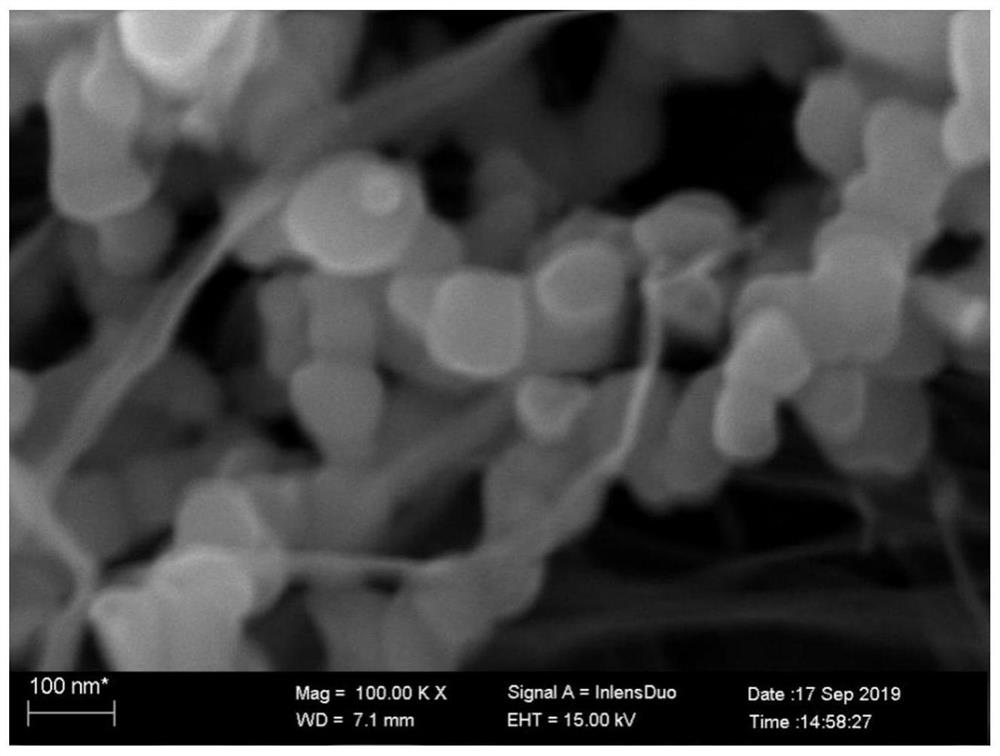
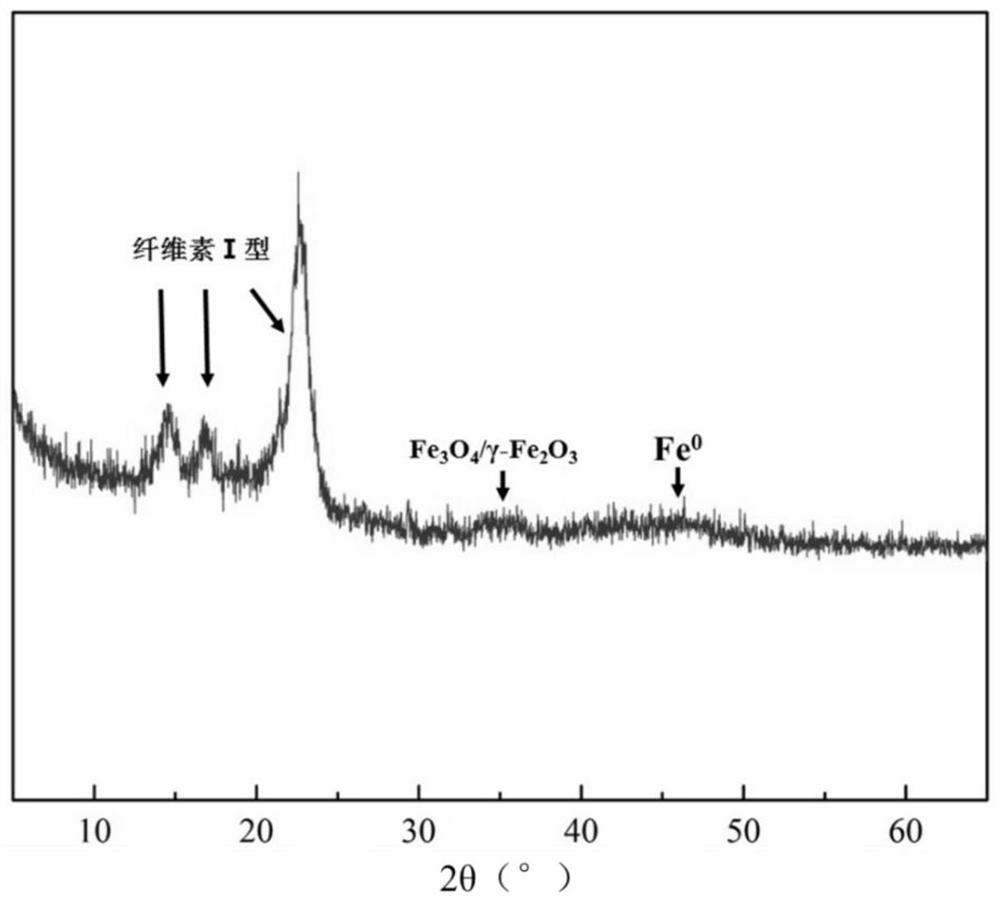
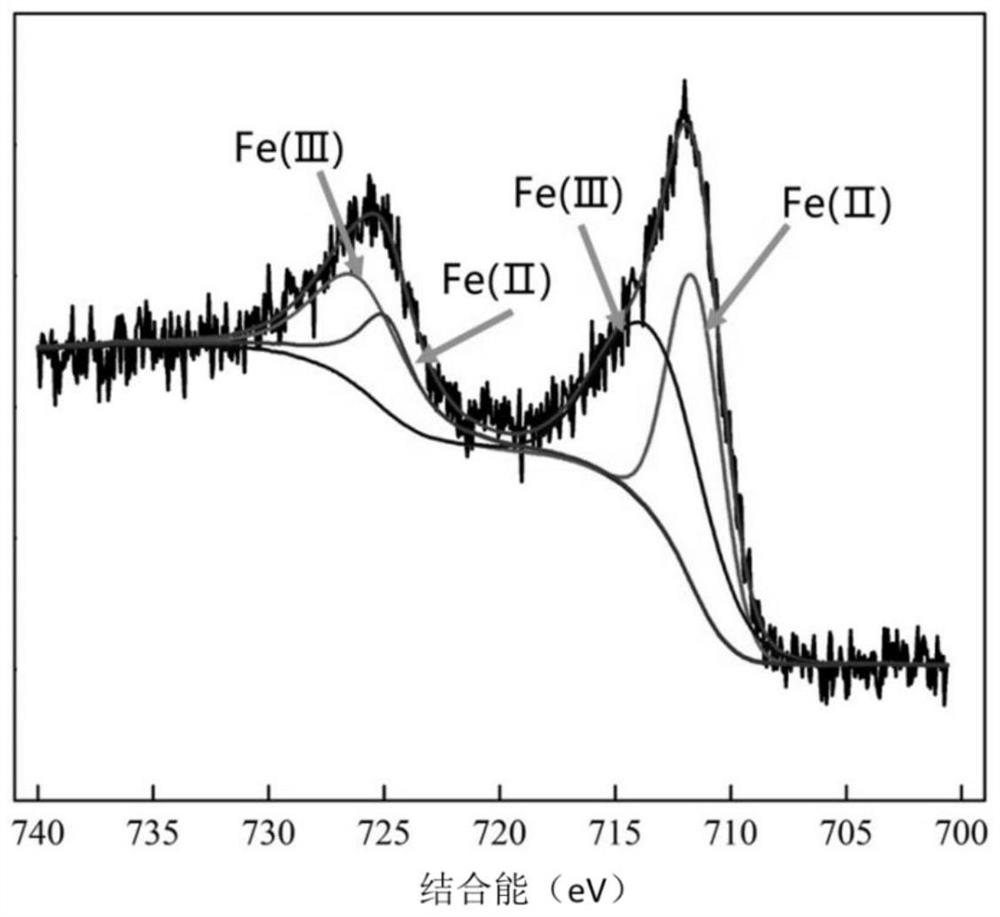
Bacterial cellulose membrane loaded nano zero-valent iron composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
A bacterial cellulose membrane, nano-zero valent iron technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, special treatment targets, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of no carcinogenicity, no biocompatibility, and improved anti-oxidation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0053] According to the present invention, the preparation method of the bacterial cellulose membrane-loaded nano-iron composite material comprises the following steps:
[0054] Step 1, cutting the bacterial cellulose membrane, and placing it in an alkaline solution at 60-90°C for activation treatment to obtain an activated-bacterial cellulose membrane;
[0055] Step 2, dehydrating the activated-bacterial cellulose membrane to obtain a semi-dehydrated-activated-bacterial cellulose membrane;
[0056] Step 3, placing the obtained semi-dehydration-activated-bacterial cellulose membrane in the ferrous salt solution, adding borohydride solution, and reacting;
[0057] Step 4, washing and drying the product obtained in step 3 to obtain the bacterial cellulose membrane-supported nano zero-valent iron composite material.
[0058] In the present invention, the type of bacterial cellulose is not particularly limited, it can be cellulose synthesized by conventional strains, for example,...
Embodiment 1
[0095] Use a mold to cut the bacterial cellulose membrane into discs of the same size D=24mm, place the obtained membranes in a container filled with 100ml of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 20g / L, and stir at 80°C for 1h , to obtain activated-bacterial cellulose membrane;
