Patents
Literature
57results about How to "Jiao Shenda" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
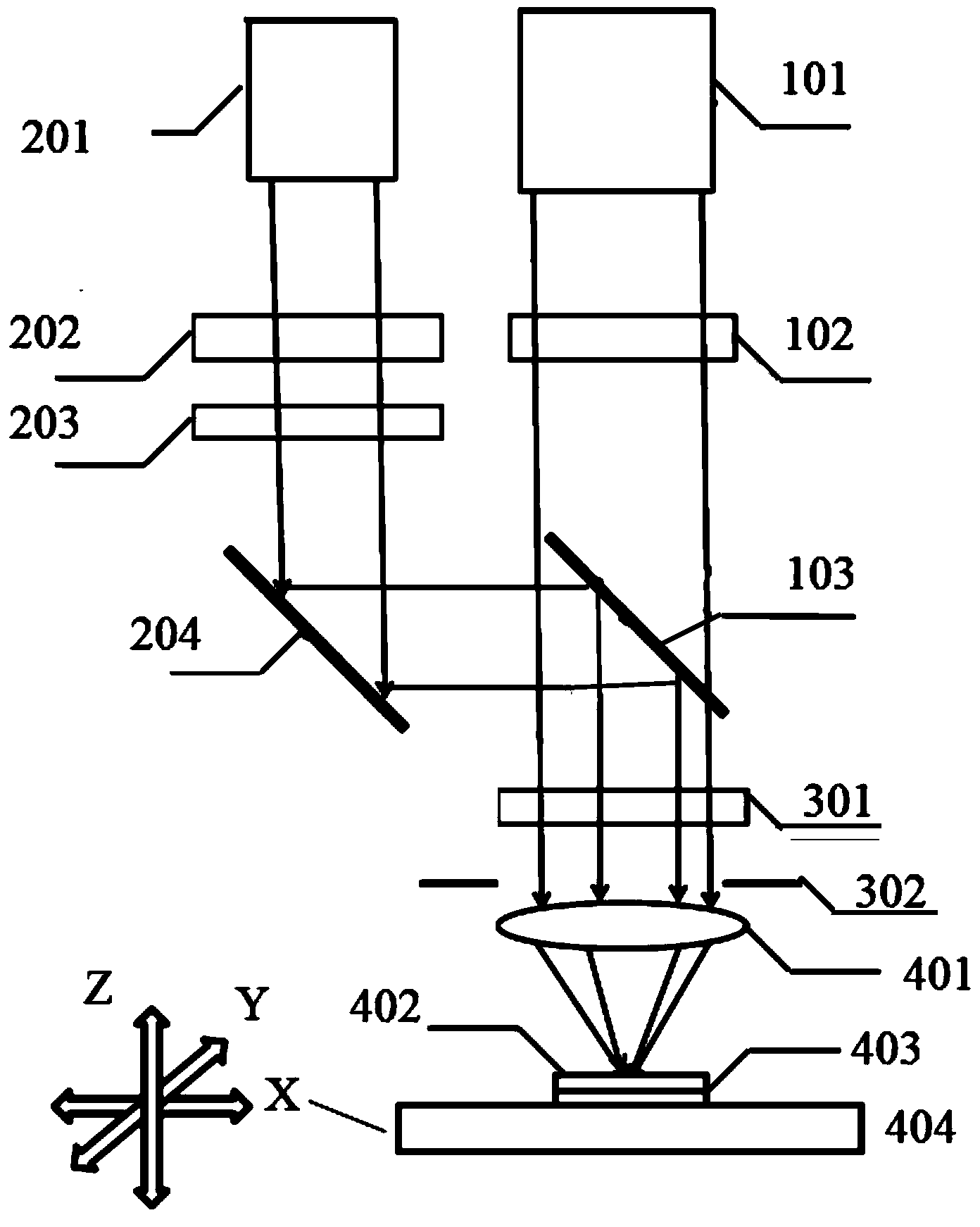
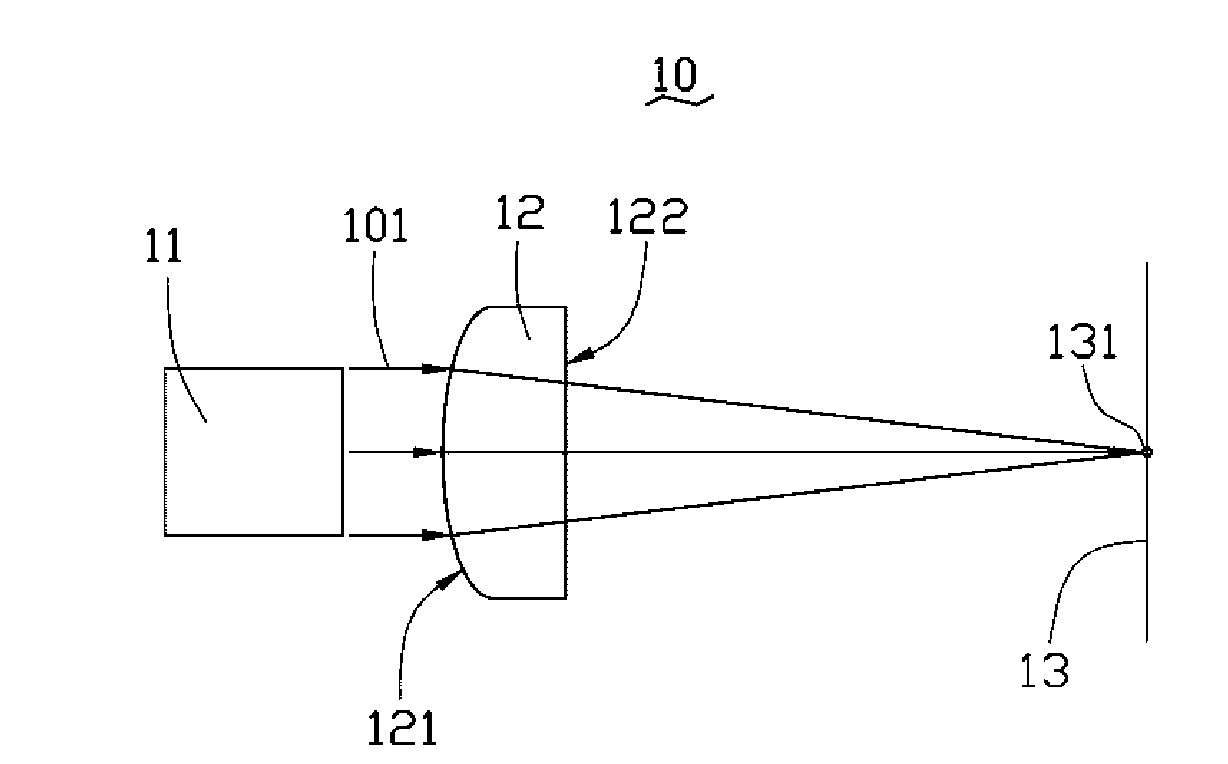
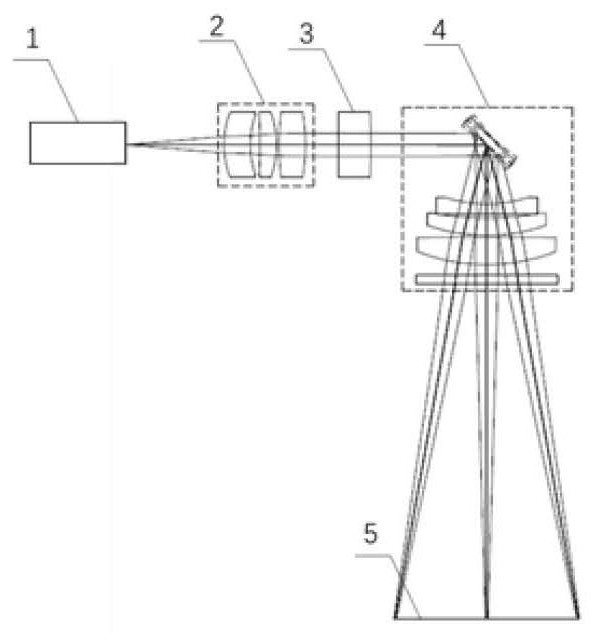
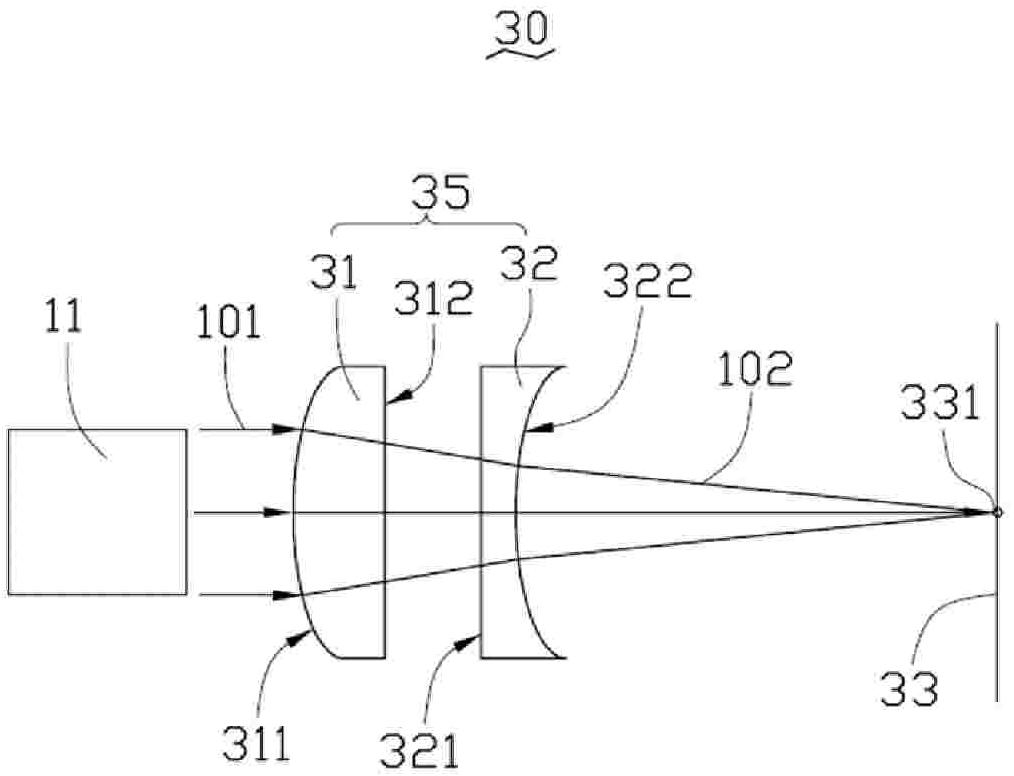
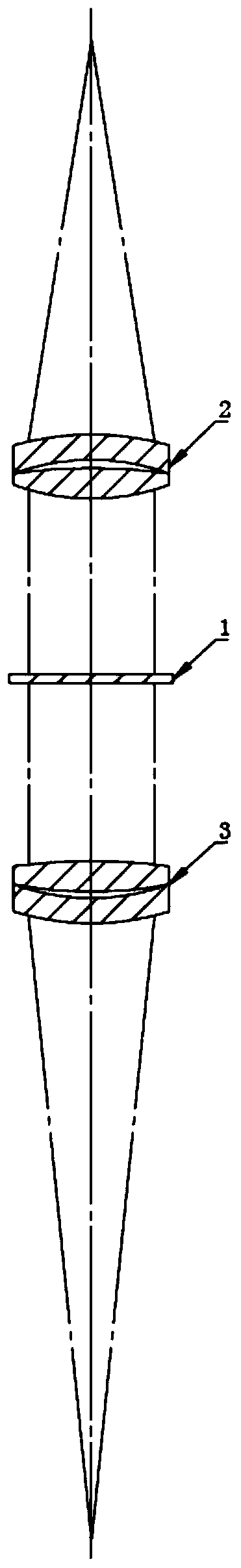
Laser direct writing exposure device based on stimulated light emission loss
ActiveCN103777473AImprove resolutionJiao ShendaPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorHigh numerical aperture
The invention discloses a laser direct writing exposure device based on stimulated light emission loss. The laser direct writing exposure device is characterized by comprising an excitation light source, a de-excitation light source, a first space light modulator, a second space light modulator, a half wave plate group, a dichroscope, a phase position type wave zone plate, an amplitude type wave zone plate, a high numerical value aperture achromatic objective and a three-dimension scanning platform. The laser direct writing exposure device provided by the invention can realize the optical exposure of high resolution and long focus depth.
