A method for recycling water treatment waste PVDF membrane
A technology for water treatment and membranes, which can be used in cleaning methods using liquids, sustainable biological treatment, osmotic/dialysis water/sewage treatment, etc., and can solve problems such as increased system maintenance costs, shortened pollution-cleaning cycles, and environmental burdens. , to achieve the effect of promoting resource recycling, improving anti-pollution performance and prolonging service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
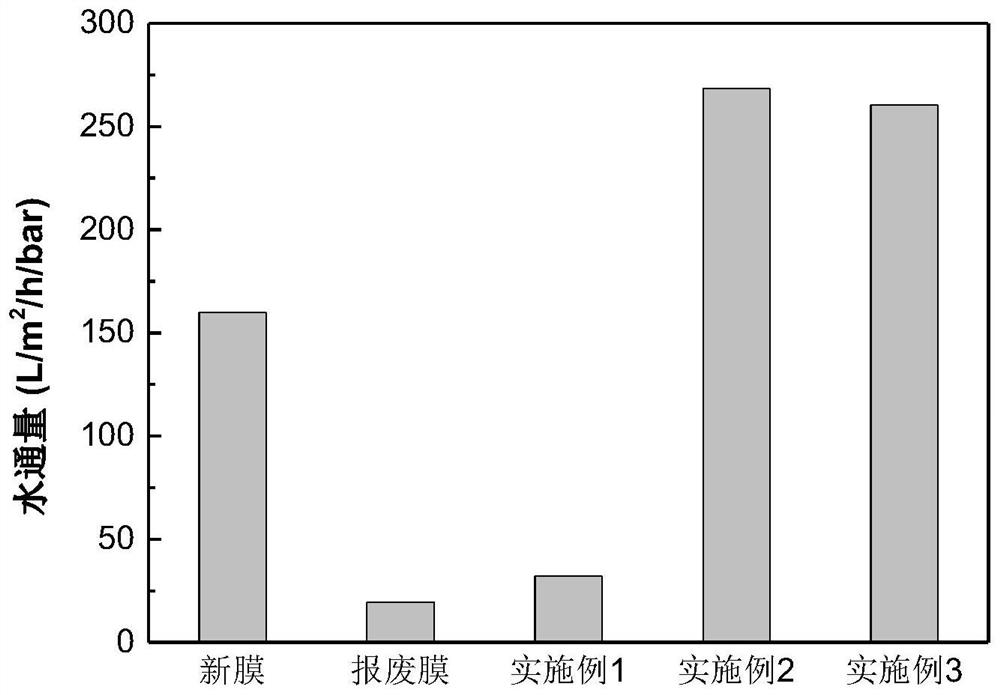
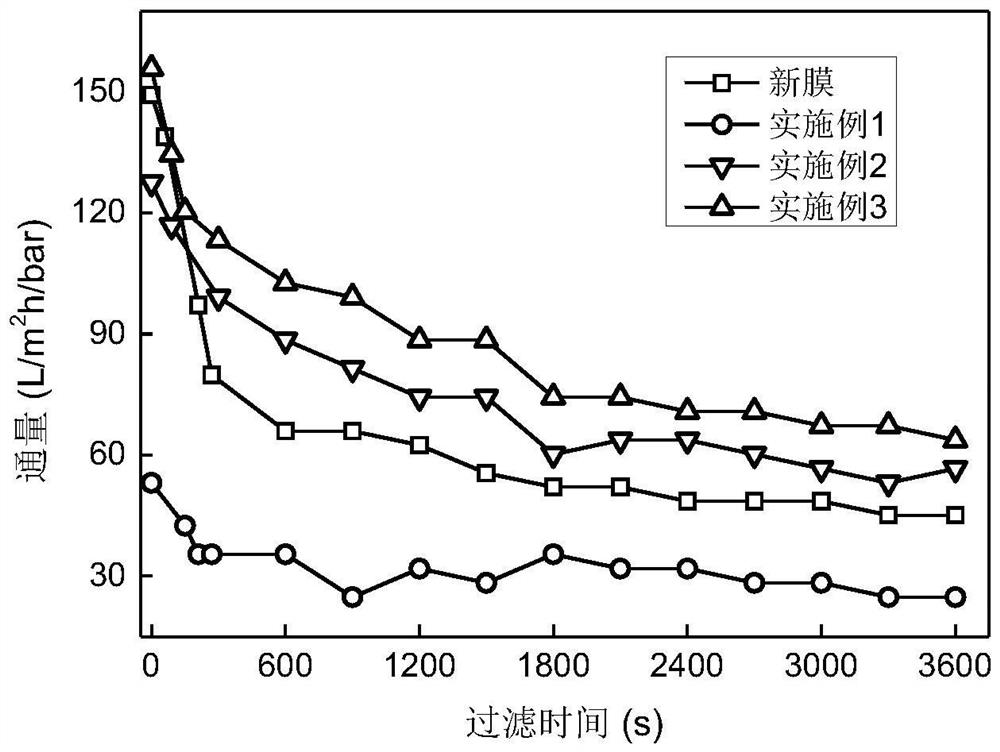
[0038] Cleaning of scrapped PVDF membranes: Soak and clean scrapped membranes with 0.5% sodium hypochlorite for 2 hours, 1.5% citric acid for 2 hours, and then rinse with deionized water to remove excess chemicals on the surface.
