Aerated concrete block prepared by doping iron tailings and preparation method thereof
A technology for air-entrained concrete and iron tailings, which is used in applications, ceramic products, household appliances, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, unsatisfactory thermal insulation performance, complicated operation, etc., and achieves low production cost, optimized raw material formula, A wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The aerated concrete block prepared by mixing iron tailings in this embodiment includes the following raw materials in parts by weight:
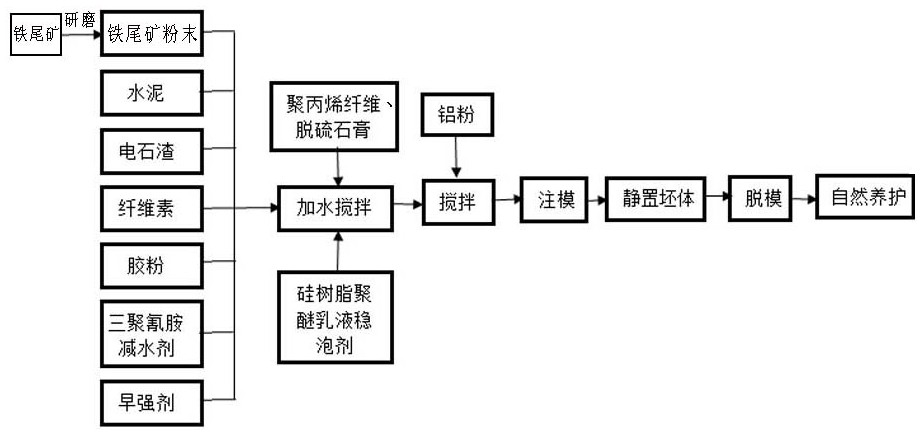
[0031] 65 parts of iron tailings, 30 parts of cement, 2 parts of early strength agent, 6 parts of cellulose, 5 parts of rubber powder, 6 parts of polypropylene fiber, 3 parts of aluminum powder, 6 parts of desulfurized gypsum, 2 parts of melamine water reducer, calcium carbide 12 parts of slag and 2 parts of foam stabilizer. The iron tailings are industrial solid wastes produced after iron ore processing, refining and sorting. The chemical composition and mass fraction of the iron tailings described in this embodiment are: SiO 2 60%-70%, CaO 5%-8%, MgO 6%-10%, Al 2 o 3 Accounting for 4%-7%, TFe accounted for 8%-12%, rich in metal oxides.
[0032] Among them: the iron tailings are rationally graded using a vibrating screen machine, screened according to different system sieve tray grid specifications, and the selected particle size ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The difference between this example and Example 1 lies in the content of the raw materials for preparing the aerated concrete block prepared by mixing iron tailings.
[0043] The aerated concrete block prepared by mixing iron tailings in this embodiment includes the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0044] 50 parts of iron tailings, 50 parts of cement, 3 parts of early strength agent, 10 parts of cellulose, 8 parts of rubber powder, 10 parts of polypropylene fiber, 5 parts of aluminum powder, 10 parts of desulfurized gypsum, 4 parts of melamine water reducer, calcium carbide 20 parts of slag and 3 parts of foam stabilizer. All the other are with embodiment 1.
[0045] The difference between the method for preparing the aerated concrete block prepared by mixing iron tailings and Example 1 in this embodiment is only:
[0046] The mold poured in step (3) is moved into a constant temperature drying oven at 65°C for 2 hours for molding;
[0047] The process of...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The difference between this example and Example 1 lies in the content of the raw materials for preparing the aerated concrete block prepared by mixing iron tailings.
[0052] The aerated concrete block prepared by mixing iron tailings in this embodiment includes the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0053] 80 parts of iron tailings, 10 parts of cement, 0.5 parts of early strength agent, 2 parts of cellulose, 2 parts of rubber powder, 2 parts of polypropylene fiber, 0.5 parts of aluminum powder, 2 parts of desulfurized gypsum, 0.5 parts of melamine water reducer, calcium carbide 5 parts of slag and 0.1 part of foam stabilizer. All the other are with embodiment 1.
[0054] The difference between the method for preparing the aerated concrete block prepared by mixing iron tailings and Example 1 in this embodiment is only:
[0055] The mold poured in step (3) is moved into a constant temperature drying oven at 75°C for 4 hours for molding;
[0056] In step (4)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com