Method for recycling graphite negative electrode of waste battery
A graphite negative electrode and waste battery technology, which is applied to battery electrodes, negative electrodes, secondary batteries, etc., can solve the problems of easy generation of waste liquid and discomfort of recycling lithium-ion battery graphite negative electrodes, and achieve environmental protection, high efficiency, and high-quality process in the recycling process. The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
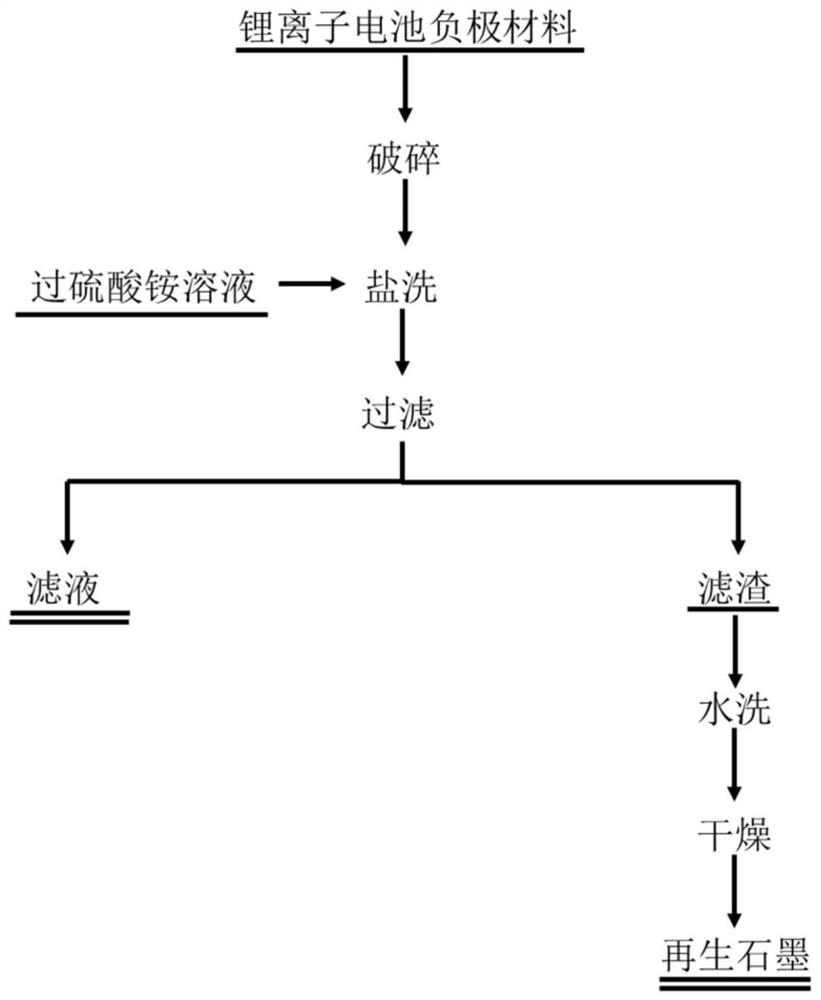
[0026] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0027] (1) Soak and discharge the graphite negative electrode of the waste lithium-ion battery in 2% sodium chloride solution for 20 hours, then dry and disassemble it to obtain 50 g of negative electrode material, and then artificially cut the negative electrode sheet into a 3 cm long and 5 cm wide negative electrode sheet;
[0028] (2) Place the obtained regenerated graphite negative electrode sheet in a 2mol / L ammonium persulfate solution at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 50g / L, heat it in a water bath to 60°C, and soak for 40min to completely dissolve the copper foil;
[0029] (3) After the reaction is completed, the graphite-containing solution is suction-filtered, washed three times with deionized water to neutrality, and dried to obtain regenerated graphite.
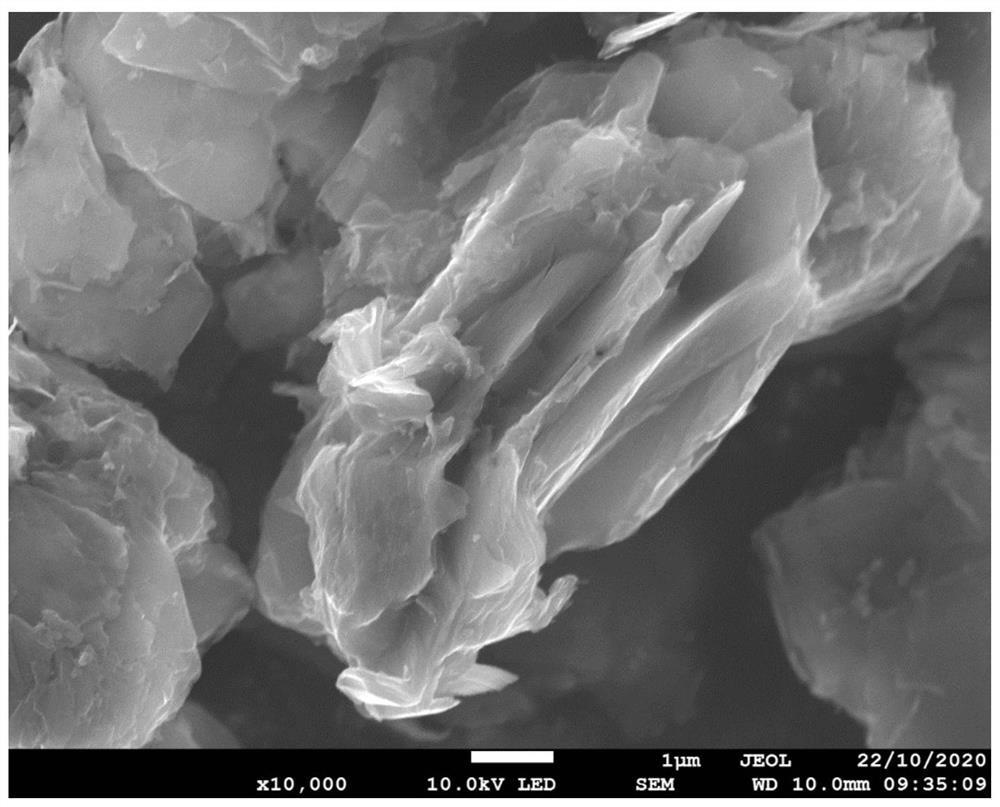
[0030] The regenerated graphite material prepared by the present embodiment is scanned by electron microscope, and the results are as follows: figure 2 As shown...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Soak and discharge the graphite negative electrode of the waste lithium-ion battery in 6% sodium chloride solution for 18 hours, then dry and disassemble it to obtain 100 g of negative electrode material, and then artificially cut the negative electrode sheet into a 3 cm long and 8 cm wide negative electrode sheet;
