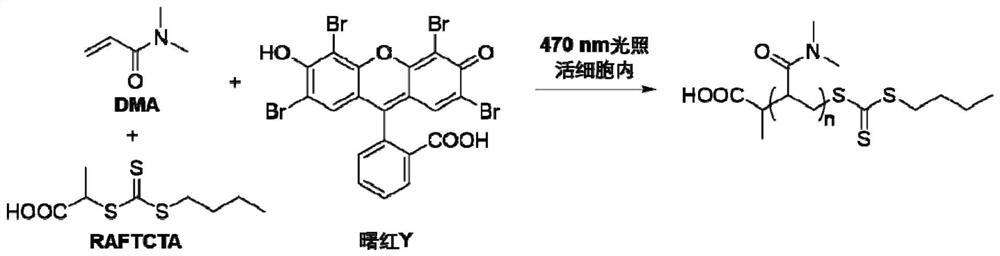
Method for inhibiting cell activity through intracellular polymerization and prodrug for implementing method
A technology of prodrugs and polymerization inhibition, which is applied in the direction of drug combination, organic active ingredients, antineoplastic drugs, etc., can solve the problems of low uptake efficiency, high molecular weight polymer molecule difficulty, and cell toxicity, etc., to reduce cell activity, Achieve highly controllable and selective effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Embodiment 1: RAFT chain transfer agent 2-(butylthiocarbonylthiothiolthio) propionic acid (RAFTCTA) synthetic steps
[0071] Within 30min, add 50mL THF solution containing 16.0g n-butanol dropwise to 150mL THF suspension containing 9.0g KOH, stir at room temperature for 30min, then add dropwise 50mL solution containing 17.0g CS 2 After stirring at room temperature for 24 hours, the THF solution was concentrated to 50 mL under reduced pressure. Under stirring, 50 mL of THF solution containing 22.4 g of n-propylammonium bromide was added dropwise to the above concentrated solution. After stirring at room temperature for 24 hours, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure to obtain the target crude product. The product was further purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain the target product as bright yellow crystals.
Embodiment 2
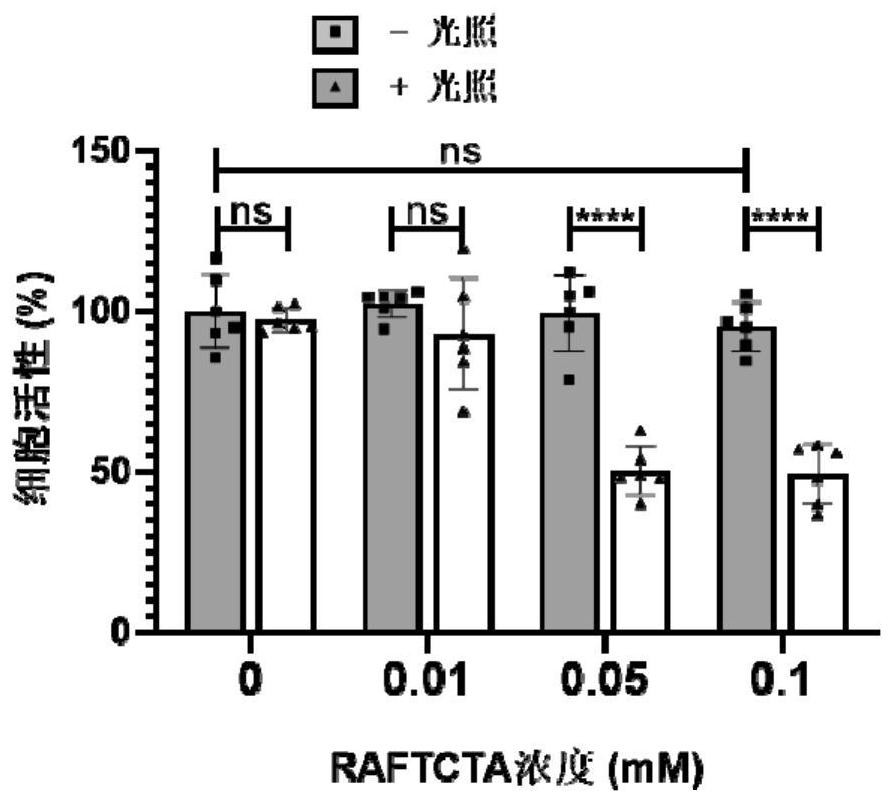
[0072] Example 2: CCK-8 test characterizes cell viability
[0073] In the CCK-8 test, HeLa cells were first treated with 1x 10 4 The density was inoculated in a 96-well cell culture plate and incubated at 37°C and 4% carbon dioxide for 18 hours at a constant temperature to ensure that the cells adhered to the wall; 2), and continue to incubate at constant temperature for 24 hours; after 24 hours, suck out the original medium and wash the cells with PBS for 3 times, add 100 μL of diluted CCK-8 solution (ratio to medium: 1:10) to each well, incubate at constant temperature for 4 hours and use The microplate reader detects the ultraviolet absorption at 450nm in each well, and compares the absorbance of the treated cells with the untreated cells to obtain the cell activity value.
