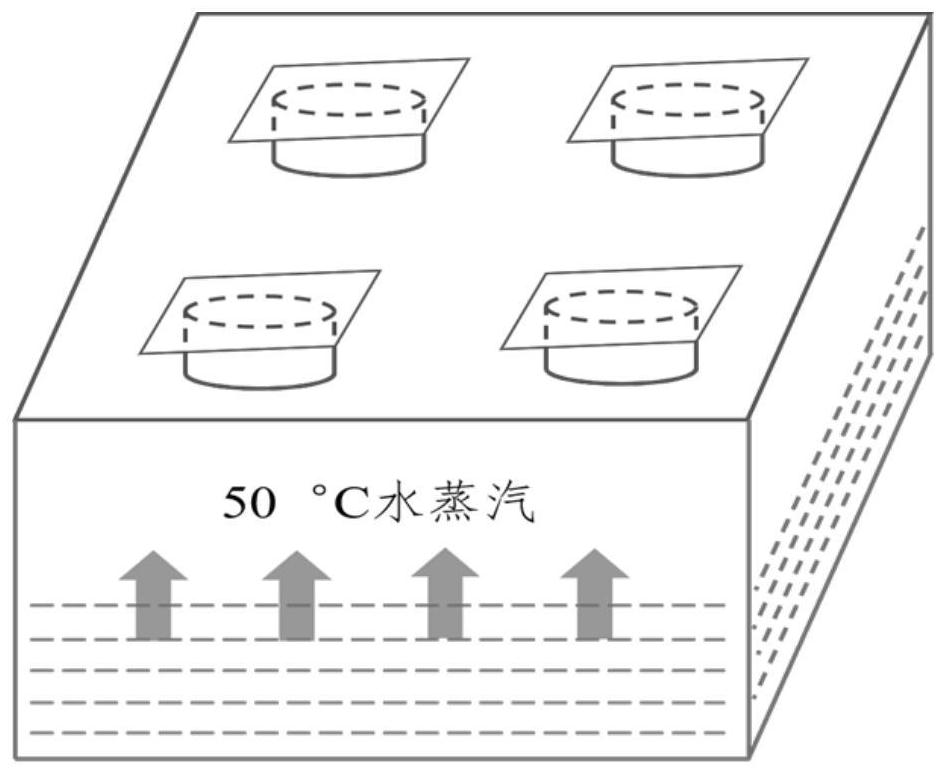
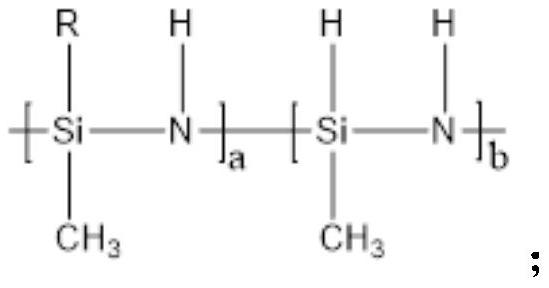
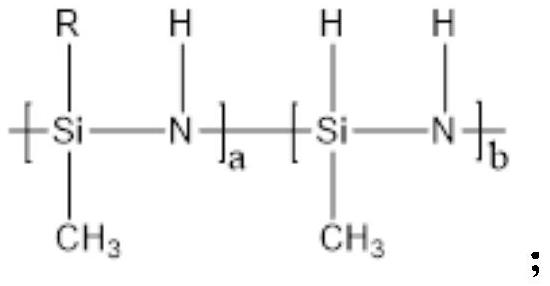
Glass antifogging agent and preparation method thereof
A technology of anti-fogging agent and glass, which is applied in the field of glass anti-fogging agent and its preparation, glass anti-fogging agent containing modified polysilazane and its preparation field, which can solve the troublesome preparation method, high energy consumption, limited application, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of simple use method, simple preparation method, and poor durability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] (1) 5g modified polysilazane is mixed with 10g solvent to obtain liquid A; the solvent is composed of n-hexane, butyl propionate and n-butyl ether, and the mass ratio of n-hexane, butyl propionate and n-butyl ether It is 4:3:3.
[0054] (2) Mix and dissolve 1.4g sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 1.4g NP-10 in 85g deionized water to form a surfactant aqueous solution; take 1g of fixative and 10g of dispersant and mix evenly and add to the surfactant aqueous solution , mix evenly to obtain liquid B.
[0055] Wherein, the fixing agent is composed of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and polyvinyl alcohol, and the mass ratio of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and polyvinyl alcohol is 1:1; the dispersant is methanol.
[0056] (3) Mix liquid A and liquid B uniformly at a mass ratio of 1:2 to form a mixed solution, and adjust the pH of the mixed solution to 7.1 with sodium hydroxide to obtain the glass antifogging agent of this embodiment.
Embodiment 2
[0058] (1) Mix 8 g of modified polysilazane with 10 g of solvent to obtain liquid A; the solvent is composed of butyl acetate and n-heptane, and the mass ratio of butyl acetate and n-heptane is 2:3.
[0059] (2) Mix 1.8g sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 1g NP-10 and dissolve in 100g deionized water to form a surfactant aqueous solution; take 2g of fixative and 20g of dispersant and mix evenly and add it to the surfactant aqueous solution , and mix evenly to obtain liquid B.
[0060] Wherein, the fixing agent is composed of carboxymethyl cellulose and sodium alginate, and the mass ratio of carboxymethyl cellulose and sodium alginate is 2:1; the dispersant is isopropanol.
[0061] (3) Liquid A and liquid B were uniformly mixed at a mass ratio of 1:4 to form a mixed solution, and the pH of the mixed solution was adjusted to 8.1 with sodium hydroxide to obtain the glass antifogging agent of this embodiment.
Embodiment 3
[0063] (1) Mix 25g of modified polysilazane with 25g of solvent to obtain liquid A; the solvent is composed of n-hexane and amyl acetate, and the mass ratio of n-hexane and amyl acetate is 4:1.
[0064] (2) 1g sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 5g NP-10 are mixed and dissolved in 150g deionized water to form an aqueous surfactant solution; 2g fixing agent is mixed with 10g dispersant and added to the aqueous surfactant solution, Mix well to obtain liquid B.
[0065] Wherein, the fixing agent is hydroxypropyl methylcellulose; the dispersing agent is ethanol.
[0066] (3) Mix liquid A and liquid B uniformly at a mass ratio of 1:6 to form a mixed solution, and adjust the pH of the mixed solution to 8.0 with sodium hydroxide to obtain the glass antifogging agent of this embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com