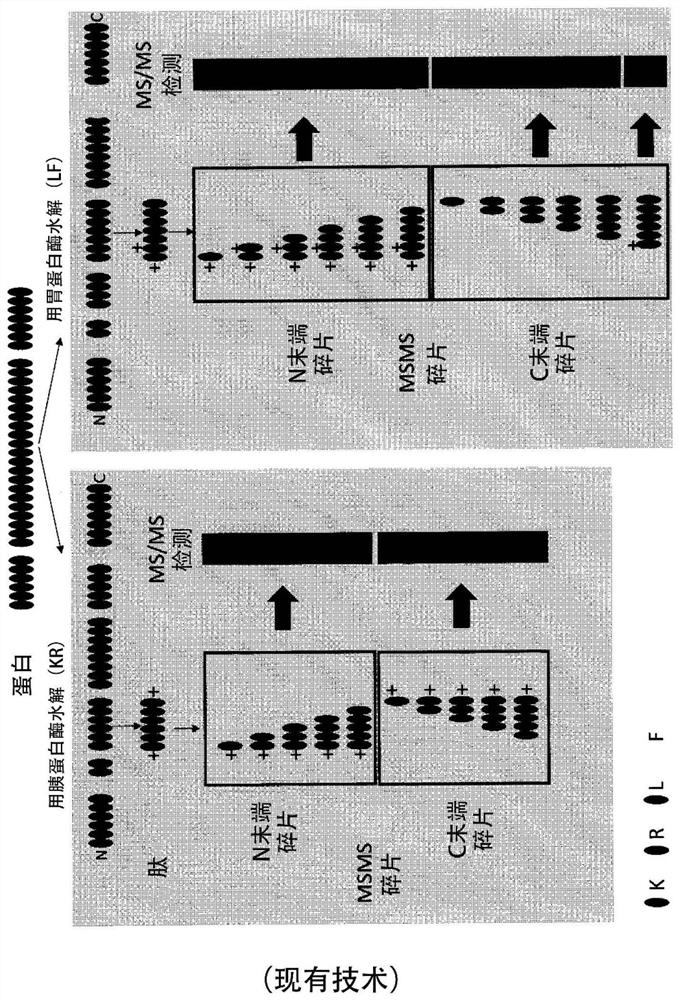
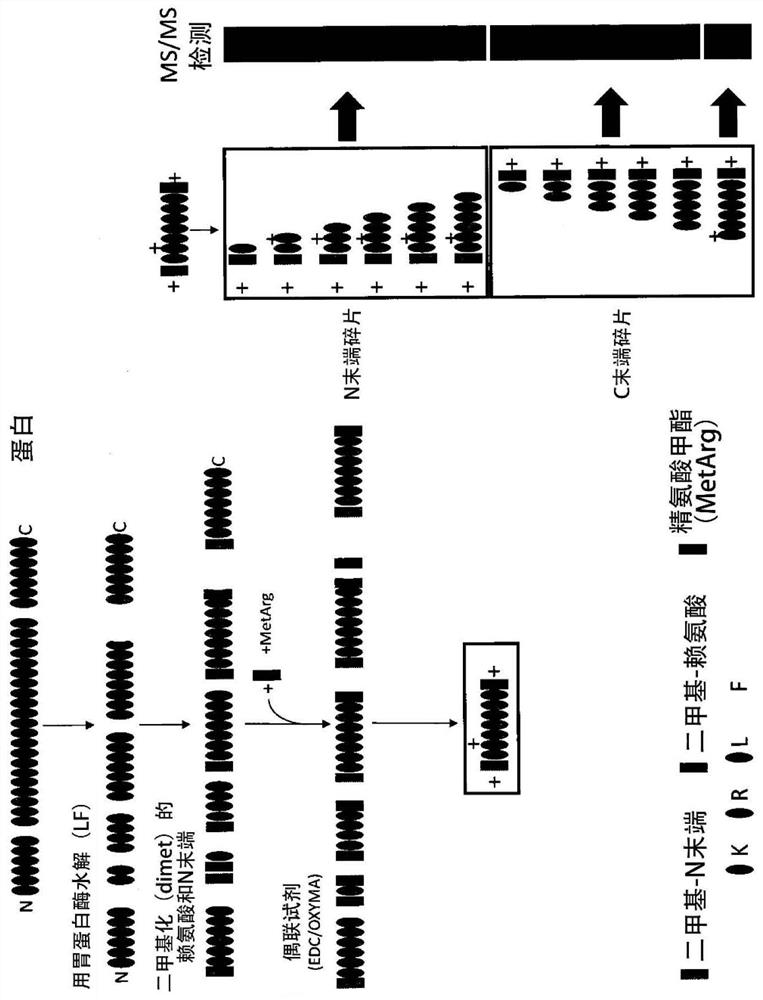
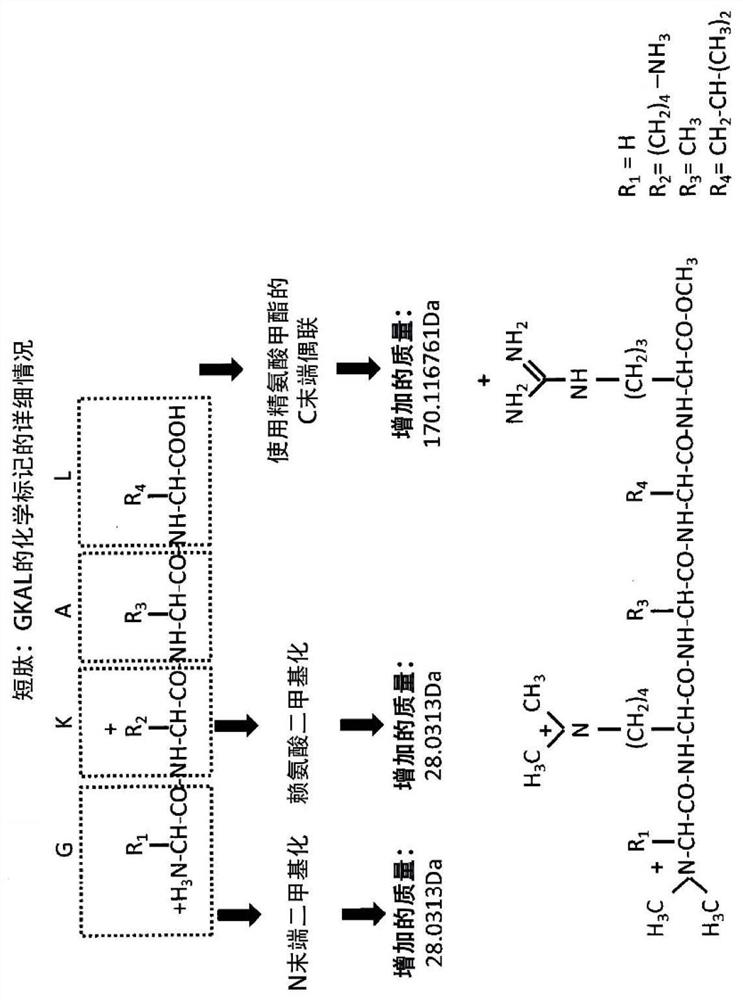
A labelling method to distinguish isobaric amino acids and amino acid combinations
An amino acid and glycine technology, which is applied in peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as strong sequence-specific deviations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0065] (I) Functional group analysis:
[0066] As discussed above, the types of functional groups that can be used in the described methods can vary as long as they can be coupled to free carboxyl groups of the peptide and have free basic groups. 3 different functional groups (molecules) were tested: 3-dimethylamino-1-propylamine (3-DMP), arginine methyl ester (MetArg) and dipeptide arginine-arginine-methyl ester (RR -omet).
[0067] In this example, using the coupling agent 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC), ethyl cyano (oximino) acetate (OXYMA) As an additive / enhancer, the coupling between the functional group and the peptide of interest is performed.