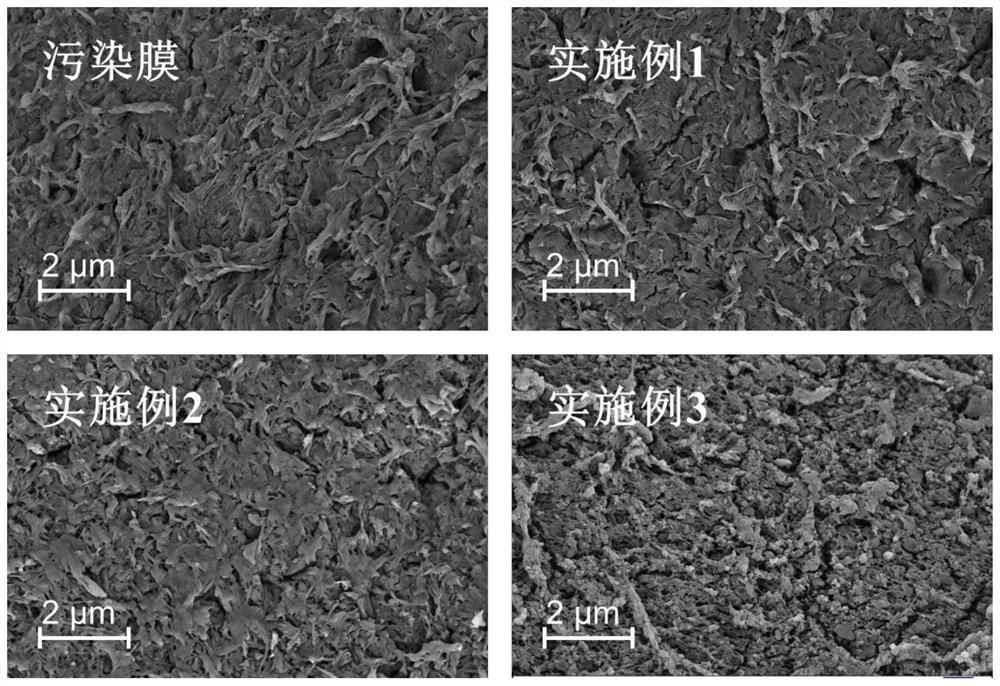
[0039] through figure 1 The scanning electron microscope observation shown shows that after cleaning, the large mud cake layer attached to the surface falls off from the membrane surface.
Embodiment 2
[0041] Structural transformation of scrap PVDF membrane: Soak the pretreated PVDF membrane in a mixed solution of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP), dimethylacetamide (DMAC) and methanol at a volume ratio of 60:10:30 at 30°C 2.0min, then fully rinsed with deionized water to remove the residual agent on the surface.
[0042] throughfigure 1 The scanning electron microscope observation shown shows that the pollutants on the membrane surface are further cleaned, and the membrane structure is partially opened.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Hydrophilic restoration of scrapped PVDF membranes: dopamine was dissolved in 15 mM Tris-HCl buffered aqueous solution (pH=8.8) to prepare a dopamine solution (2 mg / mL). The membrane was immersed in the dopamine solution at 30° C., placed in a shaker at a rotation speed of 100 rpm, and reacted for 8 hours. After the reaction, wash with flowing deionized water to remove weakly bound polydopamine.
[0045] through figure 1 According to the scanning electron microscope observation shown, a uniform and dense polydopamine hydrophilic layer is formed on the surface of the membrane.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com