Negative electrode material, negative electrode slurry, battery cell, fast charging battery and preparation method thereof
A negative electrode material and negative electrode slurry technology, which is applied in negative electrodes, battery electrodes, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as poor kinetic performance, uneven distribution, and uneven current density distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] A preparation method for a fast charging battery, comprising the steps of:
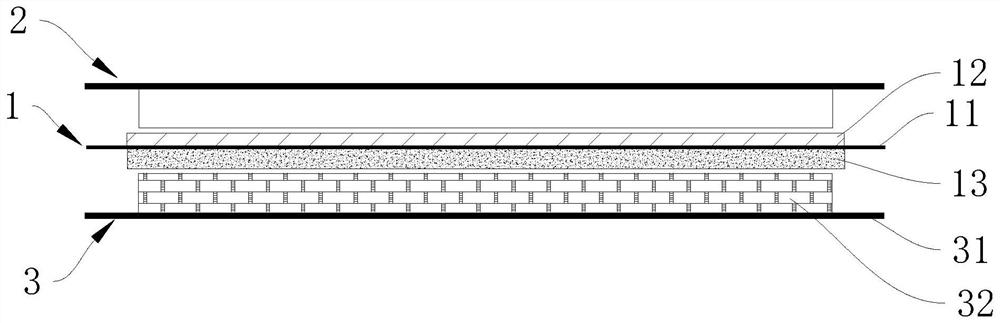
[0050] a, preparing positive electrode sheet 2, separator 1 and negative electrode sheet 3;
[0051] b. Stack the positive electrode sheet 2, the separator 1 and the negative electrode sheet 3 in sequence, and use a laminated structure to make a cell;
[0052] c. Weld the positive pole lug on the positive pole piece 2, and weld the negative pole pole lug on the negative pole piece 3;
[0053] d. Put the battery cell prepared in step b into the casing, perform ultrasonic welding, electrolyte injection, formation and volume separation in sequence to obtain a fast charging battery.
[0054] Specifically, the preparation of the negative electrode sheet 3 in step a includes the following steps:
[0055] A1, add deionized water in the stirrer;
[0056] A2. Add the first binder and stir until the first binder is completely dissolved; the first binder is preferably PVDF, 6020, etc.;
[0057] A3. Ad...
Embodiment 1
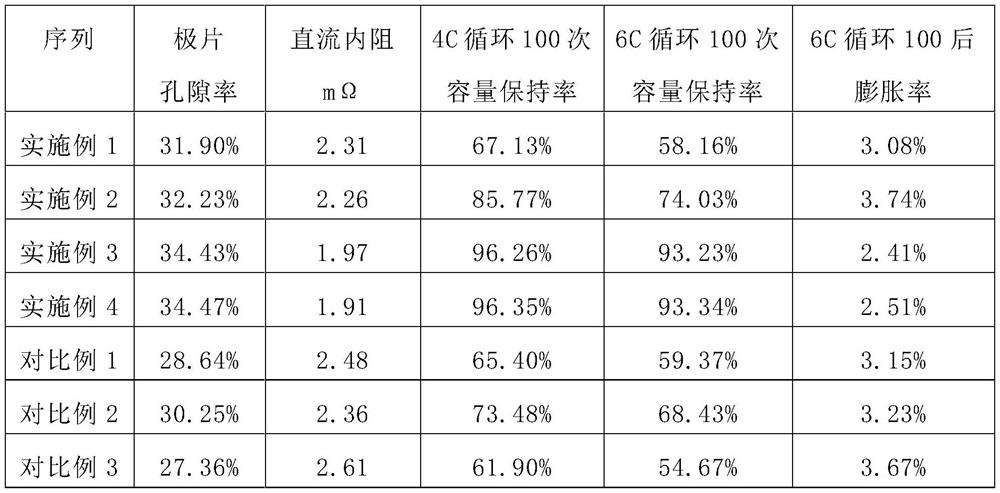
[0075] In this embodiment, in the positive electrode slurry, the weight ratio of the positive electrode active material, the fourth binder and the second conductive agent is 96.5%: 1.3%: 2.2%, wherein the fourth binder uses PVDF, and the second conductive agent The agent adopts SP. In the negative electrode slurry, the weight ratio of the negative electrode active material, the first binder and the first conductive agent is 96%: 2.5%: 1.5%, wherein the first binder uses PVDF, the first conductive agent uses SP, and the negative electrode The weight ratio of the hard carbon in the active material is 25%, and the inorganic solid electrolyte is 5% of the weight of the hard carbon. The weight ratio of the lithium salt in the first diaphragm coating 12 is 97%, the weight ratio of the binding agent is 3%, and the weight ratio of the inorganic solid electrolyte (lithium lanthanum zirconium oxide) in the second diaphragm coating 13 is 97%. The weight ratio of binder is 3%.
Embodiment 2
[0077] In this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that in the positive electrode slurry, the weight ratio of the positive electrode active material, the fourth binder and the second conductive agent is 97%:1.0%:2.0%. In the negative electrode slurry, the weight ratio of the negative electrode active material, the first binding agent and the first conductive agent is 98.5%: 1.0%: 0.5%, the weight ratio of hard carbon in the negative electrode active material is 50%, and the inorganic solid electrolyte is hard carbon. 10% by weight of carbon. The weight ratio of the lithium salt in the first diaphragm coating 12 is 98%, the weight ratio of the binding agent is 2%, and the weight ratio of the inorganic solid electrolyte (aluminum lithium germanium phosphorus) in the second diaphragm coating 13 is 98%, and the adhesive The weight ratio of binder is 2%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com