Method for high-throughput rapid detection of pathogenic microorganisms
A technology of pathogenic microorganisms and microorganisms, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measurement/inspection of microorganisms, bioinformatics, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, influence of pathogenic microorganism detection methods, and inability to fully analyze microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
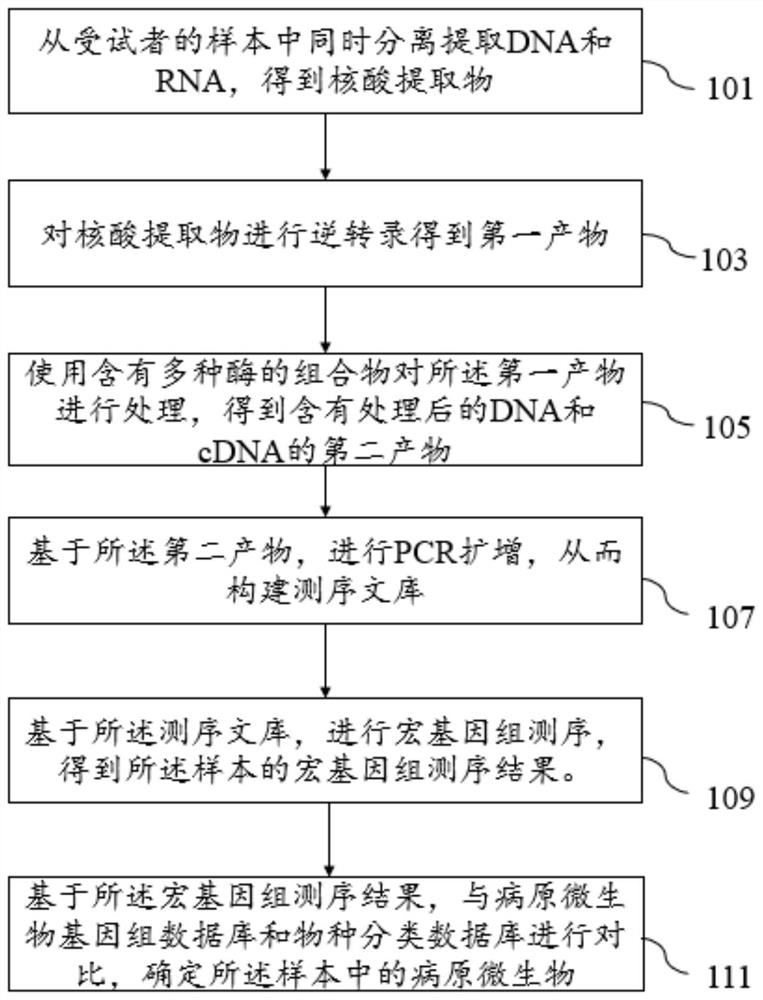
[0057] Embodiment 1, sample nucleic acid extraction
[0058] 1.1 Nucleic acid extraction from non-blood samples
[0059] Take an appropriate amount of samples (sputum 100ul, lavage fluid 200ul, pleural effusion 1ml, fresh punctured tissue the size of a sesame seed) and 8% formalin solution as a negative control, centrifuge at 3300rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant;
[0060] Wash the pellet with PBS buffer, repeat twice and then centrifuge to remove the supernatant;
[0061] Add 200ul of H 2 O mixed with the precipitate;
[0062] Add 50ul of propidium azide bromide with a concentration of 0.4M, shake and mix;
[0063] Avoid light at room temperature for 5 minutes;
[0064] Illumination for 25 minutes. At this stage, the sample needs to be placed on the shaker. During the illumination, pay attention to the lower layer of ice to reduce the temperature of the light;
[0065] Add 20ul of proteinase K with a concentration of 20mg / ml, add 1ul of 20% SDS solution;
[0066] F...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment 2, reverse transcription and purification
[0076] Take 10ul of the collected nucleic acid solution and add 10ul of 1st RT mix to mix, start the PCR program: 25°C, 10min; 42°C, 30min; 70°C, 15min for reverse transcription reaction;
[0077] After the reaction, add 30ul of 2st RNA mix and mix well. Reaction program: 16°C, 60min; 4°C, keep, to obtain the reverse transcription product;
[0078] Purification: Add 90ul of purified magnetic beads (beads) to the reverse transcription product for purification, mix and incubate for 5min, place on a magnetic stand, slowly aspirate and discard the supernatant, add 200ul of 80% ethanol to rinse once, and wait for 20s;
[0079] Discard the supernatant, and repeat the 80% ethanol rinse again;
[0080] After waiting for the magnetic beads to dry, add 53ul of H 2 O was eluted to obtain the purified product.