Owner:BEIJING GUOWANG OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Optical system of annular light spot
PendingCN111338089AEasy to implementHigh edge energyLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsOptical pathEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of laser processing, and discloses an annular light spot optical system. The system comprises a collimation unit, a phase modulation unit and a focusing unit which are sequentially arranged along a light path. The phase modulation unit comprises at least one spiral phase plate positioned in the light path; a laser beam can be added with a spiral phase factor to realize phase modulation through a spiral phase plate in an optical path, so the energy distribution of the laser beam is changed into annular distribution. Furthermore, the spiral phase plates can bearranged on the rotating shaft, and the states in the light path and outside the light path are switched by rotating around the rotating shaft, so variable annular light spots can be realized by switching the spiral phase plates. By improving the components of the optical system and the matching action mode among the components, the annular light spot with concentrated energy distribution at the edge, larger diameter and longer focal depth can be obtained, the size of the light spot is further adjustable, and the optical system is suitable for various laser processing fields such as laser cutting and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical digital mixed imaging system and method
InactiveCN101477253AOptimal phase distribution functionLarge defocus invarianceImage enhancementOptical elementsPhotovoltaic detectorsFiltration
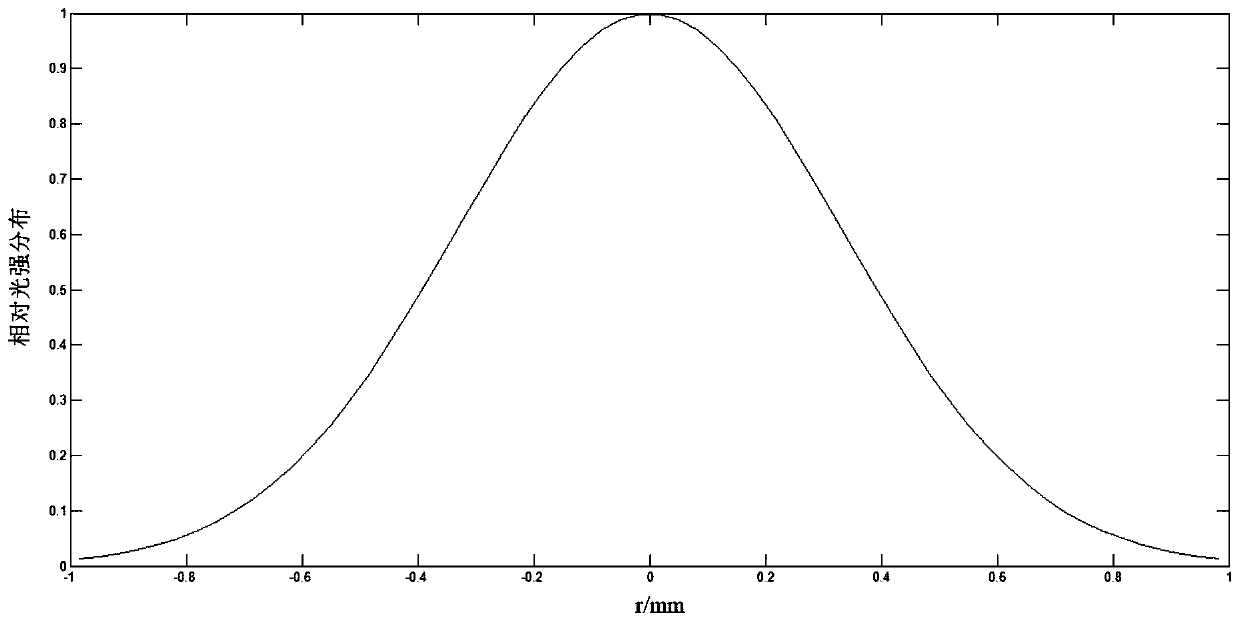
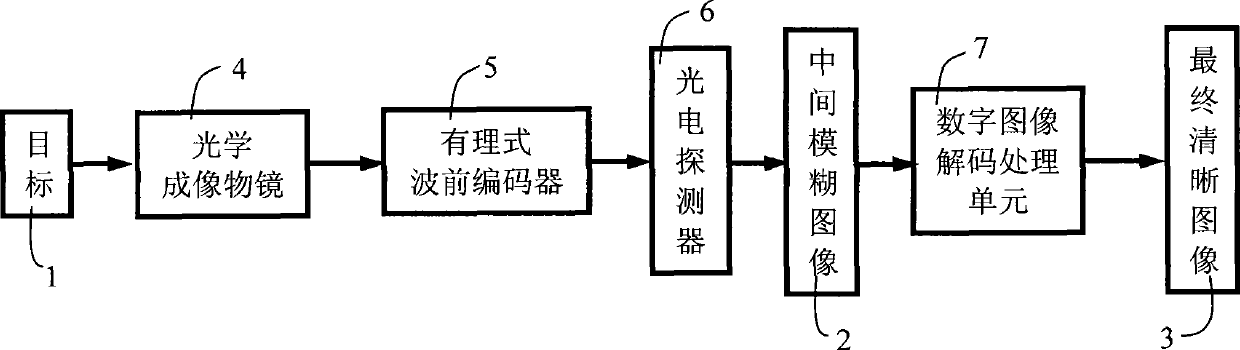
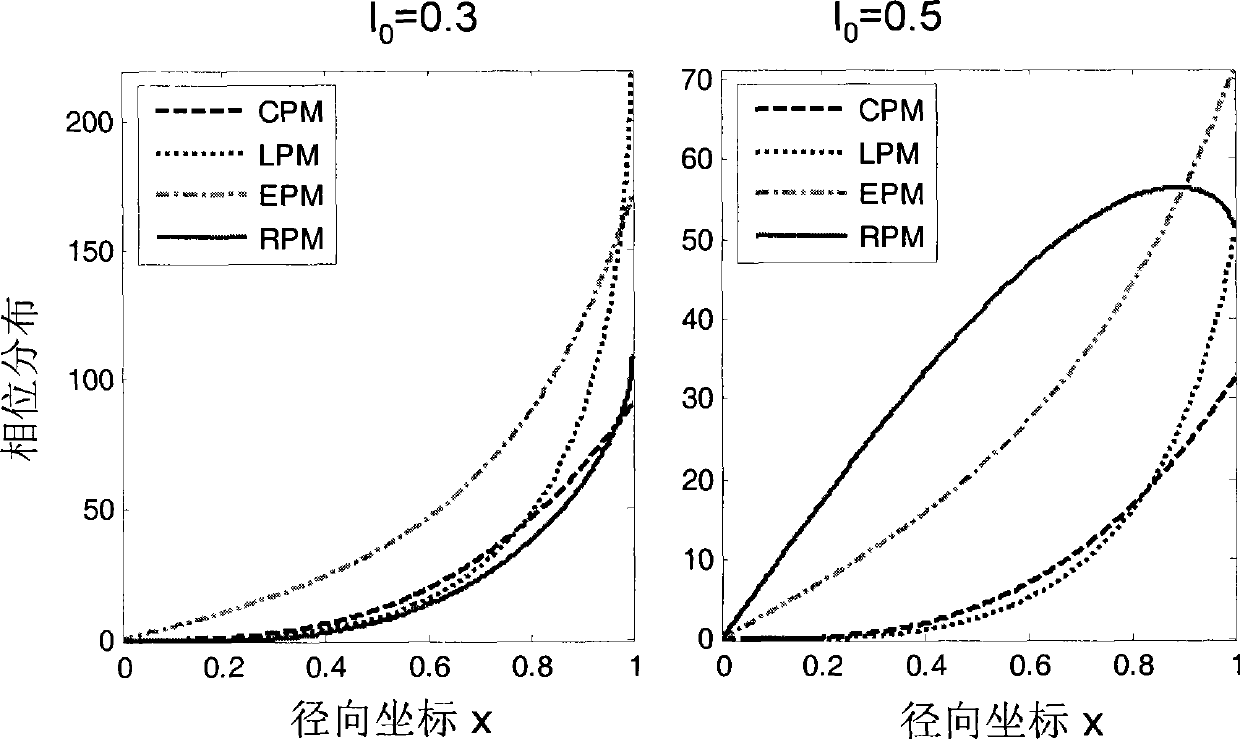
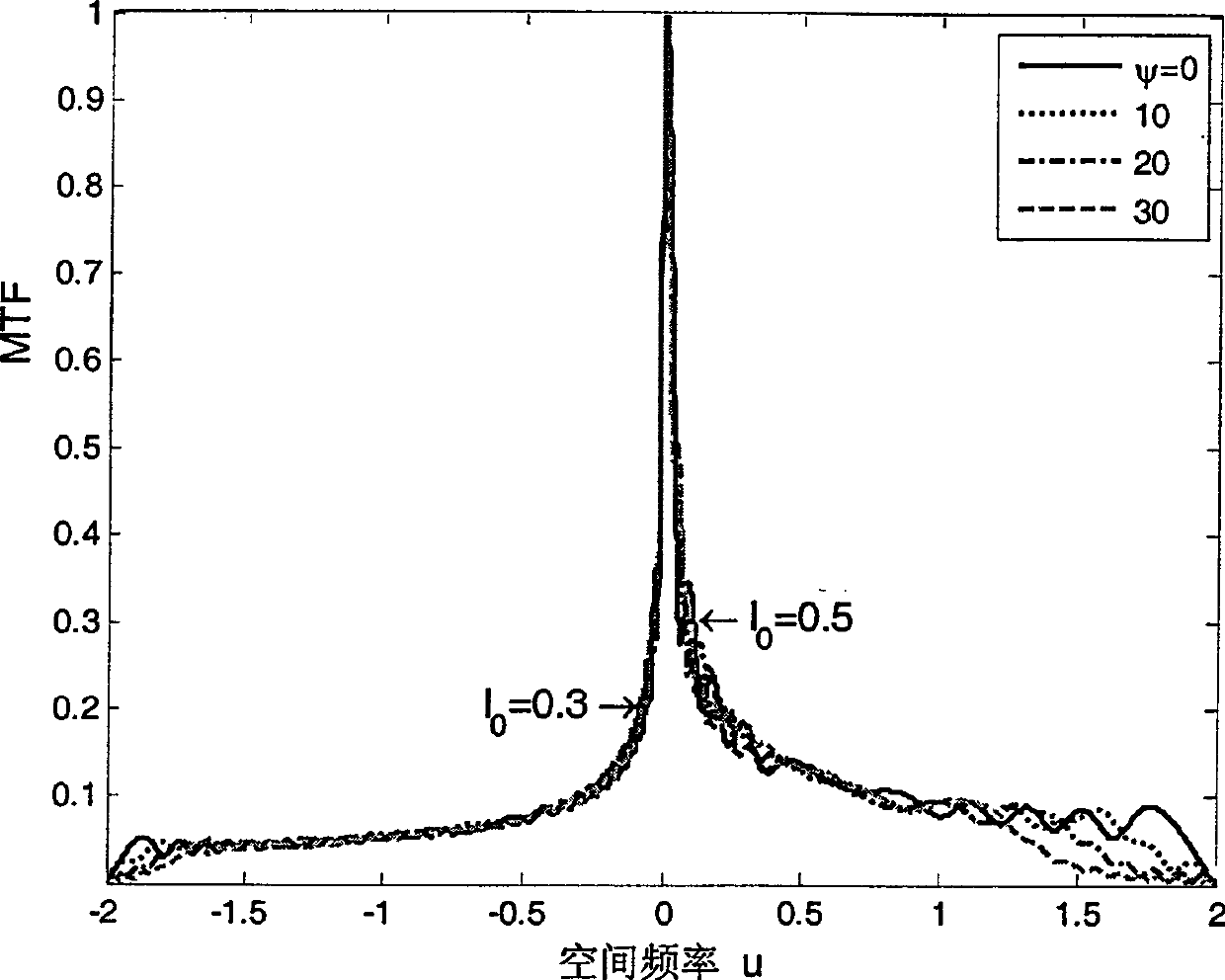
The invention relates to a system and a method for optical and digital mixed imaging. The system comprises an optical imaging object lens, a rational form wavefront coder, a photoelectrical detector and a digital image decoding and processing unit. The method adopts the rational form wavefront coder to code a wavefront phase of an incident light wave. Phi RPM(x) as an introduced phase distribution function is equal to sigma sign(x)an|x|(1+ sigma bm|x|), wherein x is a normalized radial coordinate; N and M are the highest power of a fraction and denominator polynomial respectively; {an} and {bm} are undetermined coefficients; and sign is a signum function. An intermediate blurred image which is not sensitive to defocusing is acquired on the photoelectrical detector after coding, and the digital image decoding and processing unit carries out deconvolution wave filtration on the intermediate blurred image to acquire the final clear image.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
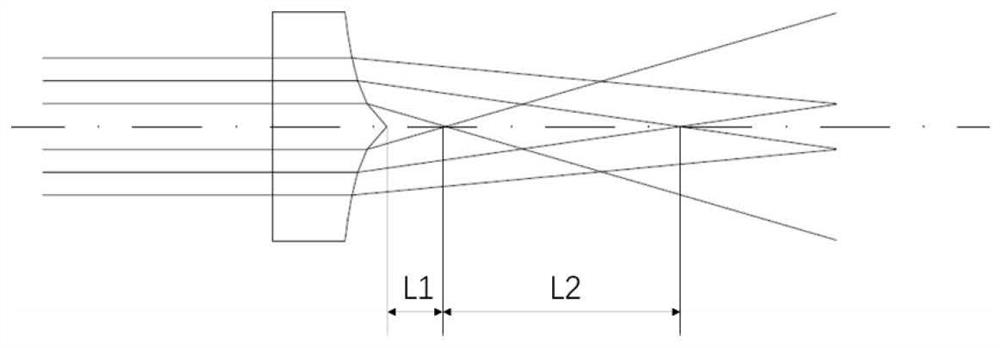
Laser device of long-focal depth and small-focal spot lens focusing system
InactiveCN104914573AMeet size requirementsCompatible with miniaturization requirementsLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsMiniaturizationOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a laser device of a long-focal depth and small-focal spot lens focusing system. The laser device includes a laser source, laser, a first surface, a first optical element, a second surface, a third surface, a second optical element, a fourth surface, an image point imaged by the first optical element, an image point imaged by a lens group, and an optical screen; the laser source emits the laser; the lens group includes the first optical element and the second optical element arranged on the optical path of the laser; the first optical element includes the first surface and the second surface; and the second optical element includes the third surface and the fourth surface. The laser device of the invention has the advantages of simple structure, low manufacturing cost and small size, and can satisfy requirements for miniaturization; and the materials and positions of the optical elements in the laser device are properly set, and related parameters of the laser source are properly selected, and therefore, the system device can further have the advantages of long focal depth, small focal spot and low requirements for workpiece flatness.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Large view field super resolution imaging device
ActiveCN106199997AEasy to manufactureEasy to implementOptical elementsElectromagnetic wave equationWavelength
The invention discloses a large view field super resolution imaging device which comprises a base and a super-surface, wherein the base and the super-surface are successively arranged in the bottom-up sequence. The super-surface is composed of nano-unit structure arrays which are arranged in succession on an ultra-thin metal or a dielectric film. A nano-unit structure is a deep sub-wavelength structure. According to the invention, geometric phase on the nanostructure is used to control the electromagnetic wave symmetry; electromagnetic waves are converted from rotation symmetry to translational symmetry to acquire large view field perfect focusing near 180 degrees; if curved face or multi-plane combination is used, large view field imaging can be realized; the work bandwidth can cover the entire electromagnetic spectrum; the resolution is close to or even beyond the diffraction limit; and the device has a wide application prospect in the field of large view field super resolution imaging.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
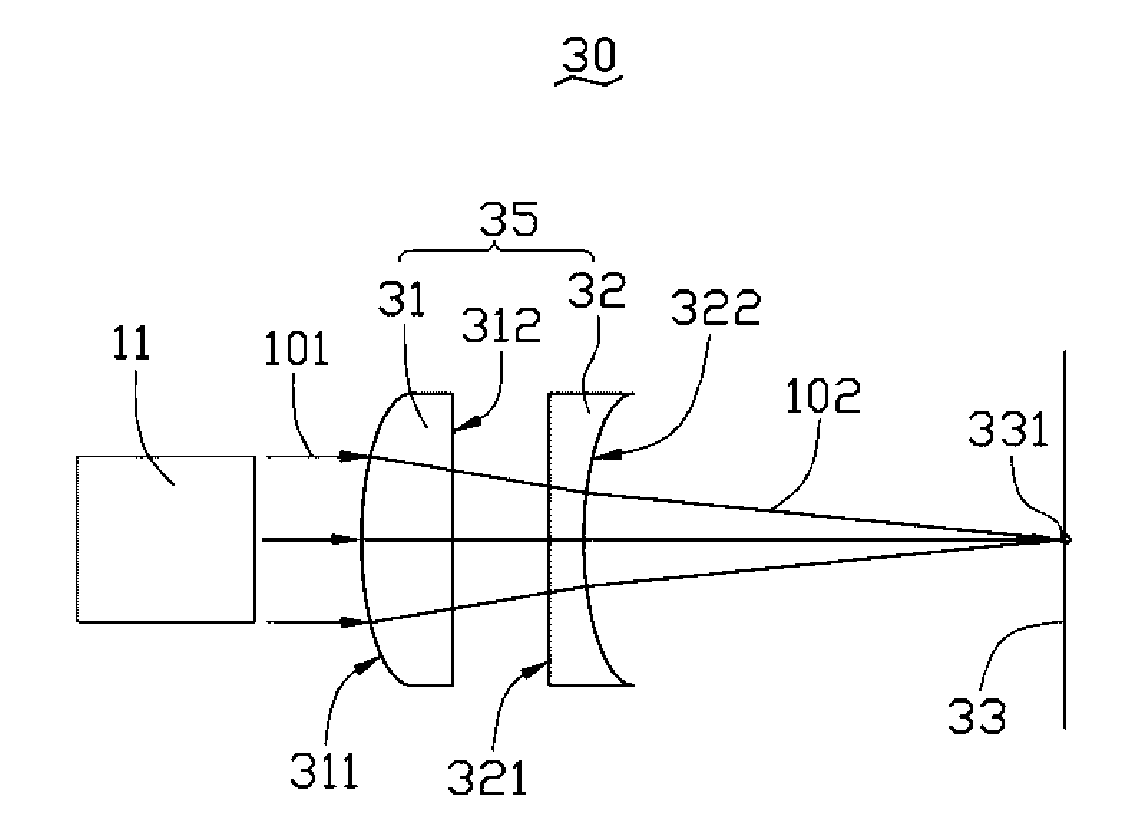
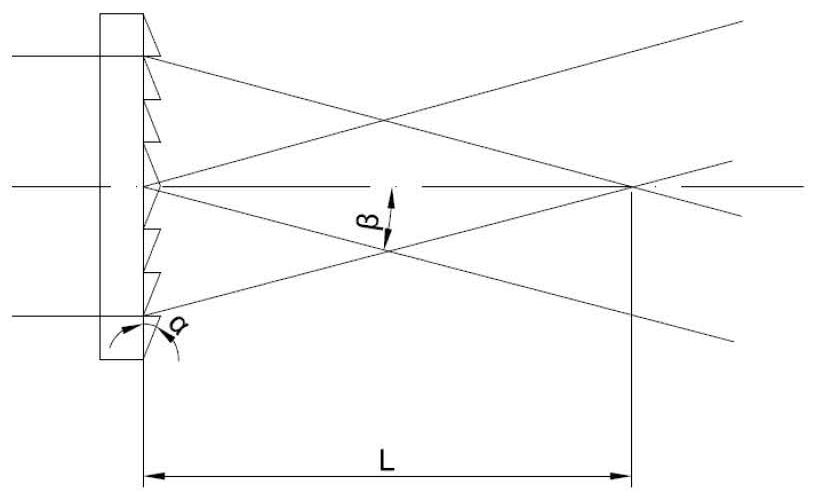
Linear variable-area wave zone plate with feature of long focal length
ActiveCN104765088AJiao ShendaIncrease horizontal resolutionDiffraction gratingsLaser cuttingWavelength
