Method for decomposing phenolic by-products
A technology for by-products and phenols, applied in the field of decomposing phenolic by-products, can solve problems such as discarding phenolic by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
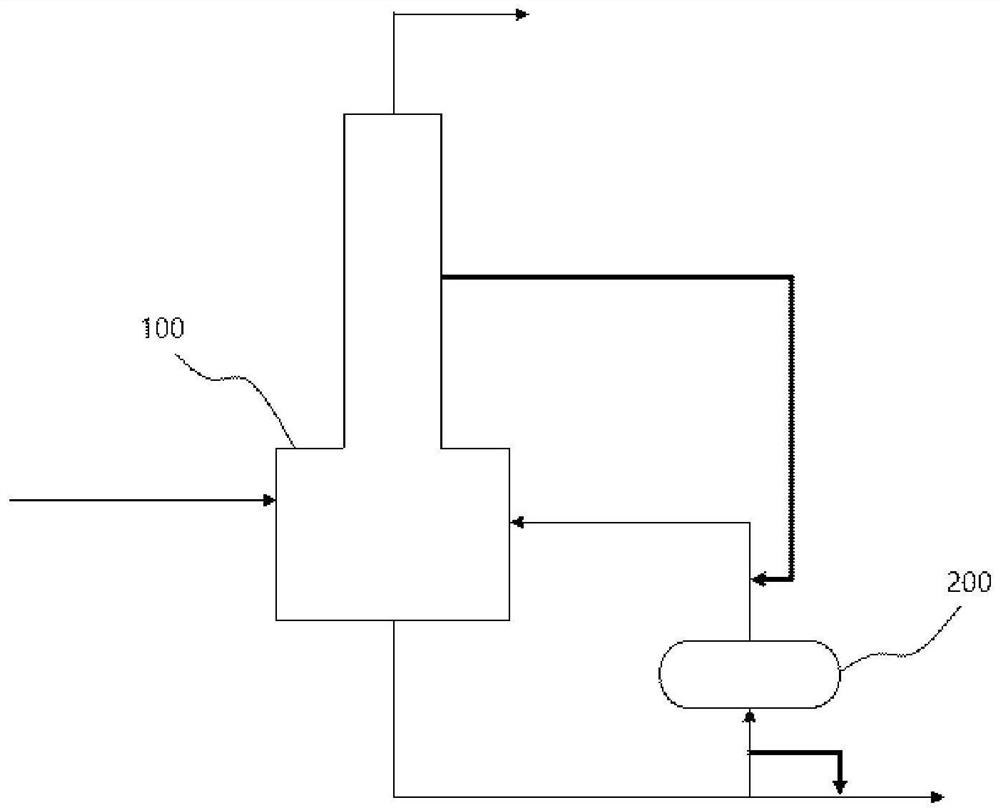
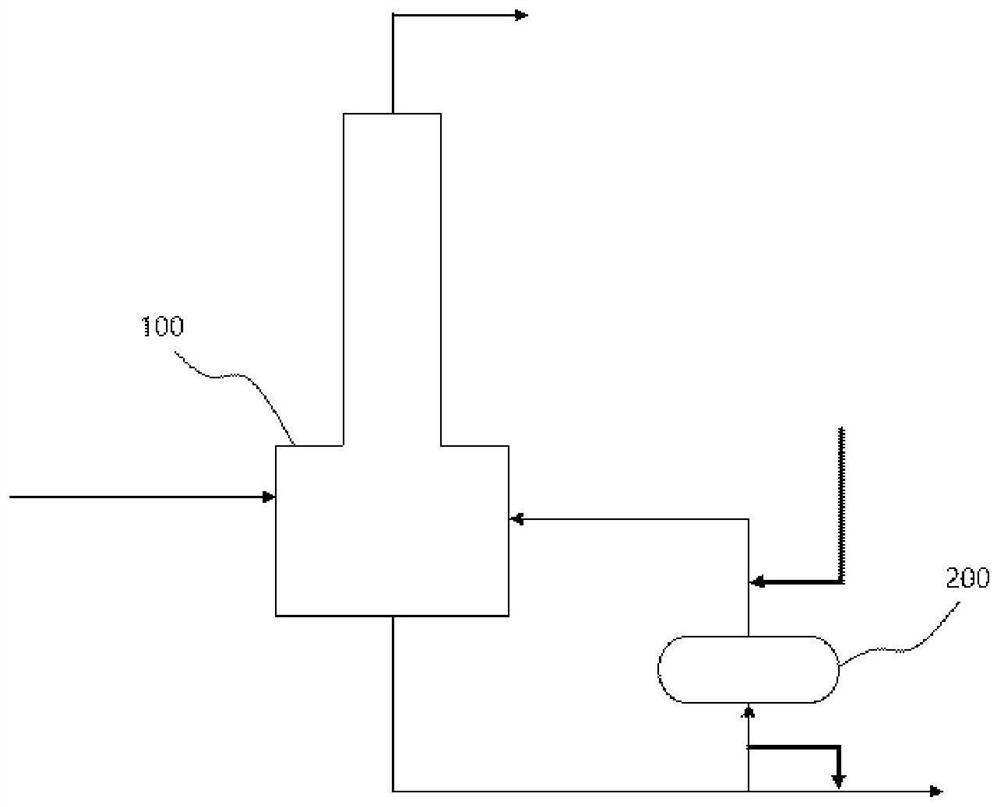
[0057] as figure 1As shown in the process flow diagram, the phenolic by-product stream of the composition shown in Table 1 is supplied to the decomposition device 100 at a flow rate of 1,000 kg / hr, and the phenolic by-product stream is thermally cracked. In this case, the working pressure of the decomposition device 100 was controlled to be normal pressure, and the working temperature of the decomposition device 100 was controlled to be 330°C. The active ingredient of the composition shown in Table 2 was recovered from the top discharge stream of the decomposition apparatus 100 . A part of the bottom discharge stream of the decomposition apparatus 100 is supplied to the reboiler 200 and the residual stream is discharged. In this case, the side discharge stream of the decomposition apparatus 100 was supplied to the reboiler 200 at a flow rate of 300 kg / hr to remove the pollutants accumulated in the reboiler 200 (solid line). The composition of the side discharge stream of the...
Embodiment 2
[0063] as figure 1 Referring to the process flow diagram shown, the phenolic by-product stream having the same composition as in Example 1 was supplied to the decomposition apparatus 100 at a flow rate of 1,000 kg / hr, and the phenolic by-product stream was thermally cracked. In this case, the operating pressure of the decomposition apparatus 100 was controlled to be normal