passes through the first scanning galvanometer 7, the second scanning galvanometer 9, and finally the focusing objective lens. , can change the focus position of the focal length surface, and perform fine laser processing such as marking, welding and cutting.
[0066] The light path of embodiment 3, the energy distribution of the light field on the focal plane is consistent with embodiment 1, because the ring-shaped ligh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com