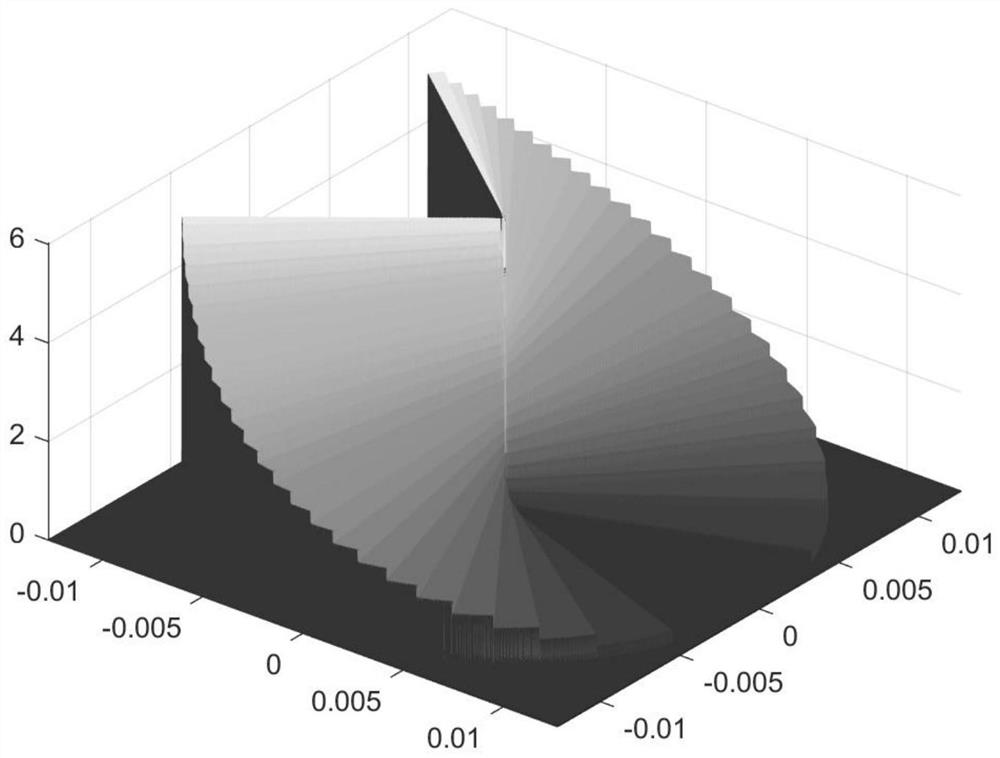
The invention provides a linear variable-area wave zone plate with the feature of a long focal length. The wave zone plate is formed by arranging a series of light-blocking half-wave zones and a series of light-transmitting half-wave zones alternately, wherein each light-blocking half-wave zone and the corresponding light-transmitting half-wave zone adjacent to the light-blocking half-wave zone form a wave zone; in each wave zone, the area of the light-blocking half-wave zone and the area of the light-transmitting half-wave zone are equal; between every two adjacent wave zones, the areas change linearly; the focal length delta f is approximately determined by the formula of delta f = N*delta S / 2*pi*lambda, N is the number of wave band rings, the delta S is the change quantity of the areas of every two adjacent wave zones, and lambda is the length of an incidence light wave. The linear variable-area wave zone plate is suitable for the fields of laser cutting, precise machining and optical imaging.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Lenses, devices, methods and systems for refractive error
ActiveCN108714063ALess ghostingImprove visual effectsSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentKeratorefractive surgeryRefractive error
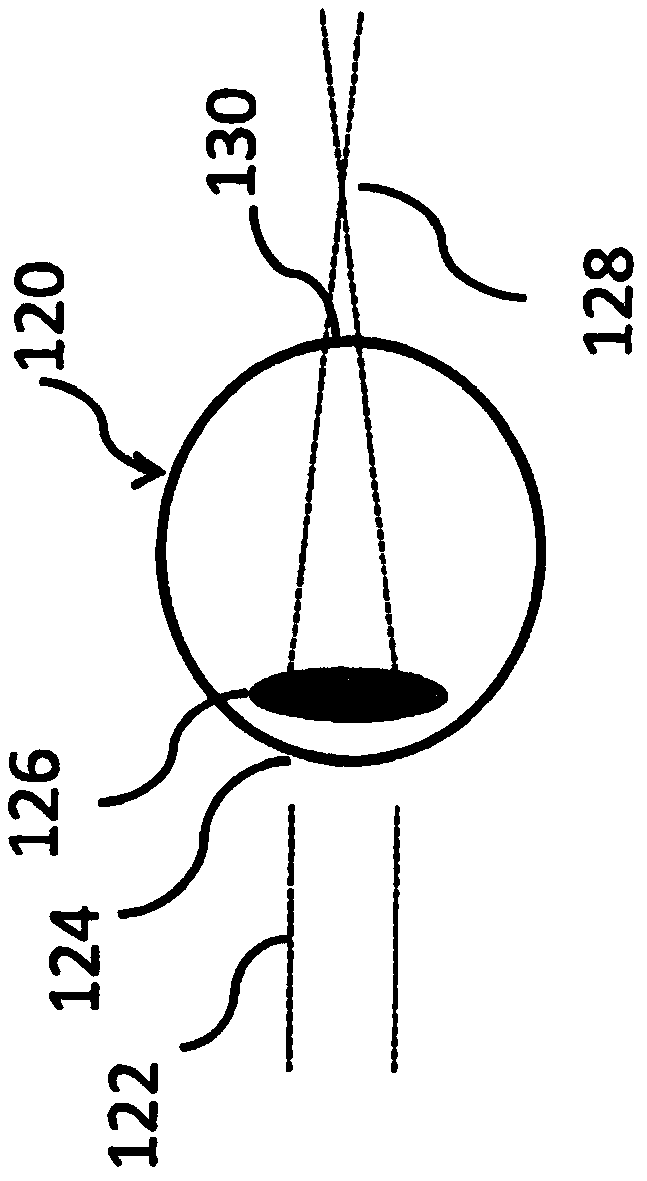
The present disclosure is directed to lenses, devices, methods and / or systems for addressing refractive error. Certain embodiments are directed to changing or controlling the wavefront of the light entering a human eye. The lenses, devices, methods and / or systems can be used for correcting, addressing, mitigating or treating refractive errors and provide excellent vision at distances encompassingfar to near without significant ghosting. The refractive error may for example arise from myopia, hyperopia, or presbyopia with or without astigmatism. Certain disclosed embodiments of lenses, devicesand / or methods include embodiments that address foveal and / or peripheral vision. Exemplary of lenses in the fields of certain embodiments include contact lenses, corneal onlays, corneal inlays, and lenses for intraocular devices both anterior and posterior chamber, accommodating intraocular lenses, electro-active spectacle lenses and / or refractive surgery.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
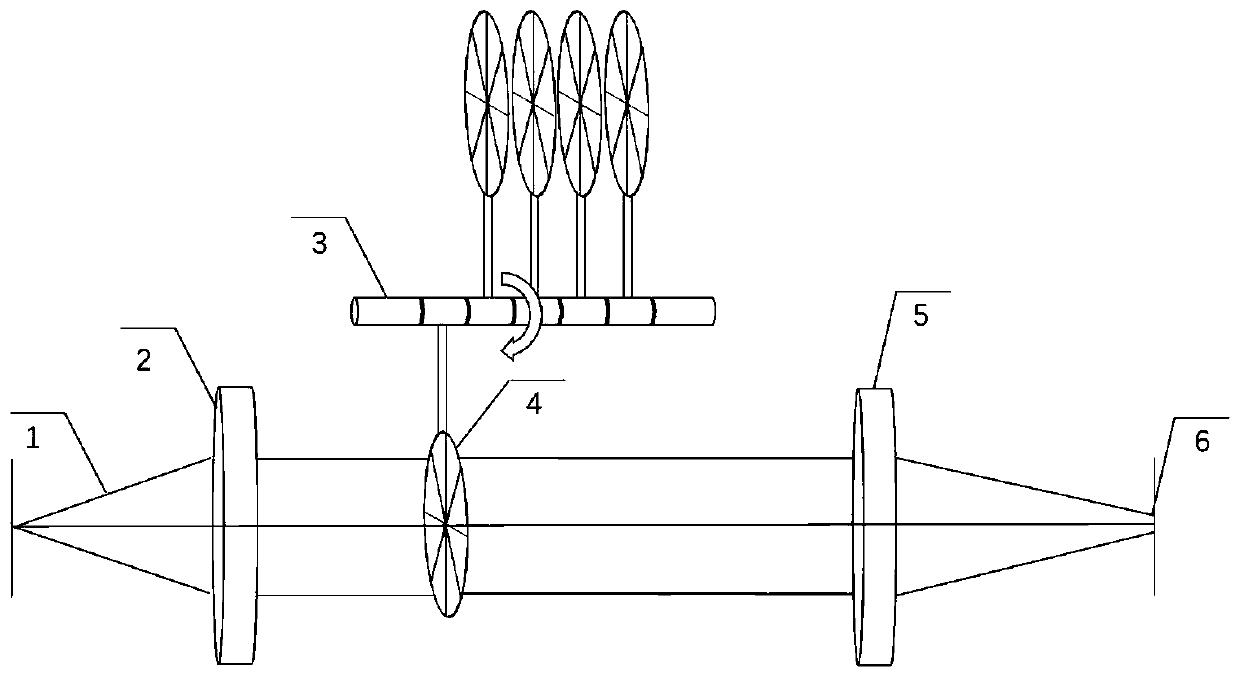
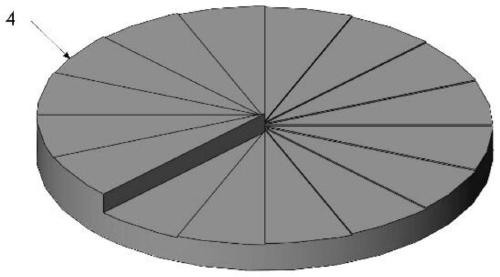
Topology-number-adjustable vortex light beam generation device, system and method
The invention discloses a topology-number-adjustable vortex light beam generation device, system and method. The topology-number-adjustable vortex light beam generation device comprises two spiral phase mirrors, wherein the phases of the two spiral phase mirrors are respectively set as A[theta]2 and -A[theta]2, the two spiral phase mirrors are sequentially disposed on an optical path, and the topological number of the obtained vortex light beam is increased by 1 by increasing the angle difference of the two spiral phase mirrors. According to the invention, after passing through the device, a laser beam can be added with a spiral phase factor to realize phase modulation, so that the energy distribution of the laser beam is changed into annular distribution; the topological number of the obtained vortex beam is adjusted by rotating one or two spiral phase mirrors to control the angle difference of the two spiral phase mirrors so as to realize an annular light spot with an adjustable size; and a group of spiral phase mirrors with second-order nonlinear spiral structures are designed and superposed to generate vortex light beams with adjustable topological numbers, so that annular light spots with concentrated energy distribution at the edge, larger diameter, longer focal depth and adjustable size are formed.
Owner:武汉先河激光技术有限公司
Novel optical lens acquiring long focal depth Bessel gauss light beams through focusing
ActiveCN105607162AWide applicabilityImproving Laser Fine Processing TechnologyLensHigh power densityPeak value
The invention discloses a novel optical lens acquiring long focal depth Bessel gauss light beams through focusing. The novel optical lens comprises a multi-zone curved surface and a focusing curved surface, wherein the multi-ring curved surface and the focusing curved surface are coaxially superposed, the multi-ring curved surface is provided with rings in a concentric-circle structure, surfaces of the rings are spherical surfaces or aspheric surfaces, ring-shaped optical axes are arranged among the adjacent rings, and the focusing curved surface is a spherical surface or an aspheric surface. The single lens is employed for focusing, so the Bessel gauss light beams are acquired, the energy distribution density at the center scope is quite high, quite-low focusing light beam segments are distributed at the edge, the power density scope is high, light spots are quite small, the focal depth is quite long, and light spot peak value power densities in the focal depth segment are similar. According to the novel optical lens, assembly precision requirements of the lens are common, the lens has relatively wide universality for laser beam modes, the fine laser processing technology can be improved and ameliorated, especially for the cutting technology of transparent materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI EMPOWER AUTOMATION TECH CO LTD
Laser device with long depth of focus
