Method for recovering and separating lanthanum, neodymium and ytterbium from dicranopteris pedata
A technology for hyper-enrichment of plants and rare earths, applied in the field of neodymium, recovery and separation of lanthanum and ytterbium, which can solve the problems of inability to separate different types of rare earth elements, secondary pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
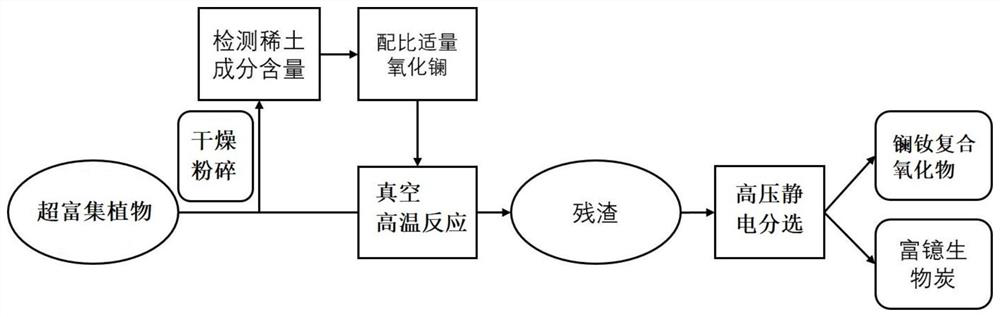
[0032] Embodiment 1 A kind of method that reclaims and separates lanthanum, neodymium, ytterbium from Osmanthus osmanthus
[0033] S1. In a rare earth tailings sand field in Ganzhou, Jiangxi, plant the super-enrichment plant Osmanthus osmanthus, collect the mature leaves and necrotic leaves of Osmanthus per hectare during the growth process, and dry them. The dried plants are placed in a shearing machine. Broken in the crusher to obtain uniform Osmanthus leaf powder;
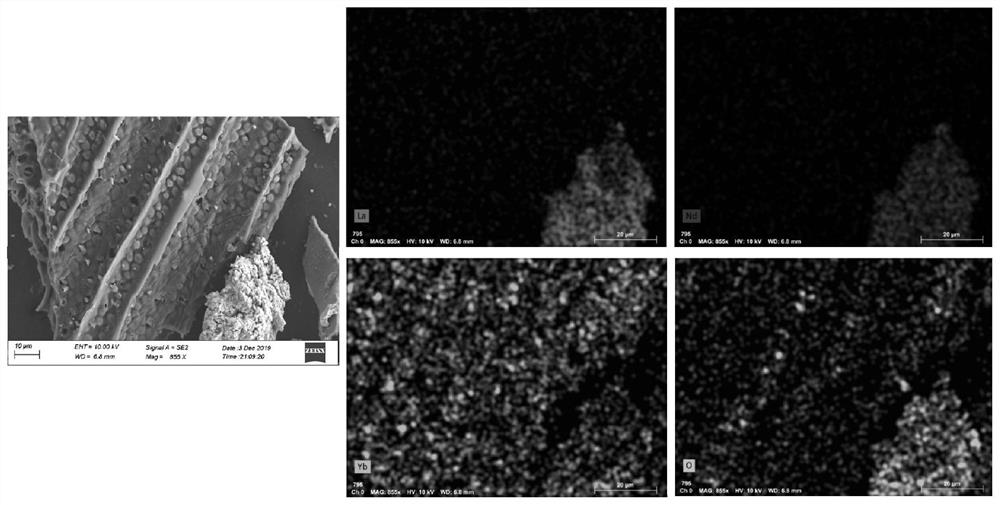
[0034] S2, get 10g of Osmanthus fragrans leaf powder obtained in step S1 and carry out microwave digestion, adopt ICP-MS to measure the content of lanthanum, neodymium, and ytterbium element in the blade, obtain lanthanum, neodymium content and be respectively 2233ug / L, 1072ug / L, according to The total amount of lanthanum and neodymium contained in Osmunda: the molar ratio of lanthanum oxide is 1:2, add lanthanum oxide powder with a particle size of 20um to the remaining Osmanthus frondosa leaf powder, shake and...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2 A kind of method of reclaiming and separating lanthanum, neodymium, ytterbium from Pokeweed
[0040] S1. Plant the super-accumulator pokeweed plant in a rare earth tailings sand field in Ganzhou, Jiangxi, collect the mature leaves and necrotic leaves of pokeweed per hectare during the growth process, and dry them. The dried plants are placed in shears. Crushing in a cutter crusher to obtain uniform pokeweed leaf powder;
[0041] S2, get 10g of Pokeweed leaf powder obtained in step S1 and carry out microwave digestion, adopt ICP-MS to measure the lanthanum, neodymium, and ytterbium element content in the leaf, obtain lanthanum, neodymium content and be respectively 2085ug / L, 1264ug / L, According to the total amount of lanthanum and neodymium contained in pokeweed: the molar ratio of lanthanum oxide is 1:2, add lanthanum oxide powder with a particle size of 20um to the remaining pokeweed leaf powder, oscillate and mix evenly, and obtain a mixed powder;
[004...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 A kind of method that reclaims and separates lanthanum, neodymium, ytterbium from crescent fern
[0046] S1. Plant the super-accumulative plant Crescent fern in a rare earth tailings sandy land in Ganzhou, Jiangxi, collect the mature leaves and necrotic leaves of Crescent fern per hectare during the growth process, and dry them. The plant is placed in a shear crusher and crushed to obtain uniform crescent fern leaf powder;
[0047] S2, get step S1 gained crescent fern blade powder 10g and carry out microwave digestion, adopt ICP-MS to measure the lanthanum, neodymium, ytterbium element content in the blade, obtain lanthanum, neodymium content and be respectively 1854ug / L, 976ug / L According to the total amount of lanthanum and neodymium contained in Crescent fern: the molar ratio of lanthanum oxide is 1:2, add lanthanum oxide powder with a particle size of 20um to the remaining Crescent fern leaf powder, shake and mix evenly, and obtain a mixed powder;
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com