Mycoplasma bovis Mbov0701 mutant gene as well as mutant strain and application thereof
A technology of mycoplasma bovis and mutant genes, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problem of lack of specific prevention and control methods for mycoplasma bovis disease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Screening and Identification of Mycoplasma bovis Growth Deficiency Mutant
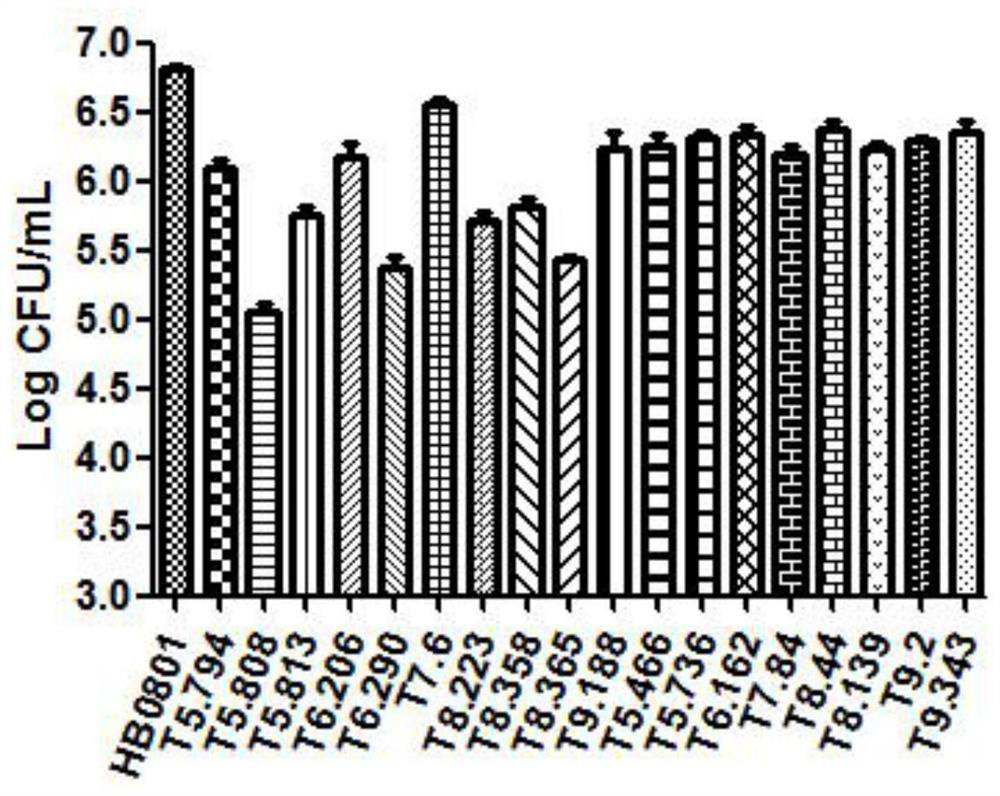
[0026] Using the cell co-culture growth defect experimental model constructed by the Ruminant Pathogen Branch of the State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, Huazhong Agricultural University, EBL cells were divided into 4×10 4 cell / cm 2 Spread them on a 24-well cell culture plate, and inoculate the 18 strains of mutants that were screened into EBL cells with an infection ratio of 0.5, and set the wild strain HB0801 as a positive control. The mutants were co-cultured with EBL cells in a 37°C carbon dioxide incubator for 72 hours. Cells were lysed after one freeze-thaw cycle (-80°C / 37°C), and the colony count of 18 mutant strains was quantitatively determined by colony counting method. The result is as figure 1 As shown, the T5.808 mutant strain showed a significant growth defect phenotype.
[0027] Using the bacterial genome extraction kit (purchased from Bao Bioengineerin...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The detection of the growth curve of embodiment 2 Mycoplasma bovis growth defect mutant
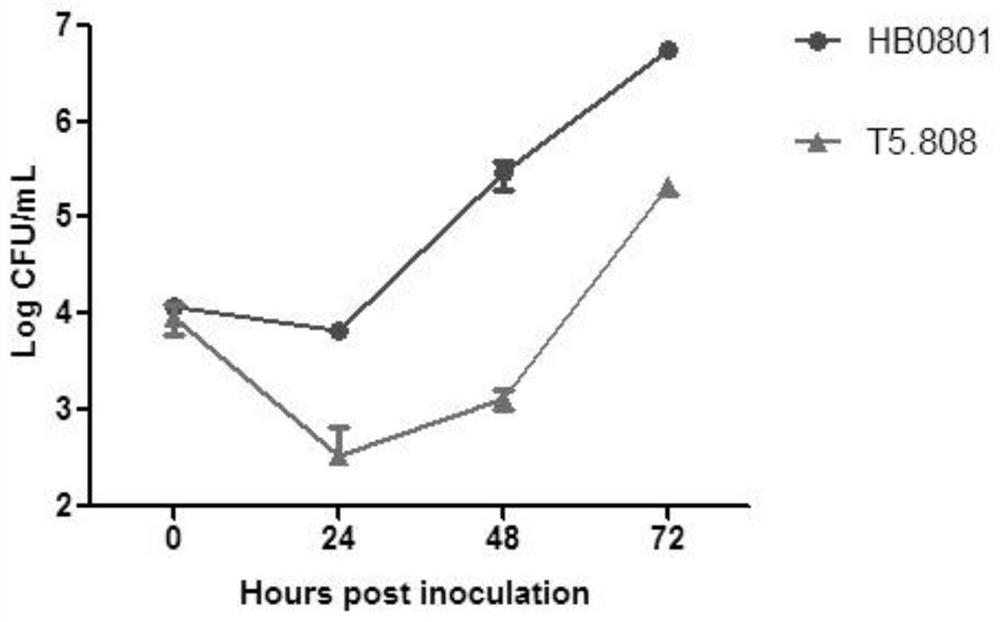
[0029] 1. Detection of the growth curve of Mycoplasma bovis in EBL cells
[0030] (1) Mycoplasma bovis cultivation and counting: Take Mycoplasma bovis HB0801 and T5.808 and inoculate them in PPLO liquid medium at a ratio of 1:1000 respectively, at 37°C, 5% CO 2 After standing in the incubator for 36 hours and reaching the end of the logarithm, count the CFU. The cultured bacterial solution is about to be diluted 10-fold, and 10 μL of the appropriate dilution of the bacterial solution is applied to the PPLO solid medium, and placed upside down at 37°C, 5% CO 2 After culturing in the incubator for 37 days, count the colonies under a stereomicroscope. The formula for calculating the number of colonies is: CFU / mL=number of colonies×dilution×100.
[0031] (2) EBL cell culture and counting: EBL cells were cultured in MEM complete medium (that is, MEM medium containing 10% heat-inactiva...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Morphological observation of embodiment 3 Mycoplasma bovis co-culture growth defect mutant
[0038] (1) Microscopically observe the colony morphology of Mycoplasma bovis
[0039] Dilute the Mycoplasma bovis HB0801 and T5.808 strains that have been cultured to the end of the logarithm, respectively, and spread them on PPLO solid medium. After culturing for 37 days in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37°C, observe the bovine strains under a stereomicroscope. The colony morphology of mycoplasma, the results showed that the colony of the T5.808 mutant strain was smaller than that of the HB0801 strain, and the morphology changed significantly, such as Figure 5 shown.
[0040] (2) Determination of the colony area of Mycoplasma bovis
[0041] The areas of 50 colonies of the wild strain HB0801 and the mutant strain T5.808 were measured respectively. The results showed that the colony area of the mutant strain T5.808 was significantly reduced compared with the colony area of the w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com