InactiveCN101620317AJiao ShendaImprove light utilization efficiencyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical ModuleUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a laser device with long depth of focus, comprising a laser source and an optical module, wherein the laser source is used for emitting single wavelength ultraviolet light. The optical module comprises a first optical element arranged on the light path of the single wavelength ultraviolet light, the first optical element is provided with a first surface which is adjacent to the laser source and a second surface which corresponds to the first surface, and at least one of the first surface and the second surface is an aspheric surface and is used for focusing the single wavelength ultraviolet light on one point.
Owner:FOXSEMICON INTEGRATED TECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) INC +1
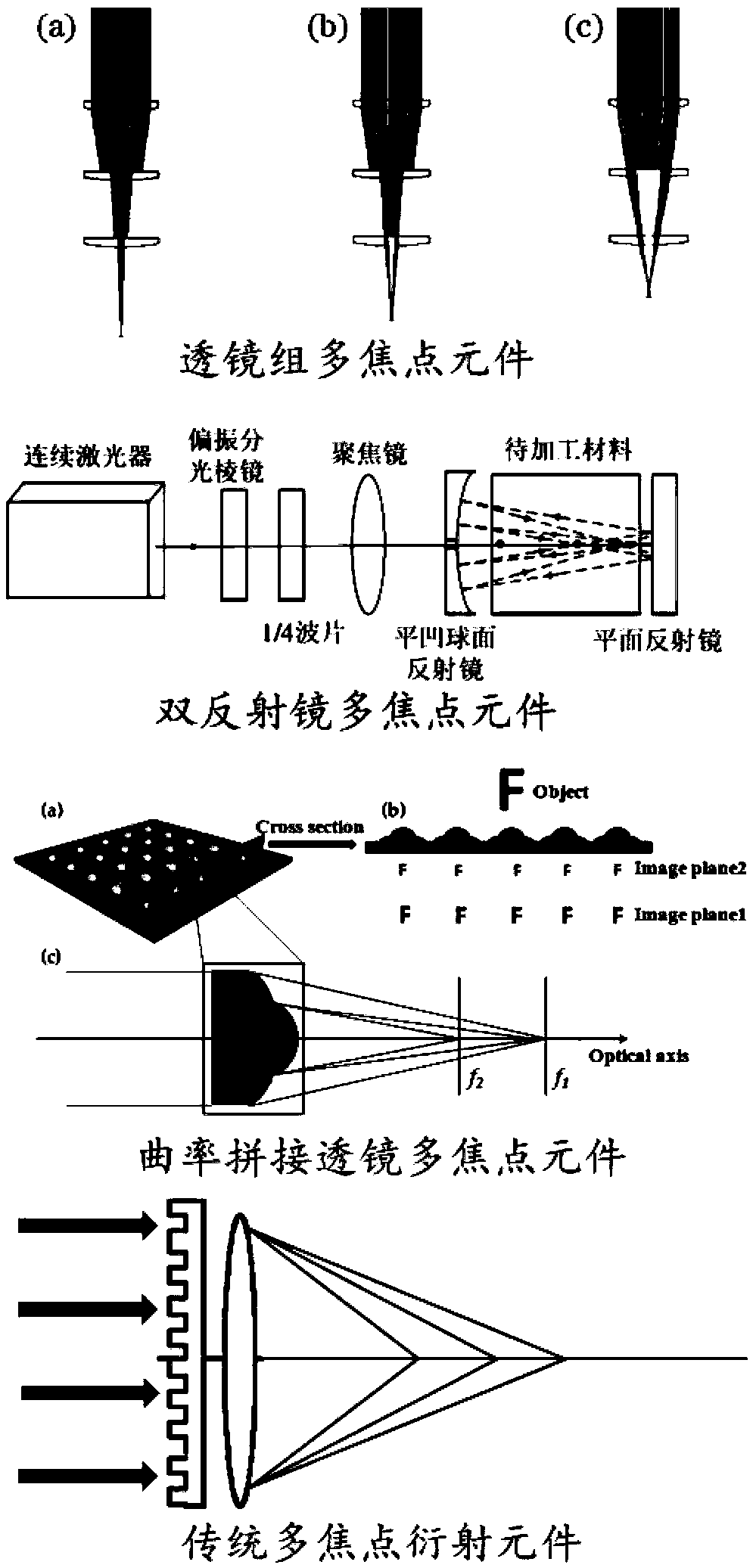
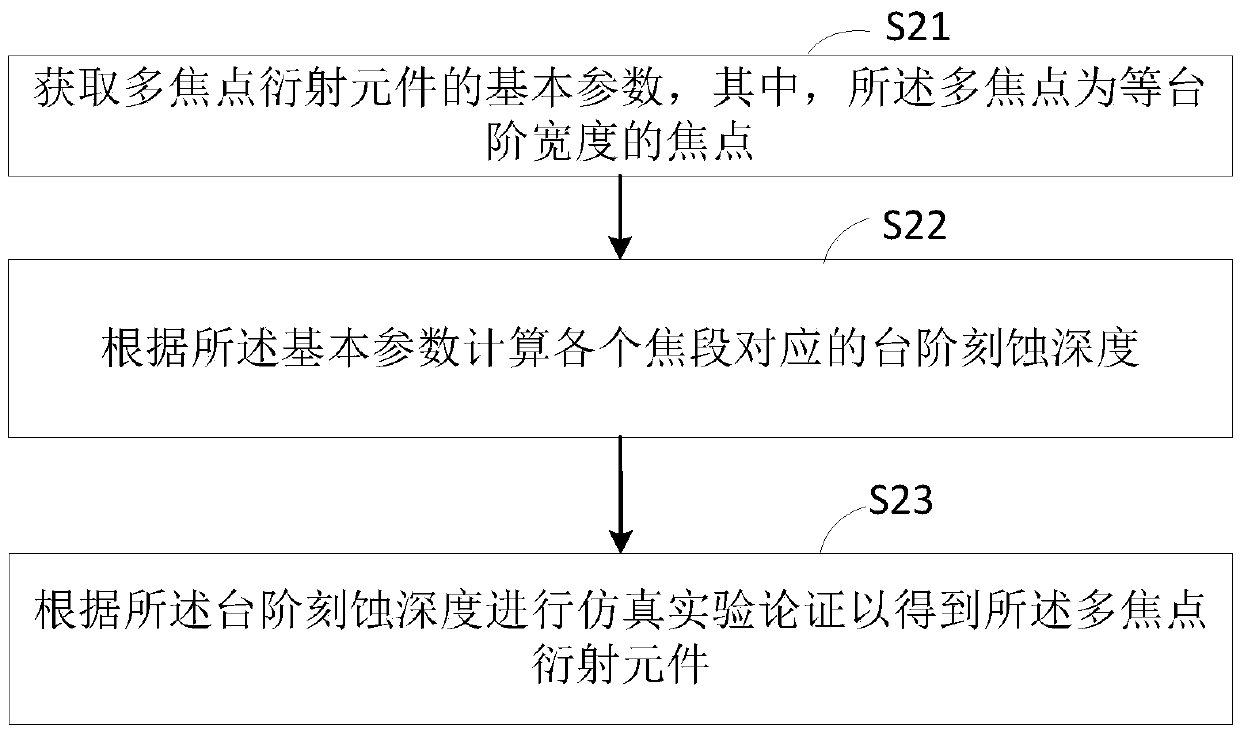
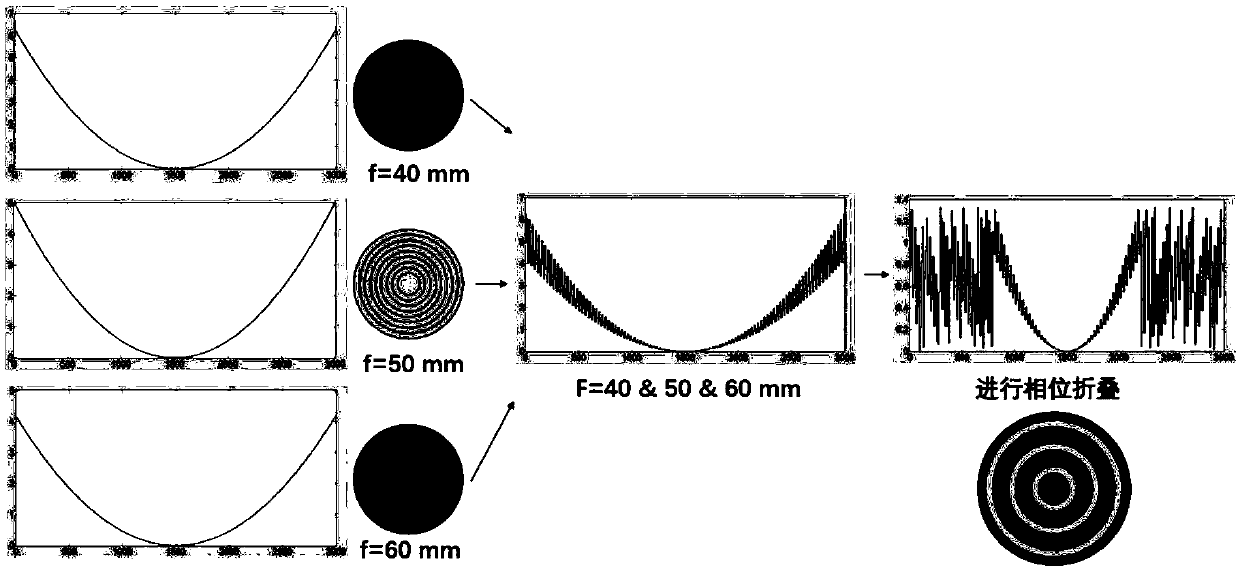
Preparation method of multi-focus diffraction element, and multi-focus diffraction element
The invention relates to a preparation method of a multi-focus diffraction element, and the multi-focus diffraction element. The preparation method comprises the steps: basic parameters of the multi-focus diffraction element are obtained; according to the basic parameters, step etching depths corresponding to all focal lengths are calculated; and according to the step etching depths, simulation experiment demonstration is conducted to obtain the multi-focus diffraction element. According to the multi-focus diffraction element, the size of the multi-focus diffraction element is decreased, the aligning problem of a plurality of optical elements is avoided, and thus usage scenarios of the multi-focus diffraction element are more flexible and wider; and the multi-focus diffraction element cangenerate a plurality of equidistant focuses, peak energy uniformity and point spread function consistency of all the focuses can both have good results through optimization, and the multi-focus diffraction element can serve as an important light splitting element in a high-precision micro-nano processing system and has a very important effect on increasing the focal depth in certain specific imaging optical systems.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radiation-sensitive resin composition
ActiveCN102150082AJiao ShendaExcellent pattern collapse characteristicsPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusHydrogen atomPhotoacid generator
A radiation-sensitive resin composition includes (A) a polymer, (B) a photoacid generator, (C) an acid diffusion controller, and (D) a solvent, the polymer (A) including a repeating unit (a-1) shown by the following general formula (a-1), and the acid diffusion controller (C) including at least one base selected from (C-1) a base shown by the following general formula (C-1) and (C-2) a photodegradable base. wherein R 1 individually represent a hydrogen atom or the like, R represents a monovalent group shown by the above general formula (a'), R 19 represents a chain-like hydrocarbon group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms or the like, A represents a divalent chain-like hydrocarbon group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms or the like, m and n are integers from 0 to 3 (m+n=1 to 3), and R 2 and R 3 individually represent a monovalent chain-like hydrocarbon group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms or the like, provided that the two R 2 may bond to form a ring structure.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
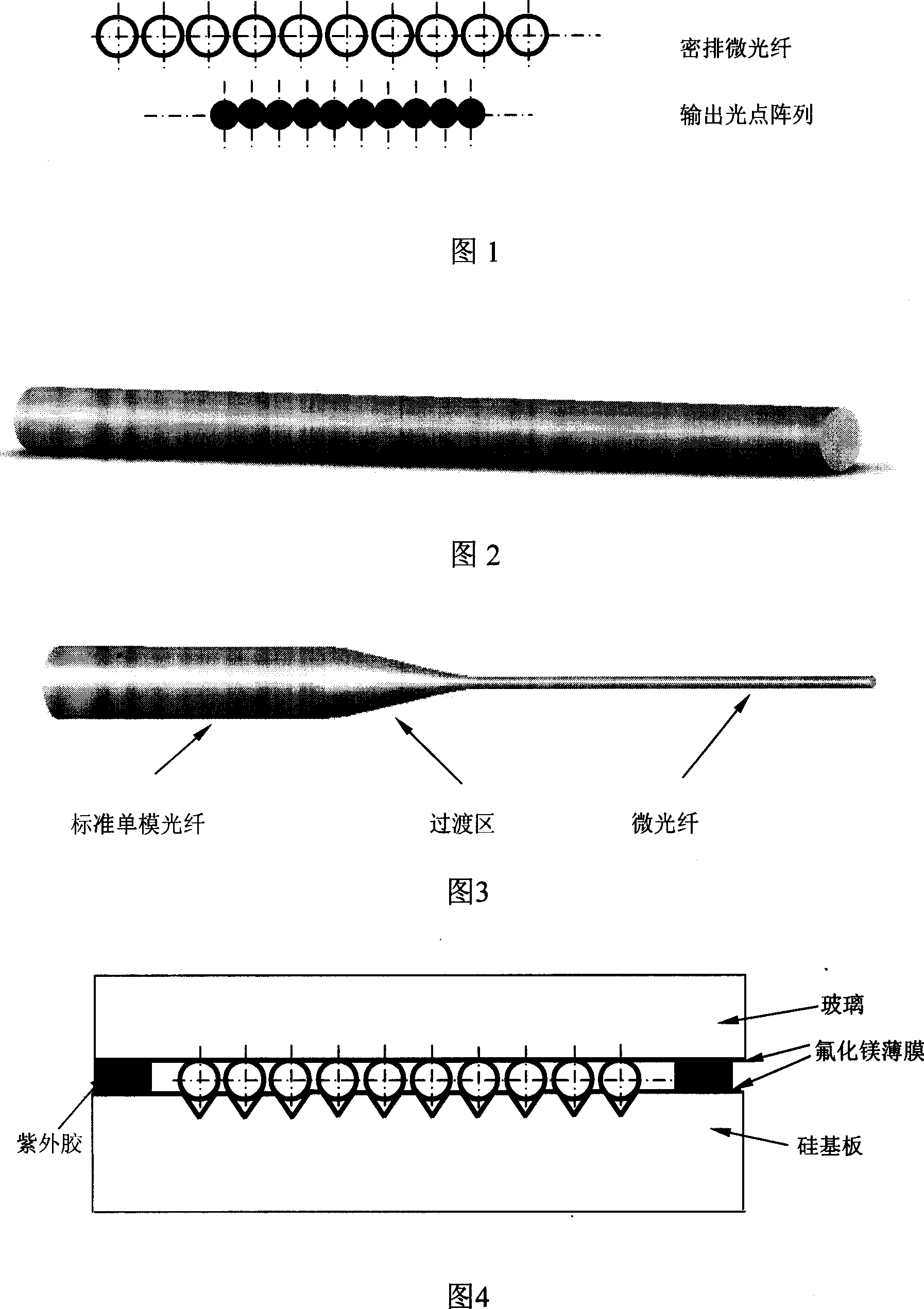
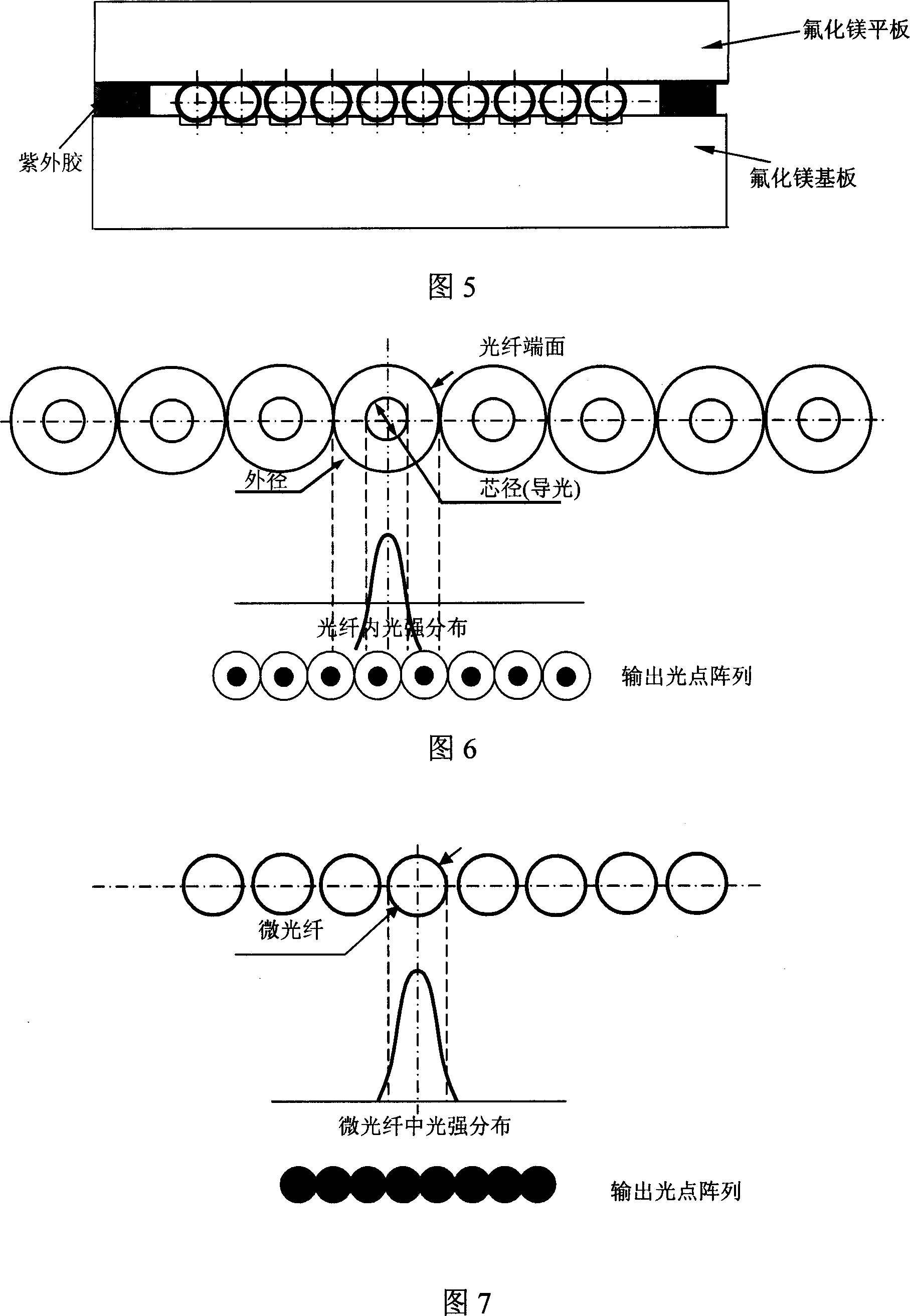
Method for realizing optical point joint seal in optical-fiber close-packed array
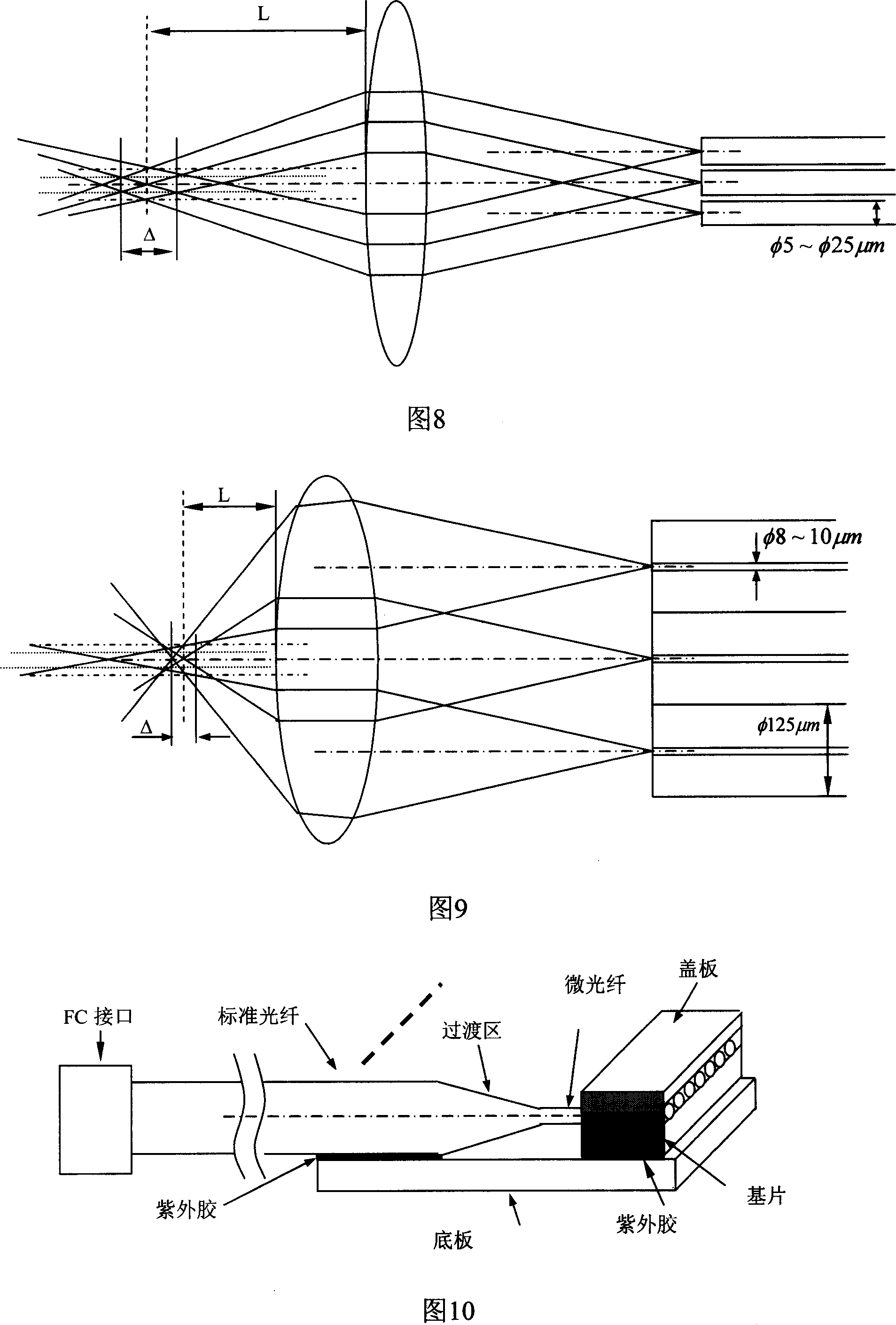
InactiveCN1936634AHigh precisionLow positioning accuracy requirementsCoupling light guidesPhotoelectric composing devicesFiber arrayMagnesium fluoride
The invention discloses a method of the spot joint seal in the optical fiber close-spaced linear array. The process is: 1) one end of the standard single mode optical fiber is draw to the micro optical fiber with diameter of 5-25 mum which includes the standard optical fiber and the transition region; 2) Many micro optical fiber which the end is interval and parallel are lain on the silicon base plate coated the magnesium fluoride on the surface with the V groove or the magnesium fluoride base plate with the rectangle groove; 3) the glass sheet coated the magnesium fluoride on the surface or the magnesium fluoride board is set on the micro optical fiber to form the micro optical fiber close-spaced array fixed with the base plate by the ultraviolet glue; 4) the end of the standard optical fiber is connected with the semiconductor laser by the FC interface and the close-spaced micro optical fiber array outputs the spot array. So the invention can improve the imaging precision of the laser phototypesetting system and the focal depth but decrease the demand of the position precision when the film exposures.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
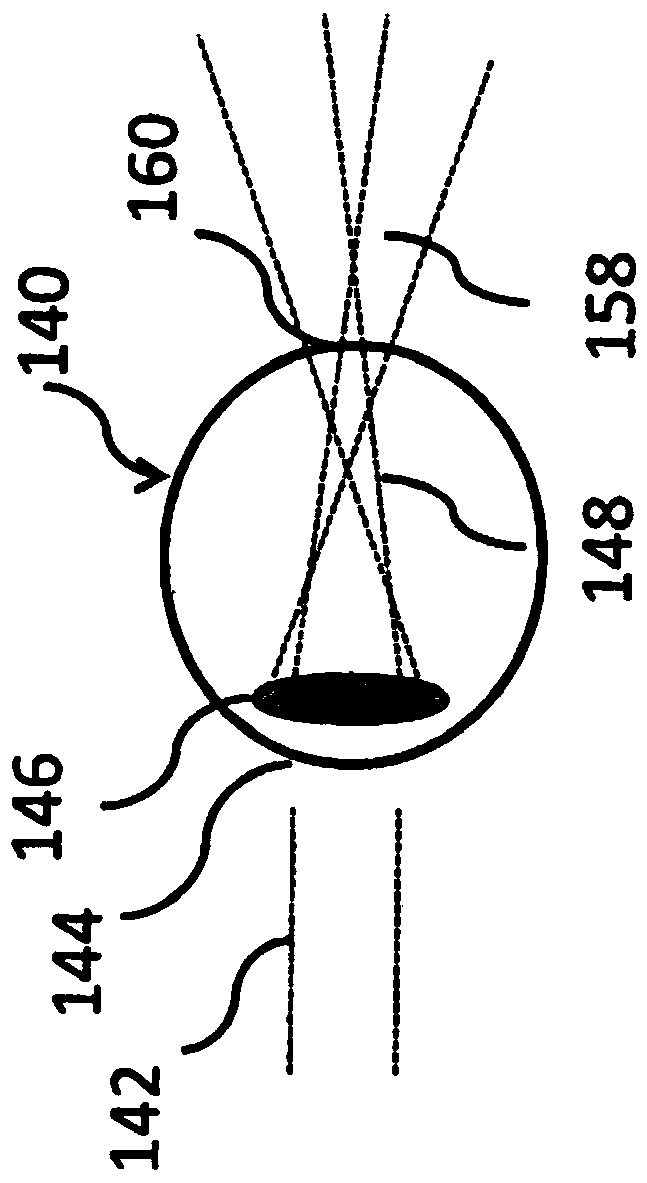
Lenses, devices, methods and systems for refractive error
ActiveCN104768499ALess ghostingImprove visual effectsSpectales/gogglesRefractometersKeratorefractive surgeryCorneal inlay
The present disclosure is directed to lenses, devices, methods and / or systems for addressing refractive error. Certain embodiments are directed to changing or controlling the wavefront of the light entering a human eye. The lenses, devices, methods and / or systems can be used for correcting, addressing, mitigating or treating refractive errors and provide excellent vision at distances encompassing far to near without significant ghosting. The refractive error may for example arise from myopia, hyperopia, or presbyopia with or without astigmatism. Certain disclosed embodiments of lenses, devices and / or methods include embodiments that address foveal and / or peripheral vision. Exemplary of lenses in the fields of certain embodiments include contact lenses, corneal onlays, corneal inlays, and lenses for intraocular devices both anterior and posterior chamber, accommodating intraocular lenses, electro-active spectacle lenses and / or refractive surgery.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