[0033] (2) Place the obtained regenerated graphite negative electrode sheet in a 4mol / L sodium persulfate solution at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 30g / L, heat it in a water bath to 80°C, and soak for 40min to completely dissolve the copper foil;
[0034] (3) After the reaction is completed, the graphite-containing solution is suction-filtered, washed three times with deionized water to neutrality, and dried to obtain regenerated graphite.
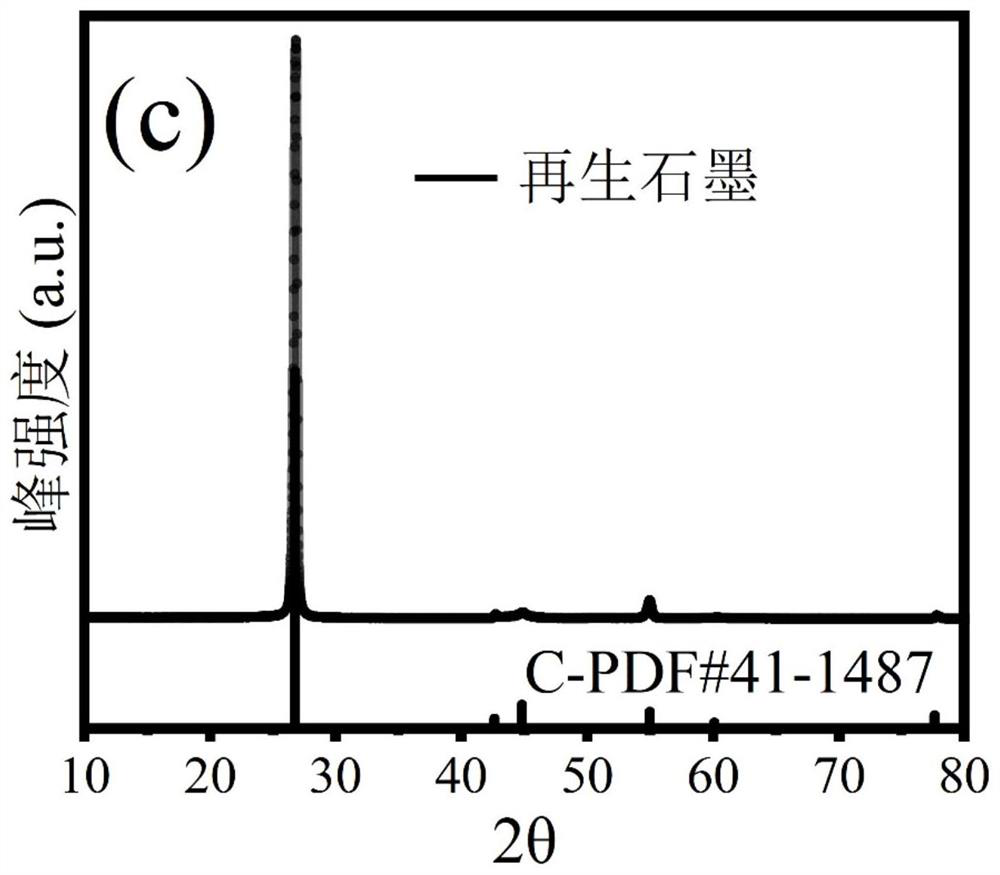
[0035] The regenerated graphite material prepared by the present embodiment is carried out XRD test, and its result is as follows Figure 4 shown, similar to figure 2 (XRD diagram), it can be seen that the regenerate...
Embodiment 3
[0037] (1) Soak and discharge the graphite negative electrode of the waste lithium-ion battery in 4% sodium chloride solution for 24 hours, then dry and disassemble to obtain 80 g of negative electrode material, and then artificially cut the negative electrode sheet into a 3 cm long and 7 cm wide negative electrode sheet;
[0038] (2) Place the obtained regenerated graphite negative electrode sheet in a 5mol / L potassium dichromate solution at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 80g / L, heat in a water bath to 80°C, and soak for 60min to completely dissolve the copper foil;
[0039] (3) After the reaction is completed, the graphite-containing solution is suction-filtered, washed 5 times with deionized water to neutrality, and dried to obtain regenerated graphite.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com