Embodiment 3
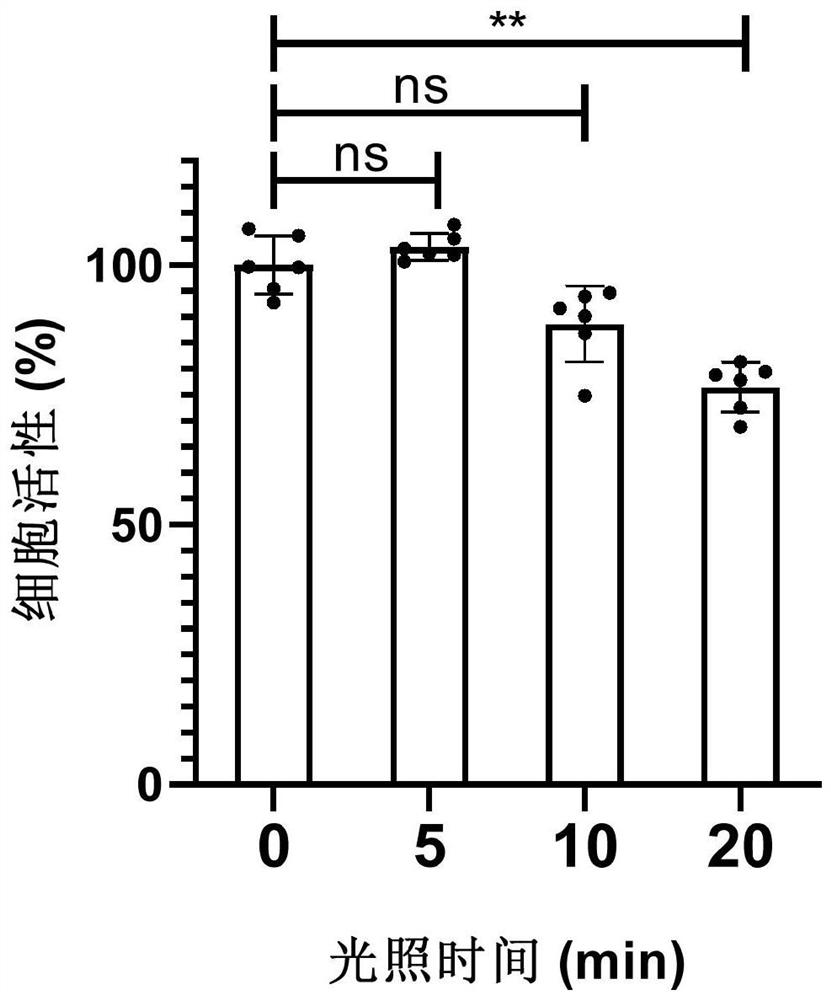
[0074] Example 3: Effects of 470nm illumination at different times on the activity of HeLa cells
[0075] HeLa cells at 1x 10 4 The densities were inoculated in three 96-well cell culture plates, and incubated at 37°C and 4% carbon dioxide for 18 hours at a constant temperature; then, 470nm LED blue light was irradiated vertically from the bottom of the three culture plates for 5, 10, and 20 minutes respectively.
[0076] Cell viability before and after light exposure can be quantitatively characterized by the CCK-8 assay as described above. (2-(2-Methoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2,4-disulfonic acid phenyl)-2H-tetrazole monosodium salt, It can be catalyzed and reduced by enzymes in the mitochondria of cells, and the amount of reduction is proportional to the number of cells, so it is widely used in the test of cell activity).
[0077] Such as figure 2 As shown, the cell viability remained above 88% after the cells were irradiated with blue light for 5-10 minutes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com