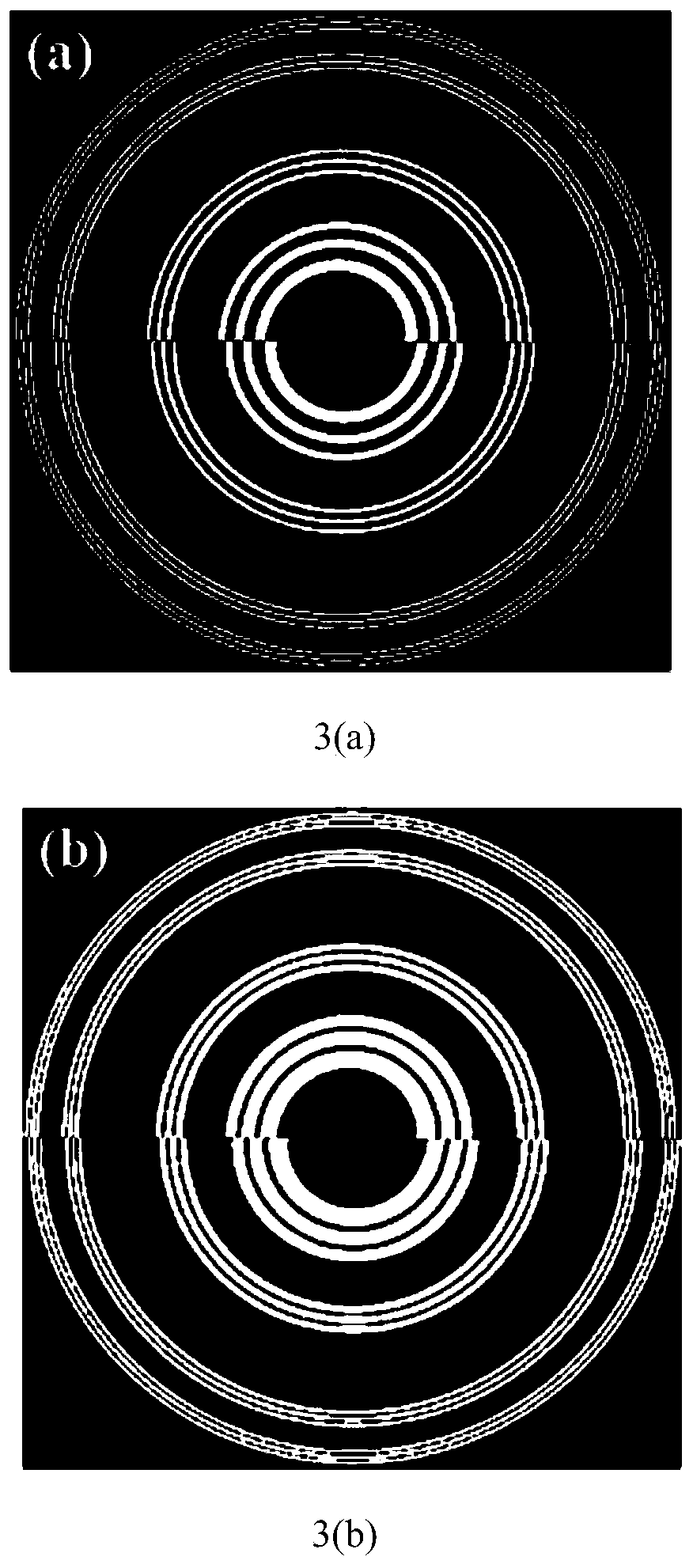
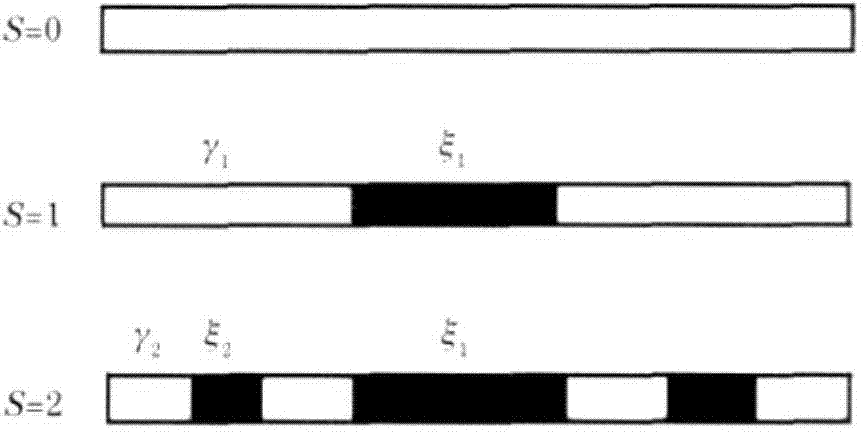
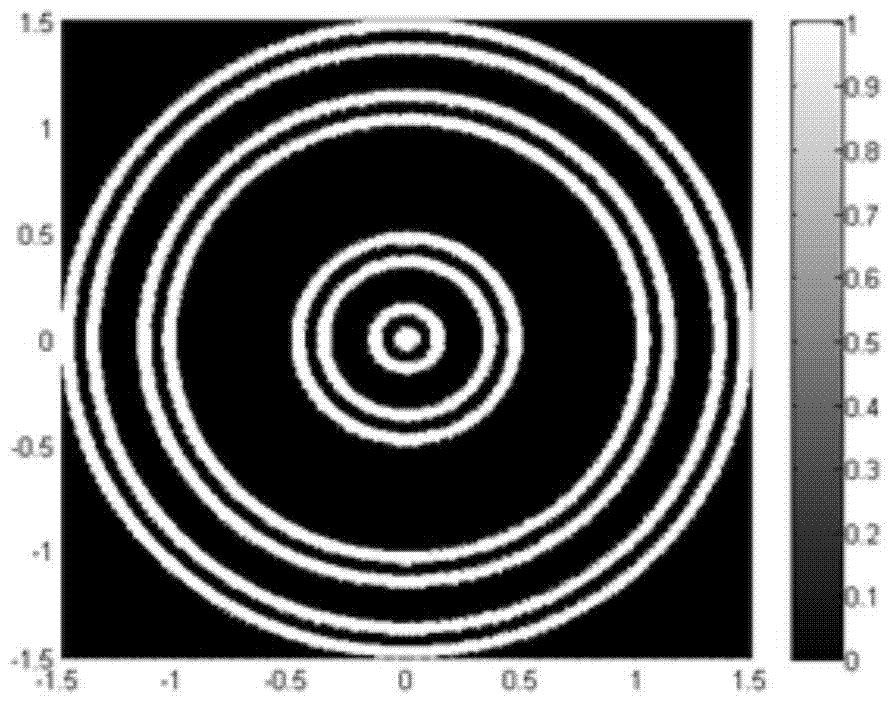
Construction method of modified single-focus fractal zone plate and zone plate thereof
InactiveCN110531453AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce image chromatic aberrationDiffraction gratingsPhotic zoneHigh transmittance
The invention discloses a construction method of a modified single-focus fractal zone plate and a zone plate thereof. The method comprises a step of determining a total number M of spiral high-transmittance bands on a corrected single-focus fractal zone plate based on the element number of a Cantor sequence of an Sth level and carrying out fractal on the modified single-focus fractal zone plate according to the Cantor sequence of the Sth level, a step of determining an alpha1 value of the modified single-focus fractal zone plate capable of generating a single main focus with a plurality of secondary focuses or determining an alpha2 value of the modified single-focus fractal zone plate capable of generating two equal-intensity main focuses with a plurality of secondary focuses, and a step of constructing the corresponding modified single-focus fractal zone plate based on the obtained alpha1 value or alpha2 value and an internal and external radius formula of the spiral light-transmittance bands of the modified single-focus fractal zone plate. The zone plate designed by the invention can only generate a first-stage focus or first-stage and second-stage focuses in an axial direction,so that a low-chromatic-aberration image can be generated, the multi-plane simultaneous imaging, particle capturing and photoetching are realized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
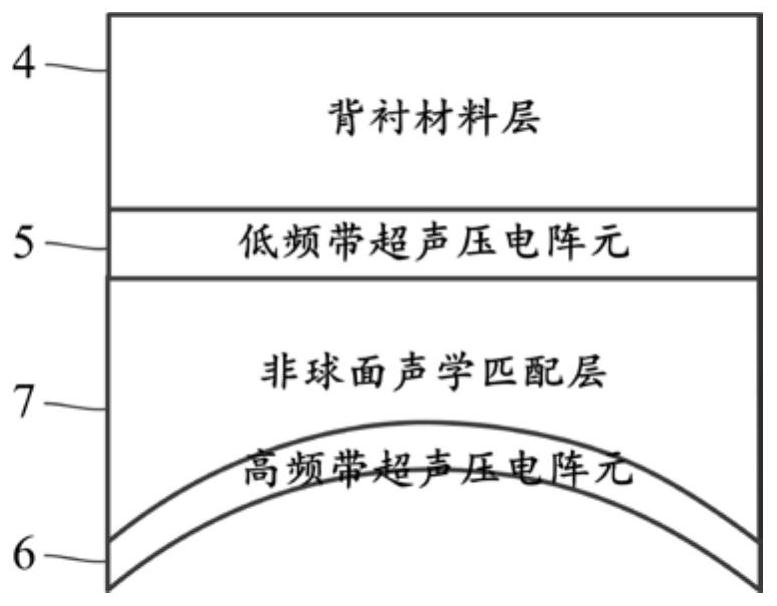
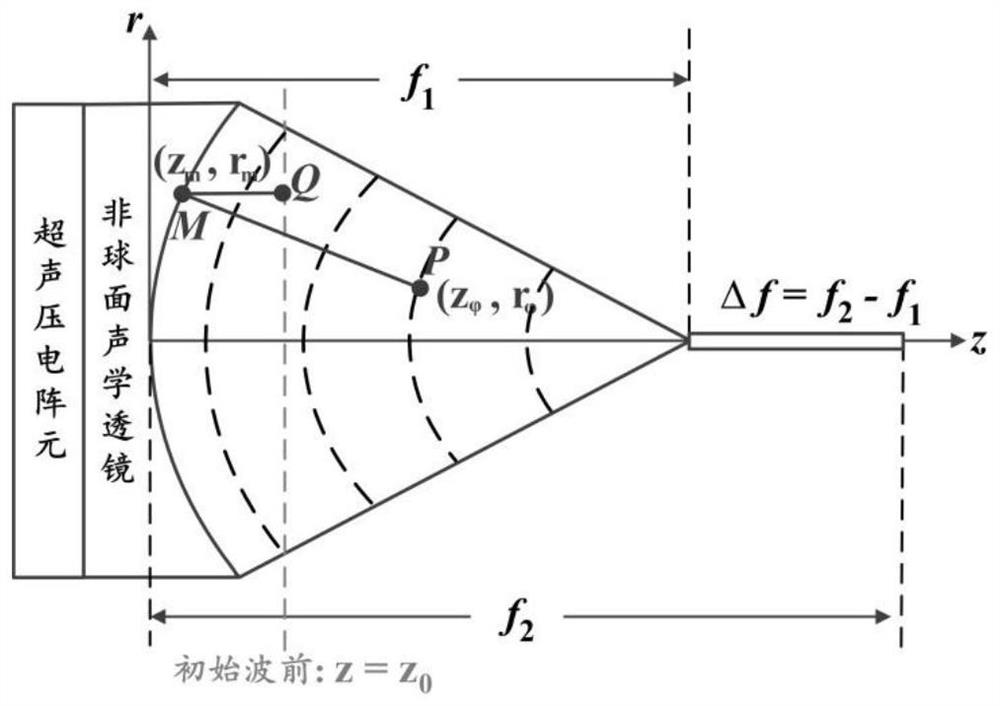
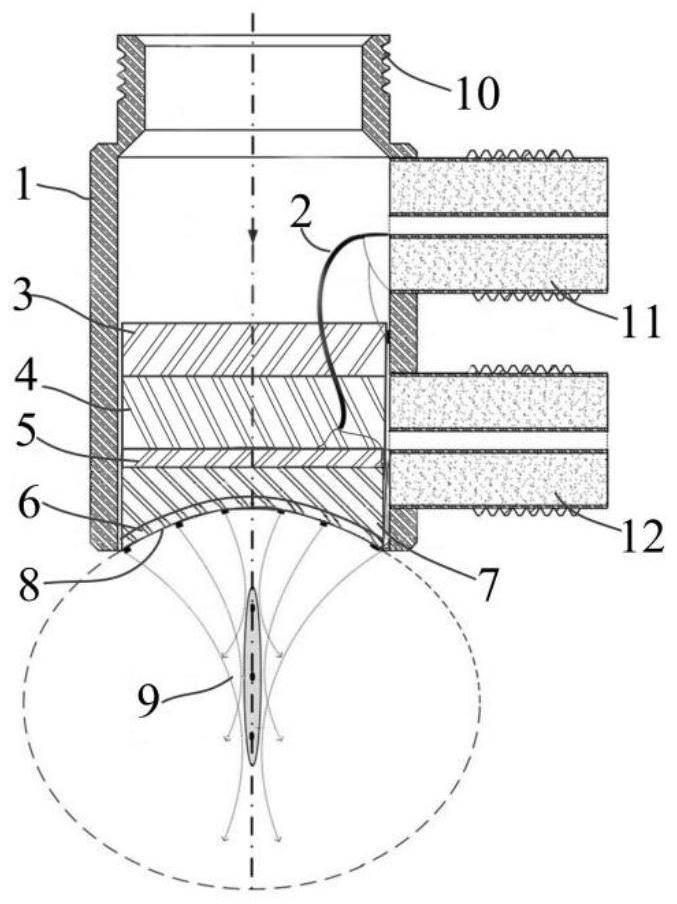
Dual-frequency long-focal-depth ultrasonic transducer based on stack arrangement
InactiveCN113477495AJiao ShendaDepth of focus is smallMechanical vibrations separationInsulation layerTransducer
The invention discloses a dual-frequency long-focal-depth ultrasonic transducer based on stack arrangement. The dual-frequency long-focal-depth ultrasonic transducer based on stack arrangement comprises a shell, a sound insulation layer, a backing material layer, low-frequency-band ultrasonic piezoelectric array elements, high-frequency-band ultrasonic piezoelectric array elements, a signal line and an aspheric acoustic matching layer; and the low-frequency-band ultrasonic piezoelectric array elements and the high-frequency-band ultrasonic piezoelectric array elements adopt a one-dimensional stack arrangement structure. The curved surface structure of the aspheric acoustic matching layer is reversely deduced by an equal sonic path distance principle and a wavefront function, and the aspheric acoustic matching layer is arranged between the low-frequency-band ultrasonic piezoelectric array elements and the high-frequency-band ultrasonic piezoelectric array elements. A scheme of combining one-dimensional stack arrangement of the dual layers of ultrasonic piezoelectric array elements and an aspheric focusing structure is adopted, so that acoustic characteristics of large depth of field and broadband ultrasonic excitation and reception can be obtained. The invention belongs to aspheric focusing long-focal-depth dual-frequency ultrasonic detectors, and belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic / photoacoustic imaging and nondestructive testing.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Presbyopia correction device based on improved fractal zone plate
InactiveCN104849792AJiao ShendaAchieve clear imagingPolarising elementsIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCataract surgery
The invention relates to a presbyopia correction device based on an improved fractal zone plate. According to the radius alpha, fractal level S, and light transmission ratio w within the period of the improved fractal zone plate, focusing of objects at different distances can be realized. A common artificial crystal material for the cataract surgery and the traditional binary phase type optical element process are used for processing. The improved fractal zone plate device can be used for presbyopia correction, thereby realizing clear object watching at a distant vision distance, a conversation distance, a computer working distance, or a reading distance. Therefore, a demand of clear imaging of objects at several kinds of distances by the presbyopia patients can be satisfied; the system has a simple structure; and convenient processing is realized. The device has the potential value in the presbyopia correction field.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Software lens
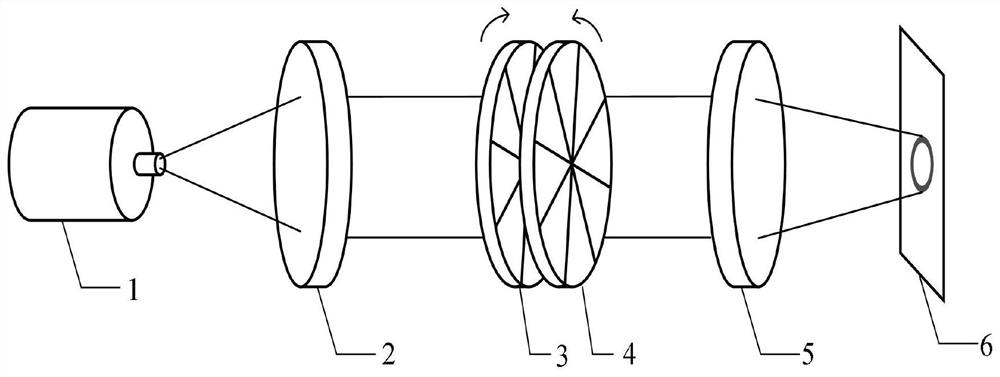
InactiveCN101753772AReduce the numberSmall sizeMountingsPictoral communicationCamera lensDigital signal processing
The invention provides a software lens method which is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding a mask at an optical pupil of an optical system; coding optical information after a light path passes through the mask and imaging a blurred image on a CCD; decoding the optical information by using a digital signal processing system, so that the MTF value of the system is correspondingly improved, thereby recovering a sharp and clear image; imaging two images for frequency domain conversion, extracting high-frequency parts of the two images and aligning and fusing the images. By adopting the software lens method, the system is not sensitive to focal depth, and the resolution ratio of the image can be improved.