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3, enzyme digestion method library construction
[0082] Take 50ul of the purified product, add 15ul of end repair enzyme, reaction program: 30°C, 10min; 70°C, 15min;
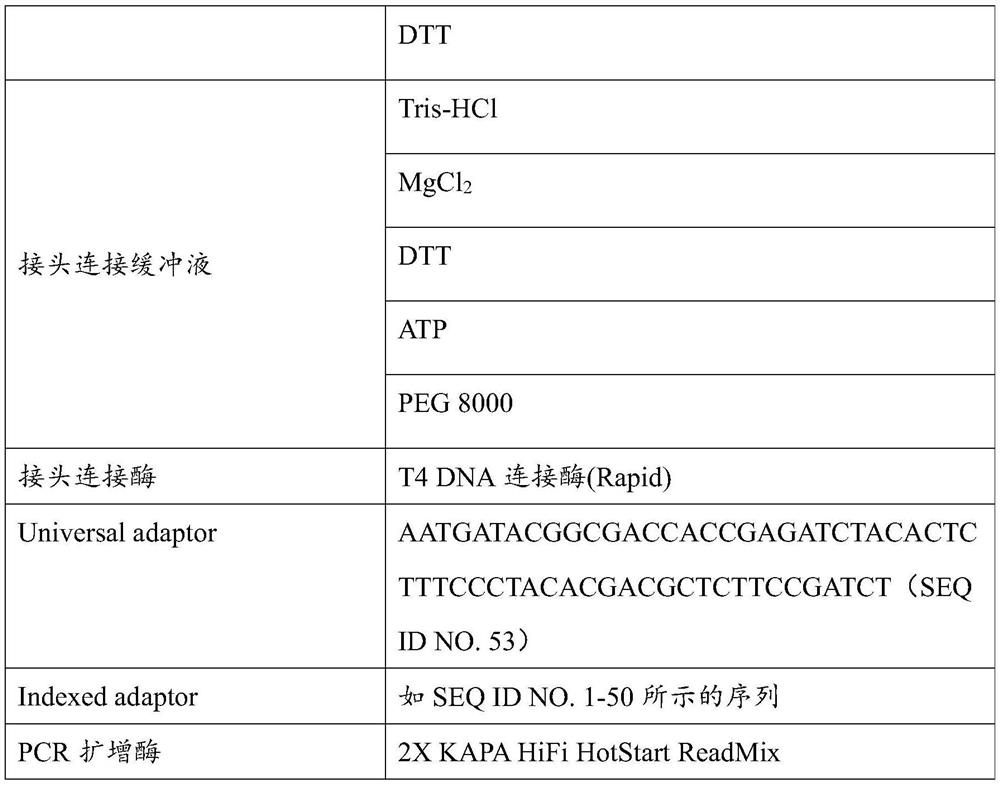
[0083] Add 25ul adapter ligation buffer, 5ul adapter ligase, 5ul adapter, reaction program: 20°C, 20min; 4°C, hold, to obtain the adapter ligation product;
[0084] 75ul beads purification, washed twice with 80% ethanol;
[0085] 22ul H 2 O was eluted to obtain a purified product;
[0086] Take 20ul of the purified product, add 25ul of PCR amplification enzyme, 5ul of primers (forward primer: AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGAT, SEQ ID No: 53, reverse primer: CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGA, SEQ ID NO: 52), and perform 6-12 rounds of PCR.
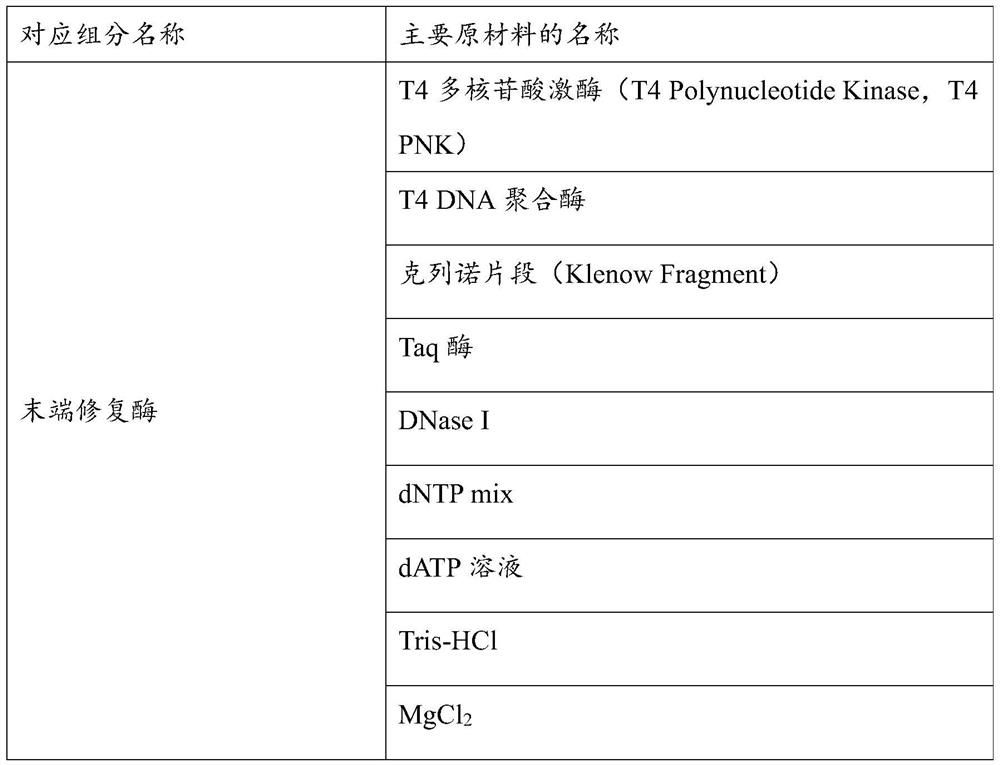
[0087] Specific materials of end repair enzymes, adapter ligation buffer, adapter ligase, adapters, and PCR amplification enzymes used in library construction by enzyme digestion can be found in Table 1 below.
[0088] Table 1 Materials contained in the components used in li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com