[0068] Using these reagents, any free carboxylic acid functionality will be derivatized, and thus the peptide C-terminal amino acid and any glutamic and aspartic acids in the peptide sequence will be coupled with: (a) if using MetArg, arginine Acid methyl ester - a mass gain of 170.116761 Da (4N 7C 14H 1...
Embodiment 3
[0084] C-terminal tagging procedure using PyAOP
[0085] The overall procedure provided below was applied to 10 ug of peptides produced from pepsin hydrolysis.
[0086] 1. Blocking of lysines and peptide N-termini: this was not done because the amine marker was added in molar excess compared to the amine from the peptide reagents, thus significantly reducing the chance of peptide-peptide coupling.
[0087] 2. C-terminal coupling reaction: Prepared as follows Amine solution : Dissolve 100 mg methyl ester arginine (MetArg) in 50 ul water and 26 ul 4-methylmorpholine (NMM). A coupling solution was prepared as follows: 66mg of 7-azabenzotriazol-1-yloxy)tripyrrolidinphosphonium hexafluorophosphate (PyAOP) was dissolved in 145ul of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). Add 10ul DMSO to dry 10ug peptide, then add 14ul Amine solution and 6ul Coupling solution . The reaction was carried out overnight at room temperature.
[0088] 3. Reaction quenching and sample cleanup: 50ul TFA and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com