Owner:周春平
Laser cleaning device
InactiveCN111715624AJiao ShendaSolve technical problems that are difficult to guarantee collimationCleaning processes and apparatusLight spotLight beam
The embodiment of the invention provides a laser cleaning device which comprises a laser generating device, a collimating lens group, a beam shaping element and a scanning focusing system. The laser generating device emits a laser beam; the collimating lens group receives the laser beam and outputs a collimated beam; the beam shaping element receives the collimated beam output by the collimating lens group and converts the collimated beam into a Bessel beam; and the scanning focusing system focuses the Bessel beam on the surface of a workpiece to be cleaned. The effects of lengthening the focal depth and improving light spot distribution are achieved through the beam shaping element, the optimized cleaning process is favorably realized in laser cleaning, and the technical effect of efficiently cleaning workpieces with large surface depth changes is achieved.
Owner:武汉光谷航天三江激光产业技术研究院有限公司
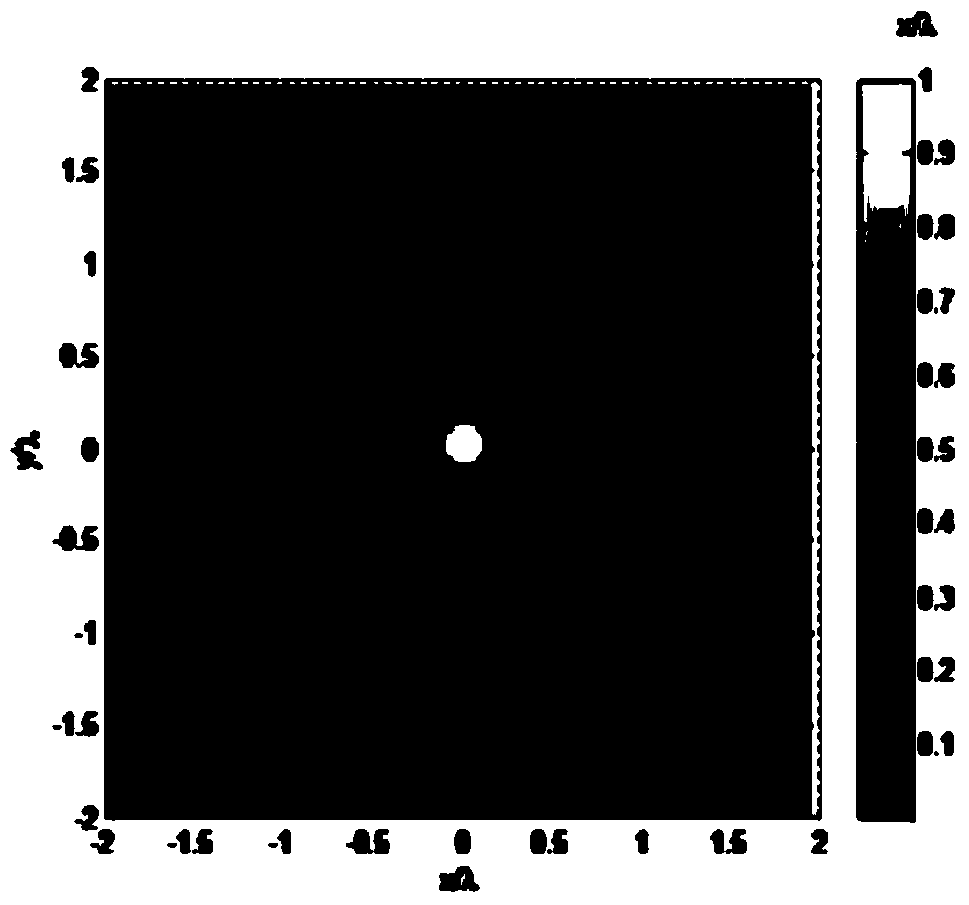
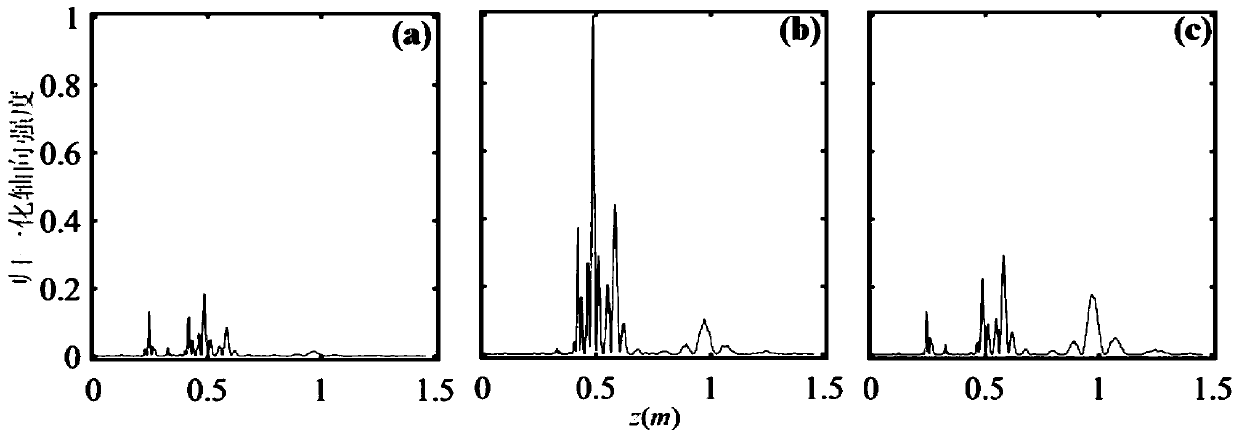
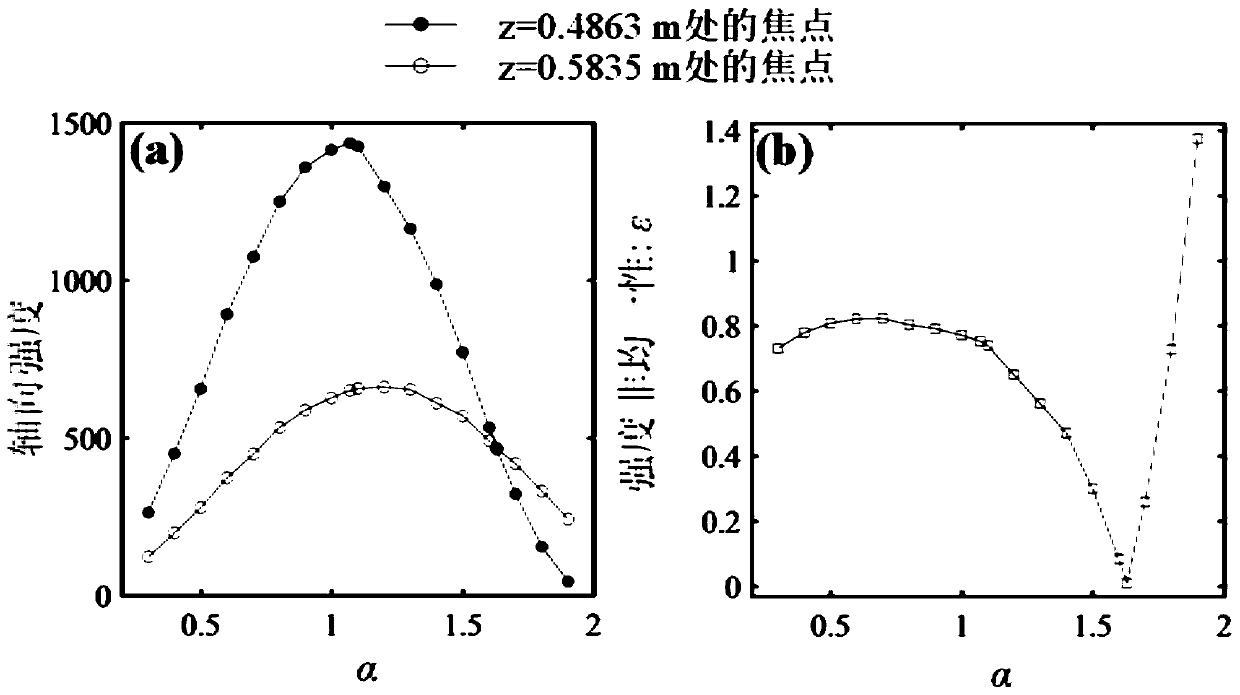
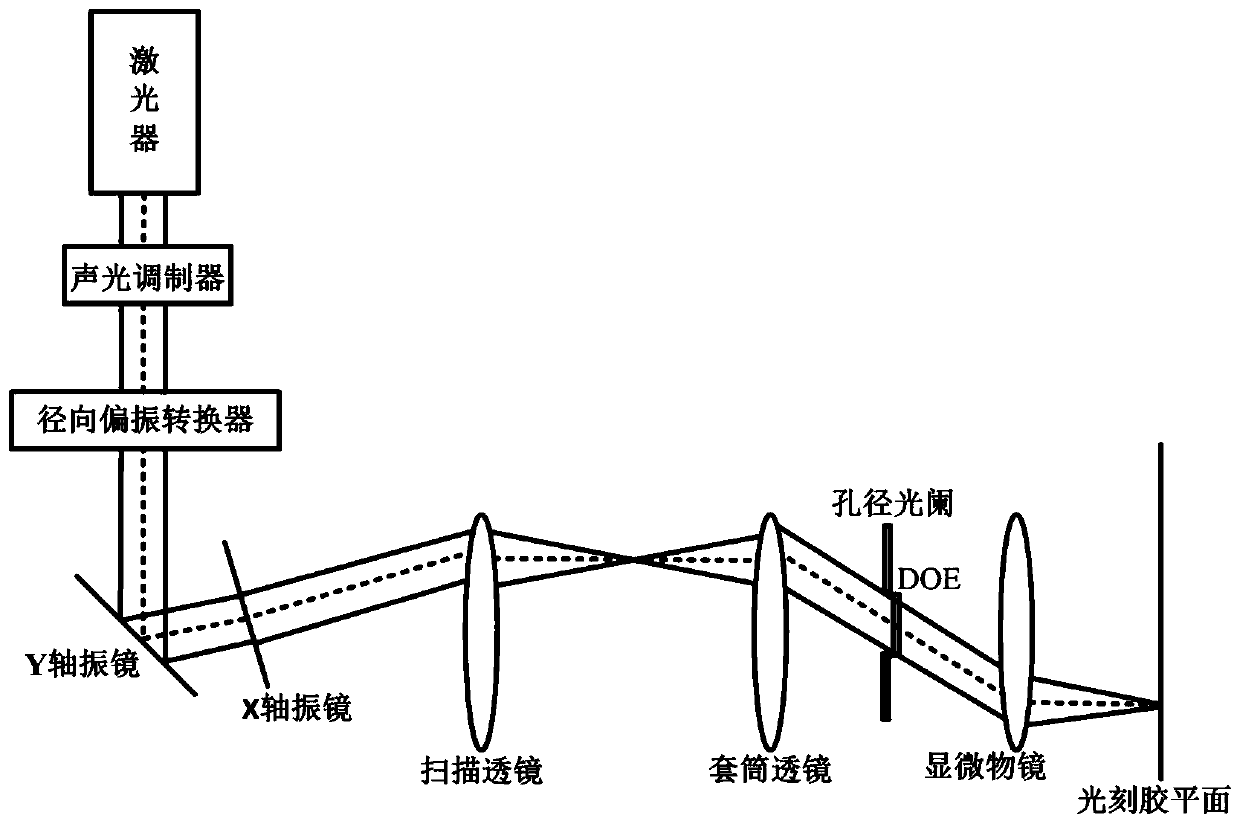
High-efficiency laser direct-writing photoetching method capable of realizing long-focal-depth small-focal-spot structure
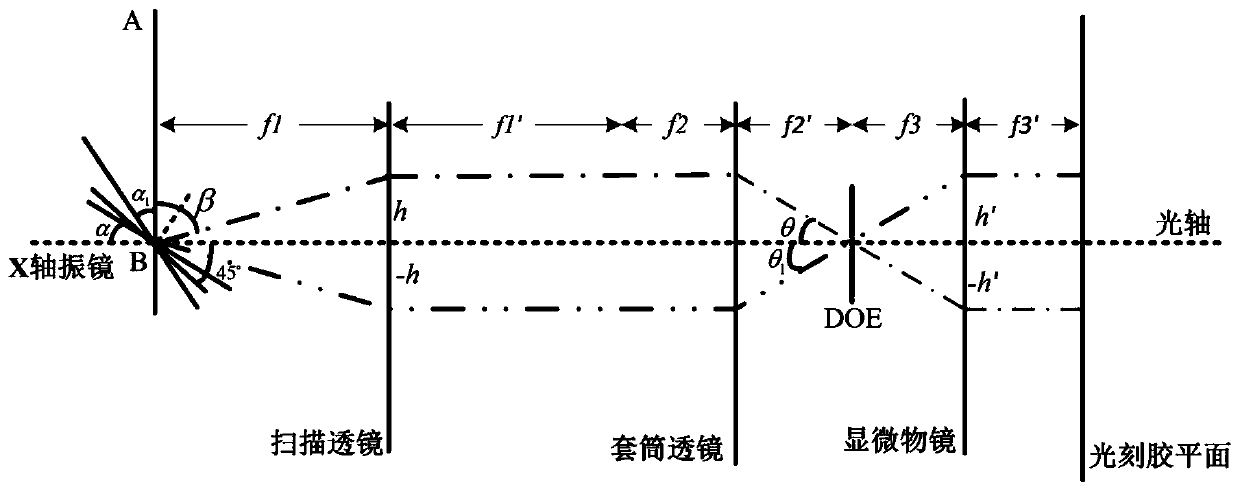
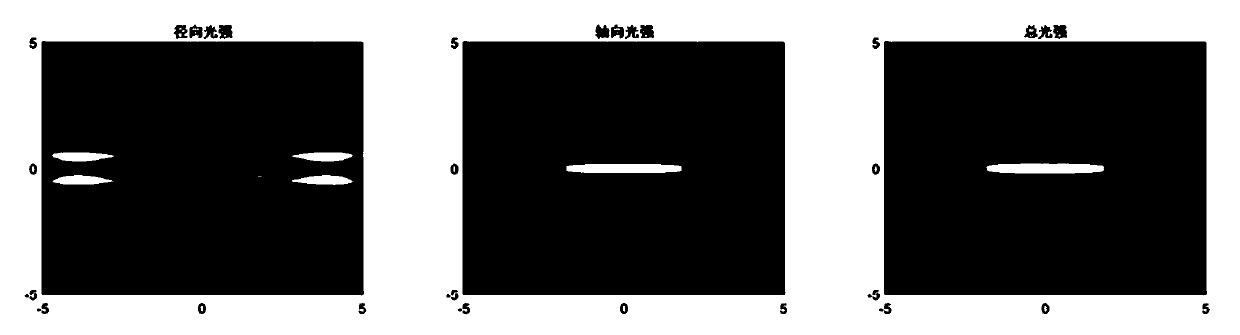
ActiveCN110837215AJiao ShendaSmall focal spotPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusHigh numerical apertureImage resolution
The invention discloses a high-efficiency laser direct-writing photoetching method capable of realizing a long-focal-depth small-focal-spot structure. Phase modulation is carried out through DOE, so that the diffraction limit can be exceeded, and the resolution and the focal depth of an optical pin are improved; movement of the optical pin on a photoresist plane can be achieved through optical scanning, and the laser direct writing photoetching speed is increased. The optical scanning system utilizes a two-dimensional galvanometer system to generate small-angle deflection of -10 degrees to +10degrees in the X-axis direction and the Y-axis direction. An X-axis galvanometer vibrates along the X-axis direction, a Y-axis galvanometer vibrates along the Y-axis direction, the galvanometers arerespectively driven by two drivers, incident radial polarized light passes through the X-axis galvanometer and the Y-axis galvanometer and then obliquely enters through a scanning lens, a sleeve lens,a pure-phase binary optical element and a high-numerical-aperture microscope objective in sequence, and then an optical pin which moves along the X axis and the Y axis and has resolution, focal depthand uniformity not affected by angle deflection is generated near a focal plane. And the resolution, the focal depth and the direct writing efficiency of laser direct writing photoetching are improved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phase coded Fresnel lens
ActiveCN109143426AHigh bandwidthReduce sensitivityDiffraction gratingsLensRefractive indexPhase Code
The invention belongs to the optical field, aims at solving the technical problem of serious chromatic aberration when the traditional Fresnel lens is used for imaging, and discloses a phase coded Fresnel lens. The phase coding technology is introduced to the field of the Fresnel lens. The surface shape of the phase coding element and the surface shape of the converging lens are integrated and then collapsed so that the vector height difference between the highest point and the lowest point of each ring band is lambda / (n-1), and finally the surface shape of the phase coded Fresnel lens is obtained, wherein lambda is the design wavelength and n is the refractive index of the base material. The phase coded Fresnel lens has the focusing function of the traditional diffraction imaging lens andalso has the phase coding function of the phase coding element. The Fresnel lens designed by this method can perform phase coding on the incident light so as to broaden the focal depth, reduce the sensitivity of the Fresnel lens to the wavelength and broaden the bandwidth of the Fresnel lens without reducing the imaging resolution of the Fresnel lens.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Position phase type ultra-high-difinition long focal iris
InactiveCN1186674CHigh diffraction efficiencyEasy to mass produce and replicateCamera diaphragmsOptical elementsPhysicsParallel plate
A position-phase type iris with long focus depth and ultra-high difinition features that the concave ring and convex ring, which are concentric with iris, are made on a parallel plate made of transparent material. After light beam passes through the iris with concave and convex rings, a retardation between said light beam and the light beam passing through other position is half of wavelenglth, so axial peaks are cancelled to elongate focus depth by more than 3 times and radical edges are cancelled to increase difinition. It can be used in microelectronic processing, photoetching and scan microscopic focusing or imaging system.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A large field of view super-resolution imaging device