[0096] The activated-bacterial cellulose membrane is cleaned with ultrapure water until PH=7;
[0097] Then the gained activated-bacterial cellulose membrane is placed in a beaker containing 100ml of ethanol / water with a volume ratio of 7 / 3, the control stirring speed is 160 rpm, and continuous stirring for 1h; the membrane is taken out and blotted dry with filter paper, Add it into ethanol again and continue to stir and extract for 1h, and dry it with filter paper again to obtain a semi-dehydrated-activated-bacterial cellulose membrane;
[0098] Take 10 pieces of semi-dehydrated-activated-bacterial cellulose membranes and place them in a four-necked flask, feed nitrogen as a protec...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Use a mold to cut the bacterial cellulose membrane into discs of the same size D=24mm, place the resulting membrane in a container filled with 100ml of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 20g / L, and stir at 60°C for 2h , to obtain activated-bacterial cellulose membrane;
[0101] The activated-bacterial cellulose membrane is cleaned with ultrapure water until PH=7;
[0102] Then the gained activated-bacterial cellulose membrane is placed in a beaker containing 100ml of ethanol / water with a volume ratio of 7 / 3, the control stirring speed is 150 rpm, and continuous stirring for 1h; the membrane is taken out and blotted dry with filter paper, Add it into ethanol again and continue to stir and extract for 1h, and dry it with filter paper again to obtain a semi-dehydrated-activated-bacterial cellulose membrane;
[0103] Take 10 semi-dehydrated-activated-bacterial cellulose membranes and place them in a four-necked flask, feed nitrogen as a protective gas, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com