Preparation method of optical fiber-doped waste mud alkali-activated phosphorous slag geopolymer
A geopolymer and optical fiber technology, applied in cement production and other directions, can solve problems such as unfavorable promotion, and achieve the effect of reducing production cost, stable structure and high activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
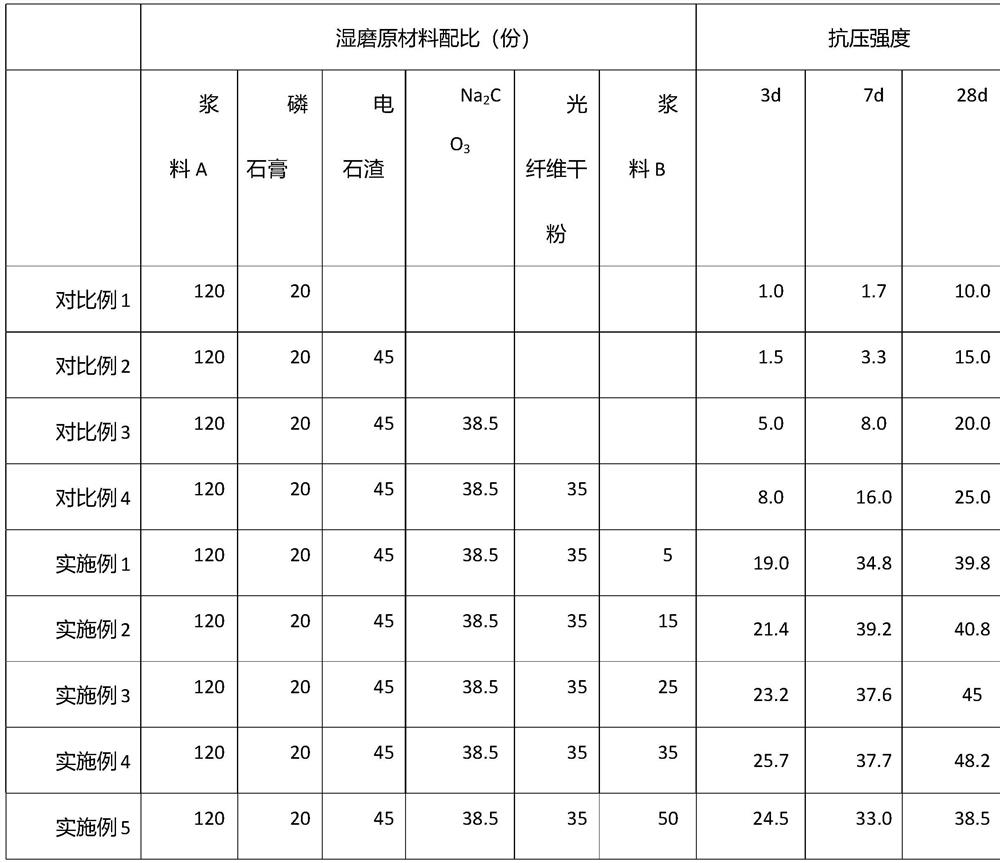
[0031] (1) Send 140 parts of phosphorus slag, 60 parts of nickel slag, and 100 parts of water into a planetary ball mill for grinding at a water-to-material ratio of 0.5. The grinding time is 40 minutes, and the speed of the planetary ball mill is 100-400rad / s to obtain slurry A .
[0032] (2) After pulverizing the waste optical fiber sludge, pass it through a 1.18mm sieve to obtain a dry powder of the optical fiber waste sludge.
[0033] (3) Send 200 parts of optical fiber waste sludge dry powder and 100 parts of water into a planetary ball mill at a water-to-material ratio of 0.5 for wet grinding. The grinding time is 40 minutes, and the speed of the planetary ball mill is 400rad / s to obtain slurry B.
[0034] (4) 120 parts of slurry A obtained in step (1), 35 parts of optical fiber waste sludge dry powder obtained in step (2), 5 parts of slurry B obtained in step (3), 20 parts of phosphogypsum, and 45 parts of carbide slag Parts, Na 2 CO 3 38.5 parts and 900 parts of san...
Embodiment 2
[0036] (1) Send 140 parts of phosphorous slag, 60 parts of nickel slag, and 100 parts of water into a planetary ball mill for grinding at a water-to-material ratio of 0.5. The grinding time is 40 minutes, and the rotational speed of the planetary ball mill is 400 rad / s to obtain slurry A.
[0037] (2) After pulverizing the waste optical fiber sludge, pass it through a 1.18mm sieve to obtain a dry powder of the optical fiber waste sludge.
[0038] (3) Send 200 parts of optical fiber waste sludge dry powder and 100 parts of water into a planetary ball mill at a water-to-material ratio of 0.5 for wet grinding. The grinding time is 40 minutes, and the speed of the planetary ball mill is 400rad / s to obtain slurry B.
[0039] (4) 120 parts of slurry A obtained in step (1), 35 parts of optical fiber waste sludge dry powder obtained in step (2), 15 parts of slurry B obtained in step (3), 20 parts of phosphogypsum, and 45 parts of carbide slag Parts, Na 2 CO 3 38.5 parts and 900 part...
Embodiment 3
[0041] (1) Send 140 parts of phosphorous slag, 60 parts of nickel slag, and 100 parts of water into a planetary ball mill for grinding at a water-to-material ratio of 0.5. The grinding time is 40 minutes, and the rotational speed of the planetary ball mill is 400 rad / s to obtain slurry A.
[0042] (2) After pulverizing the waste optical fiber sludge, pass it through a 1.18mm sieve to obtain a dry powder of the optical fiber waste sludge.
[0043] (3) Send 200 parts of optical fiber waste sludge dry powder and 100 parts of water into a planetary ball mill at a water-to-material ratio of 0.5 for wet grinding. The grinding time is 40 minutes, and the speed of the planetary ball mill is 400rad / s to obtain slurry B.
[0044] (4) 120 parts of slurry A obtained in step (1), 35 parts of optical fiber waste sludge dry powder obtained in step (2), 25 parts of slurry B obtained in step (3), 20 parts of phosphogypsum, and 45 parts of carbide slag Parts, Na 2 CO 3 38.5 parts and 900 parts ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com