The invention discloses a large view field super resolution imaging device which comprises a base and a super-surface, wherein the base and the super-surface are successively arranged in the bottom-up sequence. The super-surface is composed of nano-unit structure arrays which are arranged in succession on an ultra-thin metal or a dielectric film. A nano-unit structure is a deep sub-wavelength structure. According to the invention, geometric phase on the nanostructure is used to control the electromagnetic wave symmetry; electromagnetic waves are converted from rotation symmetry to translational symmetry to acquire large view field perfect focusing near 180 degrees; if curved face or multi-plane combination is used, large view field imaging can be realized; the work bandwidth can cover the entire electromagnetic spectrum; the resolution is close to or even beyond the diffraction limit; and the device has a wide application prospect in the field of large view field super resolution imaging.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Super-diffraction imaging device for improving resolution based on phase shifting principle and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102096334BImprove modulation efficiencyIncrease profitPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusNanolithographyPhase shifted
The invention discloses a super-diffraction imaging device for improving resolution based on a phase shifting principle and a manufacturing method thereof. Adjacent light transmission areas of the super-diffraction imaging device realize phase delay and phase advance respectively by alternately filling two materials with a positive dielectric coefficient and a negative dielectric coefficient and the phase difference modulation of the material thicknesses is enhanced greatly, so that the device is easier to realize a pi phase difference; therefore, the imaging resolution of the device is further improved. The scheme solves the technical difficult problem that a conventional super-diffraction imaging device is difficult to realize the resolution below the line width of 40 nm and has a broadapplication prospect in super-diffraction imaging and nano-lithography technologies.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
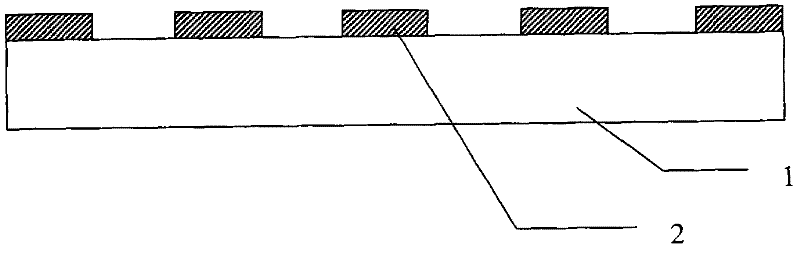
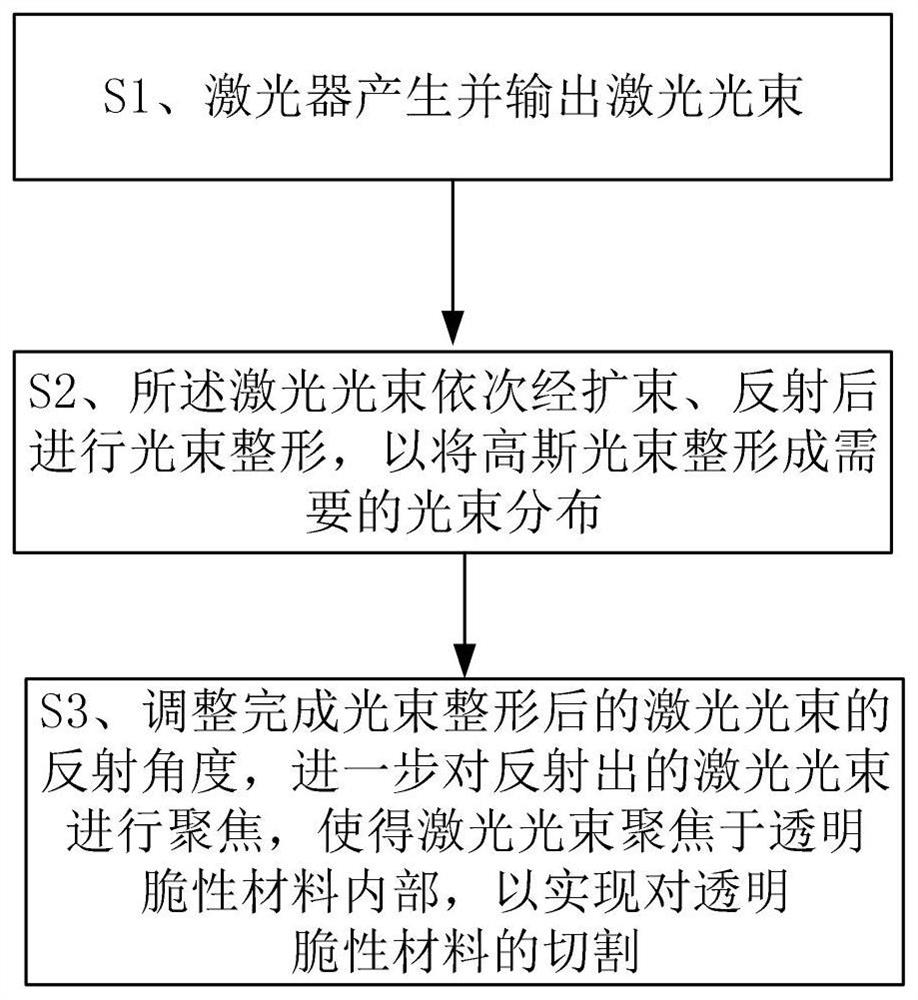
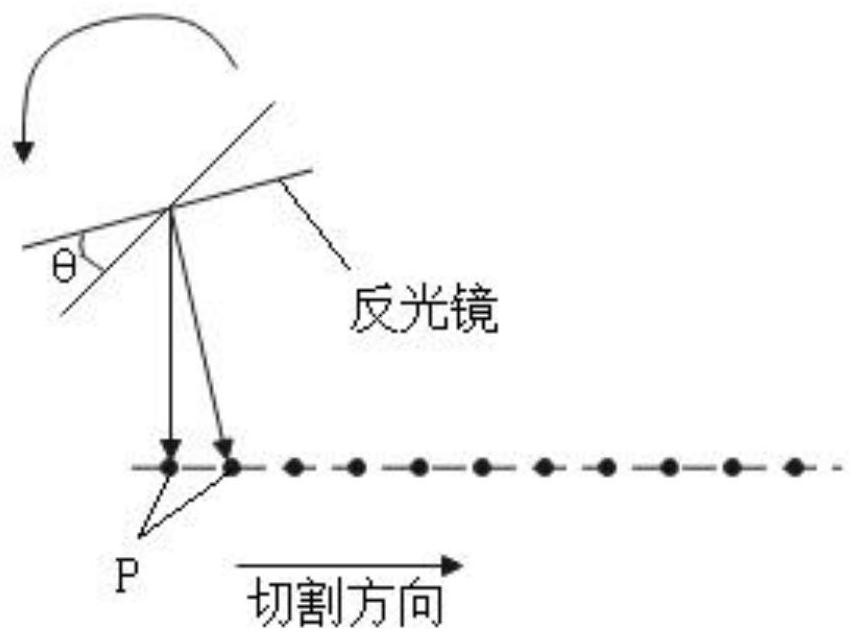
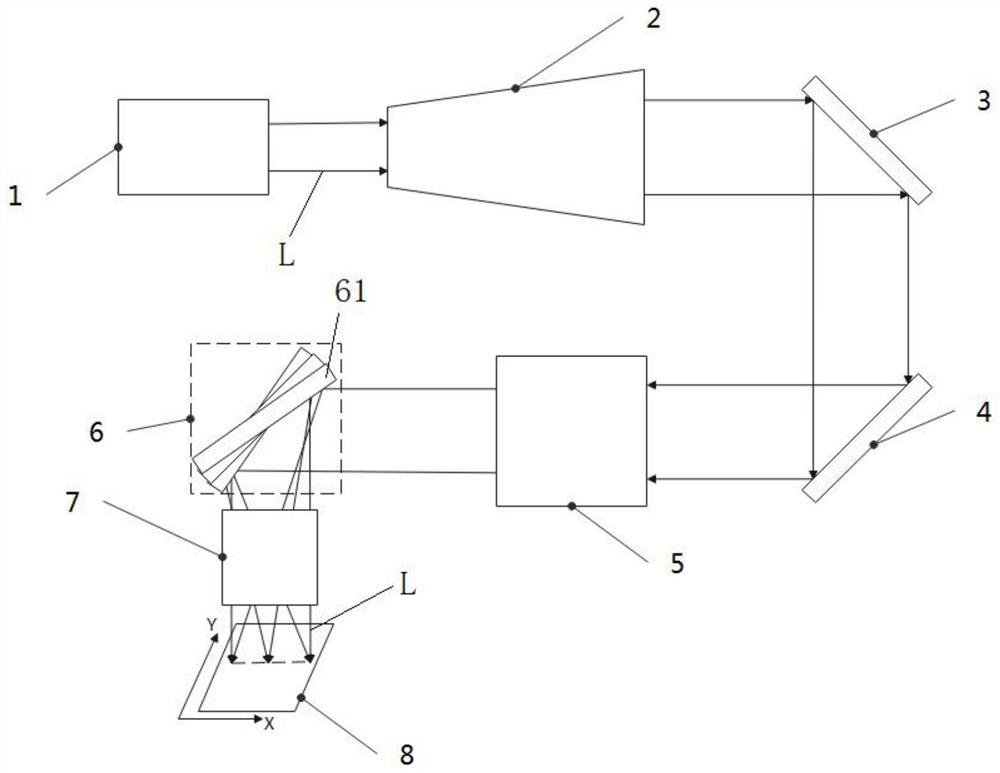
Method and apparatus for cutting transparent brittle material
InactiveCN112719635AHigh densityLower requirementWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamLaser light
The invention relates to a device and method for cutting a transparent brittle material. The method comprises the following steps that S1, a laser generates and outputs a laser beam; S2, beam shaping is carried out on the laser beam after the laser beam is expanded and reflected in sequence; and S3, the reflection angle of the laser beam after beam shaping is adjusted, and the reflected laser beam is focused, so that the laser beam is focused in a transparent brittle material, and cutting of the transparent brittle material is achieved. Through beam shaping, reflection angle adjustment and focusing of the laser beam, scanning type cutting of the transparent brittle material with a preset thickness can be achieved, and the performance requirement and the use cost of a laser light source are reduced while the machining efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:WUHAN HGLASER ENG CO LTD
1.7 mu m waveband non-diffraction light source biological imaging system with controllable coherence degree
PendingCN112557346AReduce absorption lossImprove imaging depthPhase-affecting property measurementsCcd cameraGrism
The invention discloses a 1.7 mu m waveband non-diffraction light source biological imaging system with adjustable coherence degree, relates to the technical field of optical imaging, and solves the problems that when a light source images biological tissues rich in moisture, the imaging depth is limited due to absorption and scattering loss of water, speckle noise is caused by high spatial coherence degree of the light source, and the imaging quality is influenced. A semiconductor laser, aerbium-doped fiber amplifier, an optical isolator, a first fiber bragg grating, a double-cladding thulium-doped fiber, a second fiber bragg grating, a multimode fiber and a fiber collimator are in fiber connection in sequence. The optical fiber collimator, a first lens, a pinhole, a second lens, a dichroscope, a polarizing film, a light beam expander and a spatial light modulator are coaxially arranged in sequence, and the pinhole is formed in a focal plane between the first lens and the second lens;the computer is connected with the spatial light modulator through a cable; the spatial light modulator, the prism, the third lens and the reflector are coaxially arranged in sequence; the CCD camera, the fourth lens, the prism, the microscope objective and the translation stage are sequentially and coaxially arranged in the longitudinal direction.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser device with long depth of focus
InactiveCN101620317BJiao ShendaImprove light utilization efficiencyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical ModuleLight spot
The invention relates to a laser device with long depth of focus, comprising a laser source for emitting single wavelength ultraviolet light, an optical module with a first optical element, a first reflective element and a second reflective element. The first optical element comprises a first surface adjacent to the laser source and a second surface face towards the first surface. At least one of the first and second surfaces is aspherical, so that the UV light having a single wavelength is focused to one point. The first reflective element and the second reflective element are arranged between the laser source and the first optical element. A focal length f1 of the first reflective element and a focal length f2 of the second reflective element have relationships as follow: |f1|+|f2|=d, |f2| / |f1|=2fw / (BGDOF), wherein d represents a distance d spanned by the apexes of the two reflective elements, f represents the focal length of the first optical element, w represents a diameter of a formed light spot, B represents a light beam diameter of the UV light, and GDOF represents a geometrical depth of focus of the laser device.
