A kind of primer, probe and kit for identifying micrococcus based on isothermal amplification technology and its application
A technology of isothermal amplification and technical identification, applied in the field of environmental bacteria detection and identification, can solve the problems of high technical requirements, small identification range, unfavorable promotion, etc., and achieve the effects of high detection sensitivity, wide identification range, and strong promotion and application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Design of Micrococcus Specific Primers and Probes
[0075] Specific steps are as follows:
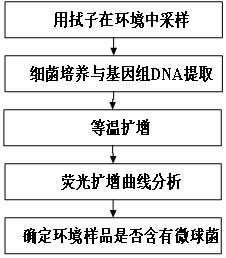
[0076] A. Collect environmental samples and separate environmental bacteria by streaking on a plate.
[0077] B. Sequence the genomic DNA of bacteria isolated from the environment with 16S rDNA universal primers, and determine the species of the isolated bacteria by sequence comparison.
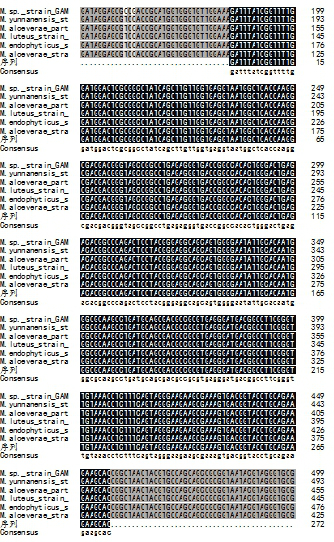
[0078] C. According to the 16S rDNA sequencing results of the isolated Micrococcus and the 16S rDNA gene sequences of Micrococcus yunnanensis, Micrococcus endophytes, Micrococcus luteus and other Micrococci in the NCBI database, design Micrococcus-specific primer pairs in the conserved region, primers The sequence is as follows:
[0079] F: 5'-GATTTATCGGTTTTGGATGGACTCGCGGCCTATC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1);
[0080] R: 5'-GTGCTTCTTCTGCAGGTACCGTCACTTTCGC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2);
[0081] D. The sequences of the amplified regions targeted by the primers were compared in NCBI, and the comparison results were al...
Embodiment 2
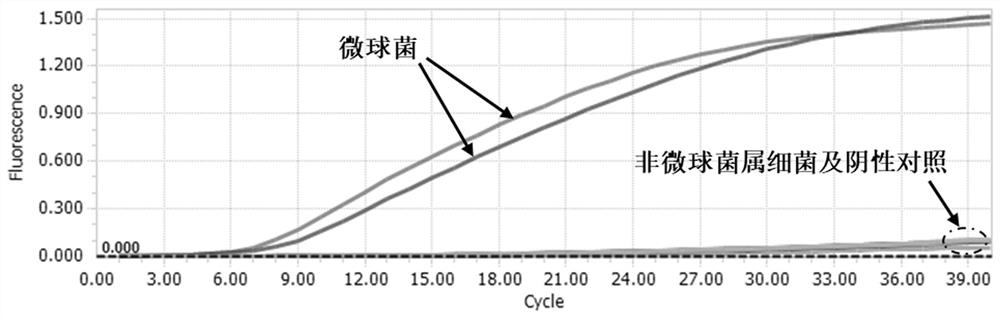
[0086] Specific detection of micrococci
[0087] A. Standard strains and bacteria of different genera isolated from the environment were shaken overnight.
[0088] Among them, the standard strains include Escherichia coli ATCC25922 (purchased from Microbiologics); Micrococcus luteus CMCC (B) 28001, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC15442, Bacillus cereus CMCC (B) 63303 (purchased from Beijing Biological Collection Center); Staphylococcus aureus NCTC8325, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC6538 (purchased from Shanghai Preservation Biotechnology Center).
[0089] Bacteria of different genera isolated from the environment include 2 strains of Staphylococcus (denoted as P-1, P-2), 1 strain of Pantoea (denoted as F-1), 1 strain of Bacillus (denoted as Y-1), 1 strain of Pseudomonas (denoted as J-1), 2 species of Micrococcus (denoted as W-1, W-2).
[0090] B. Extraction of bacterial genomic DNA from overnight cultures.
[0091] C. Genomic DNA of different bacteria is used as a template, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Sensitivity testing experiment
[0107] Specific steps are as follows:
[0108] A. Micrococcus luteus CMCC (B) 28001 and a micrococcus isolated from the environment (randomly selected from the micrococcus bacteria isolated from the environment) were shaken overnight.
[0109] B. Extraction of genomic DNA from overnight cultured micrococci.
[0110] C. Carry out 10-fold serial dilution to the extracted Micrococcus luteus and the Micrococcus genomic DNA isolated from the environment.
[0111] D. Perform isothermal amplification using micrococcal genomic DNA with different concentration gradients as a template, and collect fluorescence signals in real time (the negative control is ddH 2 O), wherein Micrococcus luteus 10 0 ~10 -5 The working concentration of each gradient genomic DNA was 13.7×10 0 ng / μL, 13.7×10 -1 ng / μL, 13.7×10 -2 ng / μL, 13.7×10 -3 ng / μL, 13.7×10 -4 ng / μL, 13.7×10 -5 ng / μL.
[0112] Environmental Micrococci (W-1) 100 ~10 -5 The working concent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com