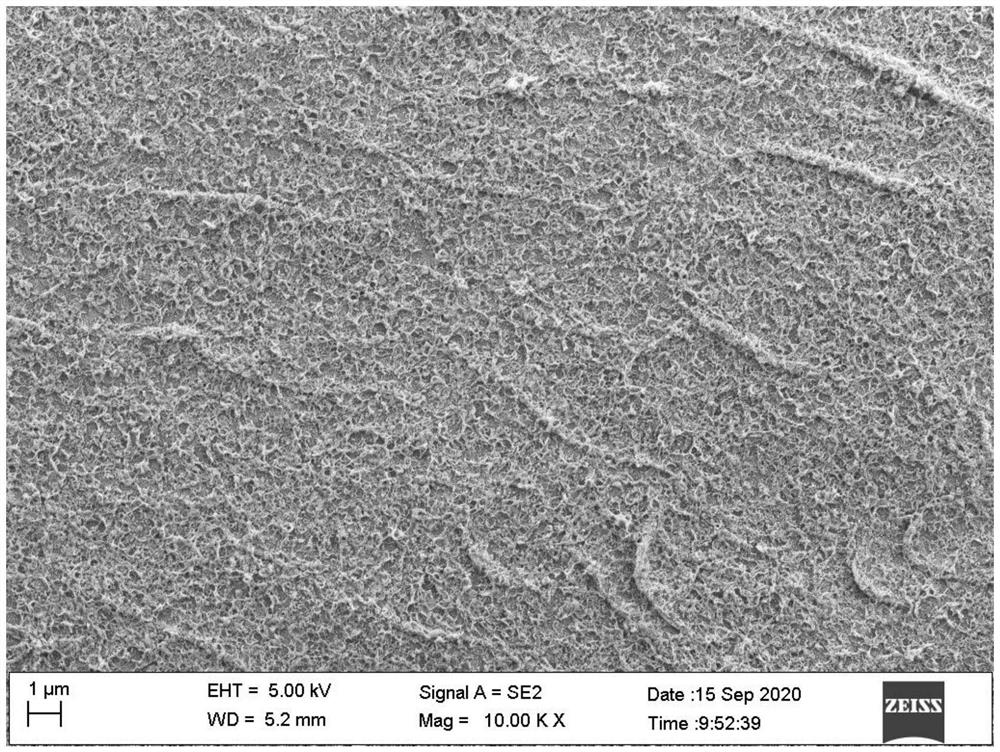
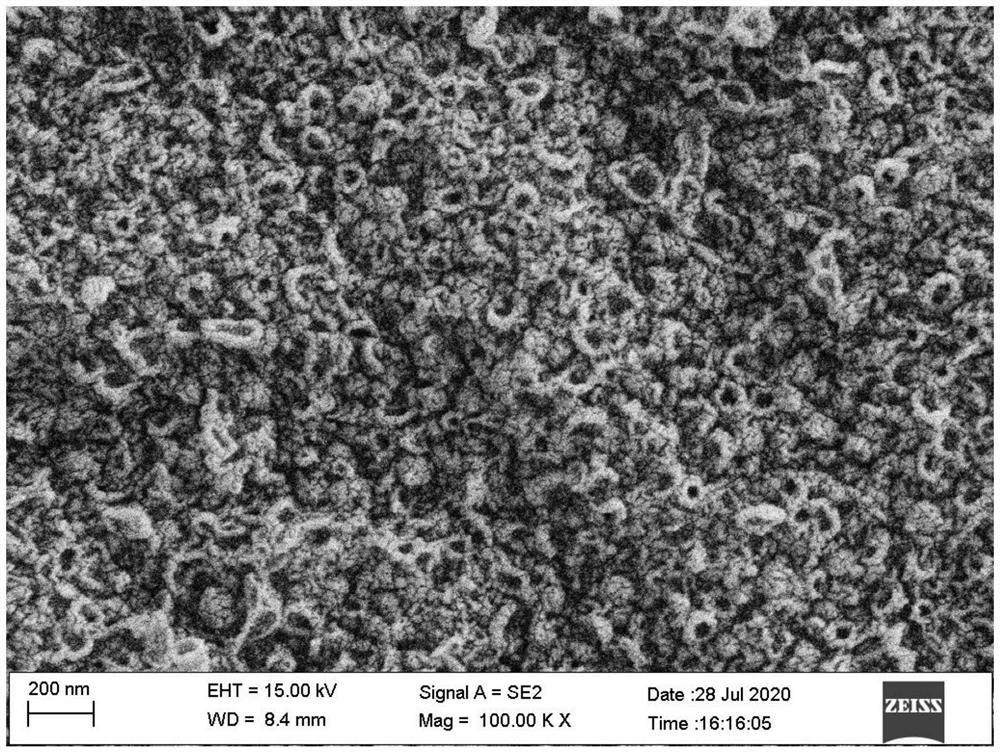
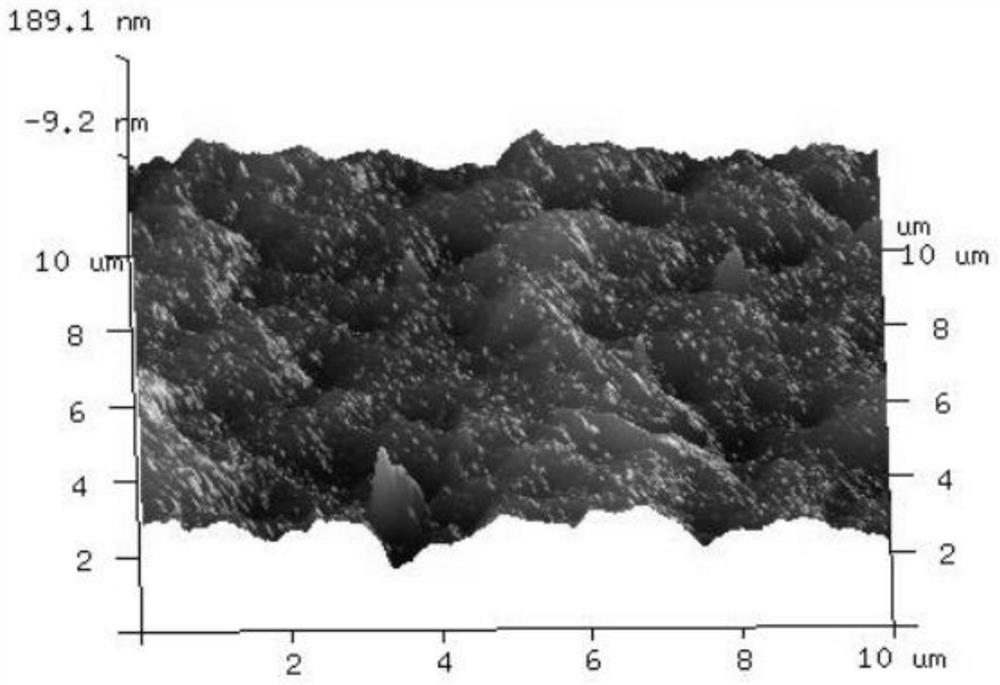
Modification method for improving chlorine resistance of polyacrylonitrile forward osmosis membrane
A polyacrylonitrile and forward osmosis membrane technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of increasing the mass transfer resistance of the membrane surface and reducing the membrane flux, and achieve the effects of simple and cheap modification methods, improved flux reduction, and reduced costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Porous PAN supports were prepared by non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) method. First, polyacrylonitrile with a mass fraction of 16.7% was dissolved in N-methylpyrrolidone solution, porogen lithium chloride was added with a mass fraction of 0.8%, and the mixture was stirred at 60 °C for 12 hours. After the casting film solution is completely dissolved, the casting film solution is put into an ultrasonic cleaning machine for degassing treatment to remove air bubbles generated during the stirring process. After 24 hours, pour the casting liquid on the glass plate, scrape the film with a film applicator, and control the thickness to be about 60 μm, and then immediately put it into the deionized water coagulation bath to obtain the support film. Then the functional layer is prepared on the prepared carrier by IP (interfacial polymerization) method. First, immerse the prepared supporting membrane in m-phenylenediamine solution (water as solvent, mass fraction of m-...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Porous PAN supports were prepared by non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) method. First, polyacrylonitrile with a mass fraction of 17.0% was dissolved in a N,N-dimethyldiformamide solution, and a porogen lithium