Owner:FOXSEMICON INTEGRATED TECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) INC +1
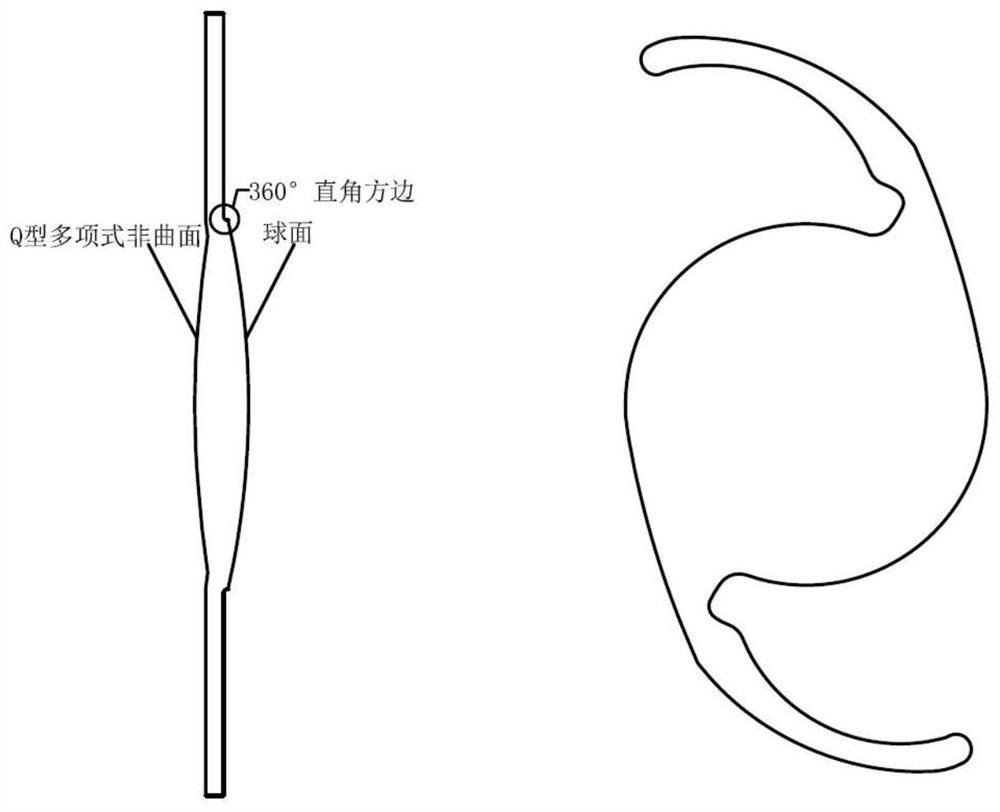
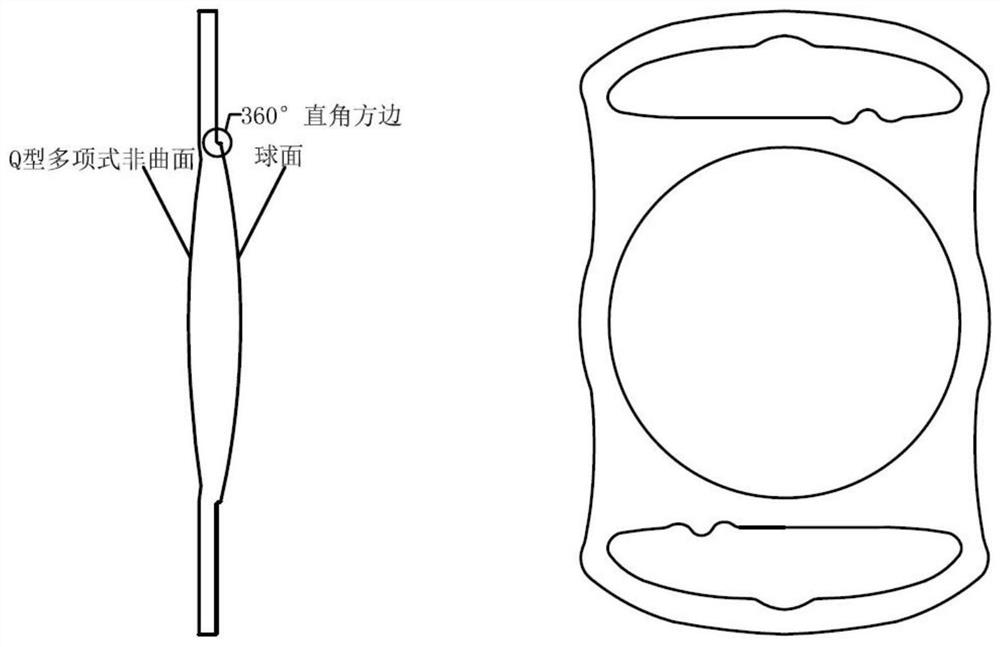
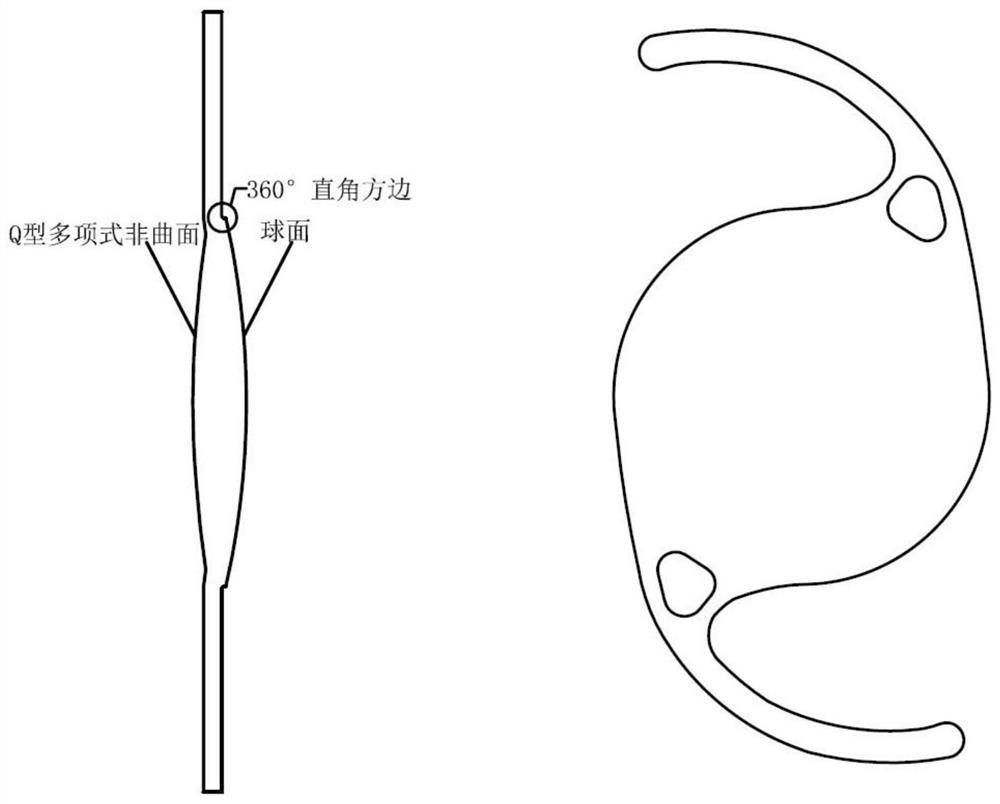
Aspheric artificial lens for resisting postoperative residual refractive error
PendingCN113599021AJiao ShendaImprove surgical error toleranceIntraocular lensRefractive errorOphthalmology
The invention discloses an aspheric artificial lens for resisting postoperative residual refractive error, the artificial lens comprises an optical main body (1), a first support loop (2) and a second support loop (3), the optical main body (1) adopts aspheric design represented by a Q-type polynomial, an optical area has a focal depth extension function, optical imaging excess resolution is reasonably utilized, and the operation fault-tolerant rate is improved; light artificial lens deviation is better adapted, the sensitivity of focal power and image quality to an implantation position is reduced, postoperative residual refractive error is resisted, and the visual satisfaction is improved; meanwhile, high-order aberration is considered, and high resolution is kept.
Owner:TIANJIN SHI JI KANG TAI BIOMEDICAL ENG CO LTD
Sheet light energy homogenization optical shaping system based on total reflection integral cavity
ActiveCN114236859AGood homogenization effectRealize precise measurement with high spatio-temporal resolutionOptical elementsGaussian beamLight energy
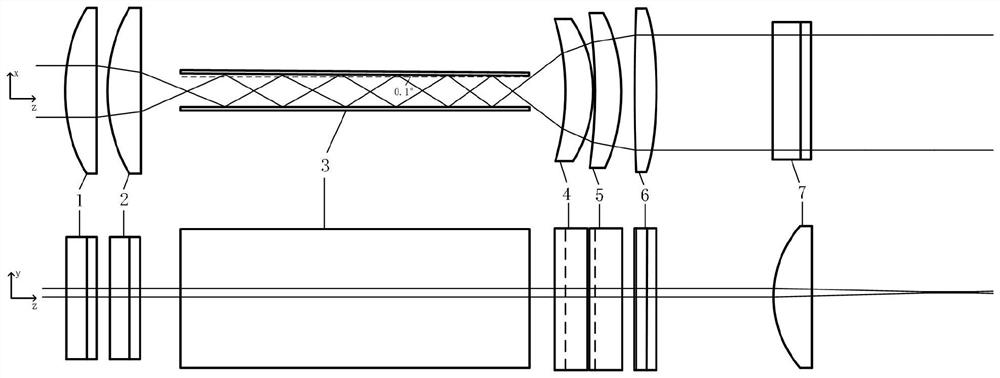
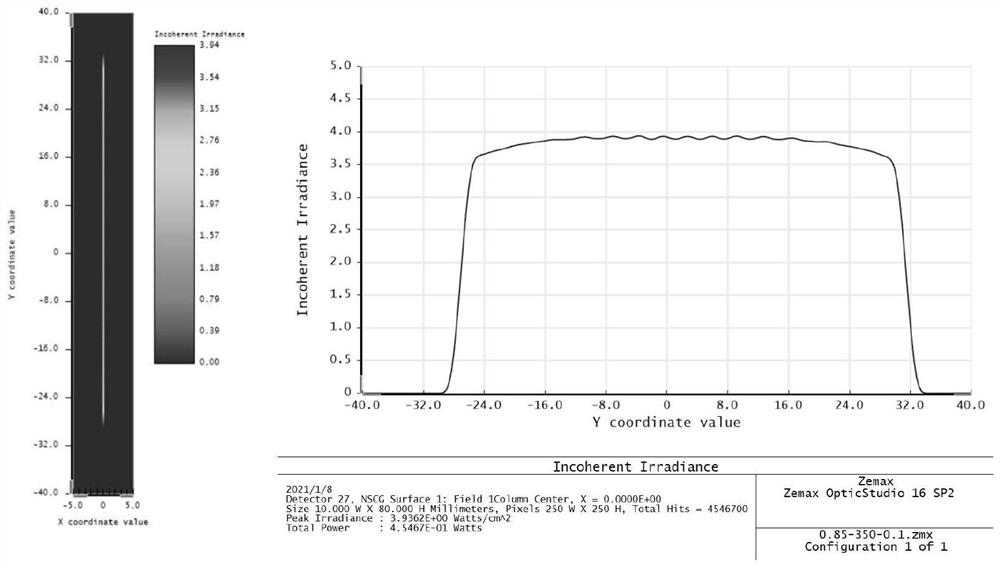
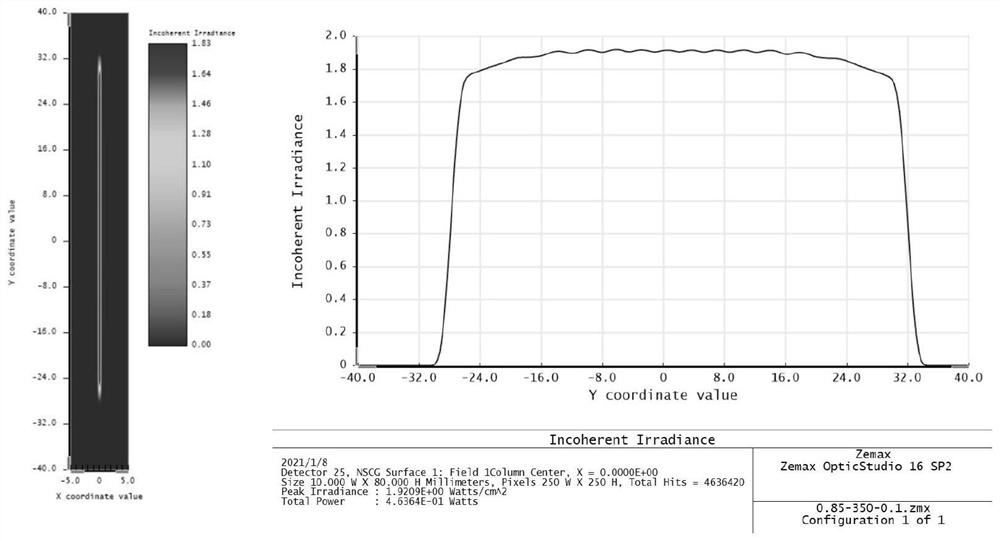
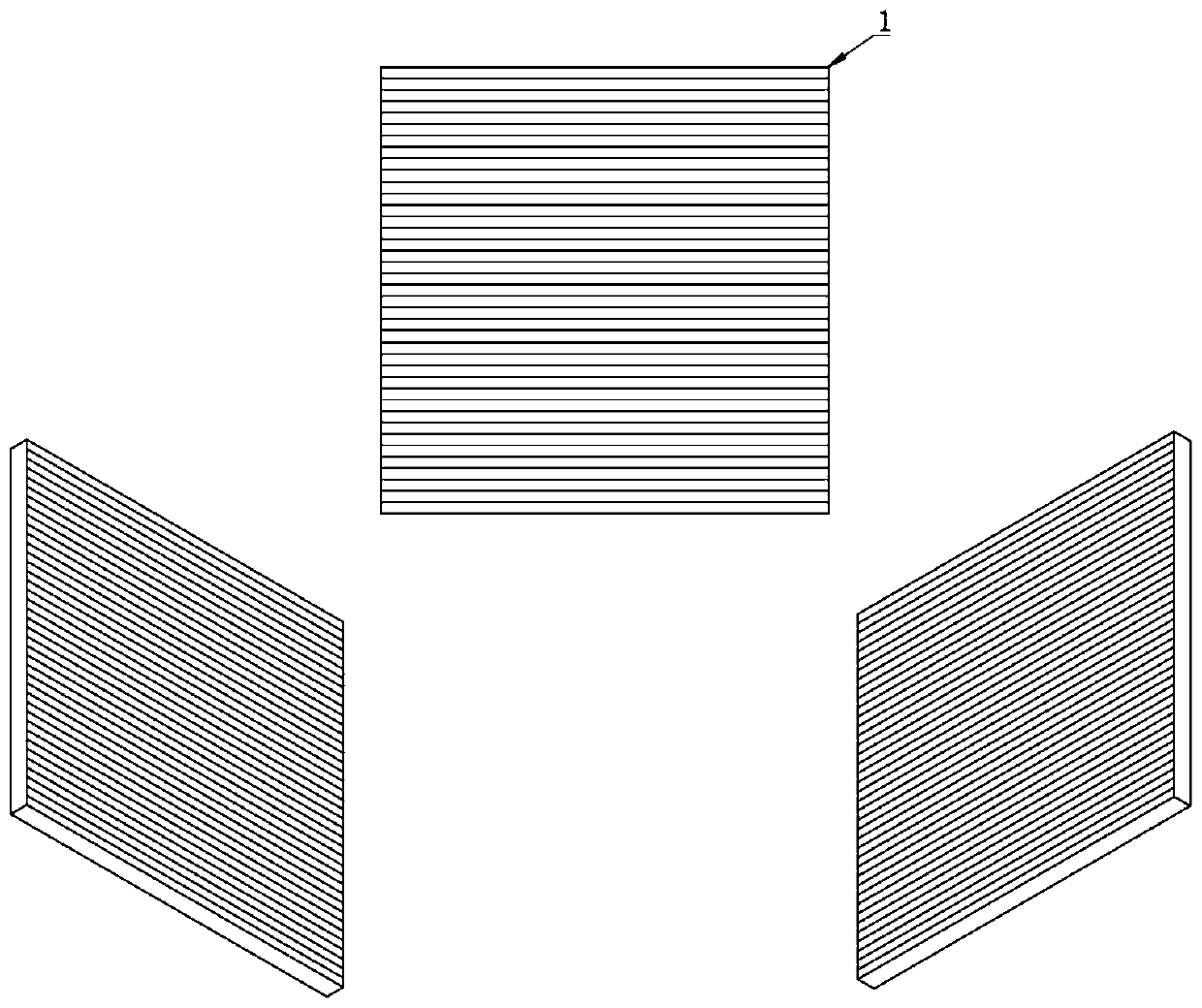
The invention discloses a sheet light energy homogenization optical shaping system based on a total reflection integral cavity, and relates to a sheet light energy homogenization optical shaping system. The optical lenses are sequentially arranged along the Gaussian beam propagation direction, the entrance pupil translation offset d is equal to 0.85 mm, the coupled optical lens group comprises a first plano-convex cylindrical lens and a second plano-convex cylindrical lens, the total reflection integral cavity consists of two light uniformizing plates and is plated with a high-reflection film, one light uniformizing plate is parallel to the Gaussian beam propagation direction, and the other light uniformizing plate forms an included angle of 0.1 degree with the Gaussian beam propagation direction. The collimation compression optical lens group comprises a first meniscus cylindrical mirror, a second meniscus cylindrical mirror, a first biconvex cylindrical mirror and a third plano-convex cylindrical mirror. The Gaussian beam can be converted into a sheet beam with uniform energy distribution, a high-quality and high-efficiency laser beam is provided for PLIF combustion diagnosis, and the complexity and processing cost of a PLIF system can be reduced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Microlens array acquiring adjustable double focuses
InactiveCN110441839AIncreasing Focus Beam Depth of FocusJiao ShendaLaser beam welding apparatusLensWeld seamSurface type
The invention discloses a microlens array acquiring adjustable double focuses. The microlens array is a column surface type lens array and is novel in structure design. The long focal depth characteristic is realized based on the microlens array; focused spots can change from a single focus to double focuses and a distance between the double focuses is adjustable with use of a focusing mirror andby rotating in a column surface cross line direction of the microlens array based on a micro-surface spectroscopic characteristic, and the focal depth of a focused beam of the double focuses is increased greatly. The microlens array acquiring the adjustable double focuses is applied to laser welding, can especially help to reduce lapping width of boards and lower clamping requirements of boards, reduces various defects of highly reflective boards in welding, improves welding seam quality and lengthens welding depth.
Owner:SHANGHAI EMPOWER AUTOMATION TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com