pressure, and the operating temperature of the decomposition apparatus 100 was controlled to be 300°C. The active ingredient of the composition shown in Table 4 was recovered from the top discharge stream of the decomposition apparatus 100 . A part of the bottom discharge stream of the decomposition apparatus 100 is supplied to the reboiler 200 and the residual stream is discharged. In this case, the side discharge stream of the decomposition apparatus 100 was supplied to the reboiler 200 at a flow rate of 300 kg / hr to remove the pollutants accumulated in the reboiler 200 (solid line). The composition of t...
experiment example
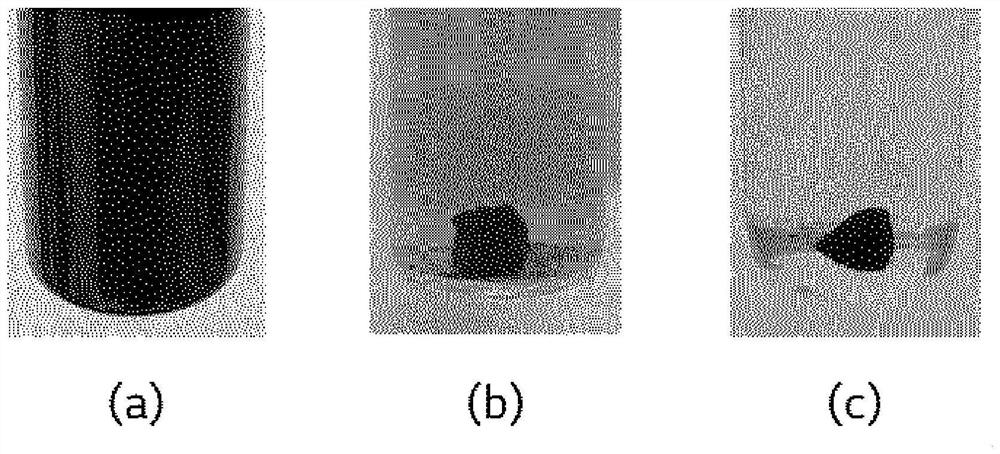
[0076] As pollutants accumulated in the reboiler 200, 5 g of tar with a high boiling point was immersed in a container containing 50 g of the side discharge stream of Example 1, a container containing 50 g of acetone of Comparative Example 1, and a container containing 50 g of the organic layer component of the APC BTM separator was placed in each of the containers, and each container was left for 7 hours, and the solubility of tar in each container was observed. The results are shown in image 3 middle. Specifically, in image 3 (a) shows a photograph showing a state in which 5 g of tar was immersed in a container containing 50 g of the side discharge stream of Example 1 and the container was left for 7 hours. image 3 (b) shows a photograph showing a state in which 5 g of tar was immersed in a container containing 50 g of acetone of Comparative Example 1 and the container was left for 7 hours. image 3 (c) shows a photograph showing a state in which 5 g of tar was immerse...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com