chloride was added with a mass fraction of 1.0%, and the mixture was stirred at 60 °C for 12 hours. After the casting film solution is completely dissolved, the casting film solution is put into an ultrasonic cleaning machine for degassing treatment to remove air bubbles generated during the stirring process. After 24 hours, pour the casting liquid on the glass plate, scrape the film with a film applicator, and control the thickness to be about 60 μm, and then immediately put it into the deionized water coagulation bath to obtain the support film. Then the functional layer is prepared on the prepared carrier by IP (interfacial polymerization) method. First, soak the prepared support membrane in m-phenylenediamine solution (water as solvent, the mass frac...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Porous PAN supports were prepared by non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) method. First, polyacrylonitrile with a mass fraction of 16.8% was dissolved in N-methylpyrrolidone solution, porogen zinc chloride was added, and the mass fraction was 0.8%, and the mixture was stirred at 60 °C for 12 hours. After the casting film solution is completely dissolved, the casting film solution is put into an ultrasonic cleaning machine for degassing treatment to remove air bubbles generated during the stirring process. After 24 hours, pour the casting liquid on the glass plate, scrape the film with a film applicator, and control the thickness to be about 60 μm, and then immediately put it into the deionized water coagulation bath to obtain the support film. Then the functional layer is prepared on the prepared carrier by IP (interfacial polymerization) method. First, soak the prepared supporting membrane in m-phenylenediamine solution (water is the solvent, the mass fraction ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com