Novel depside dimeric compounds for skeletal muscle modulation, methods and uses thereof
A compound, the technology of depsidic acid, applied in the field of novel depsidic acid dimerization compounds, can solve the problem of low regeneration potential of myoblasts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0247] Example 1: Selection of compounds that modulate muscle stem cells
[0248] Selection of human skeletal muscle myoblasts
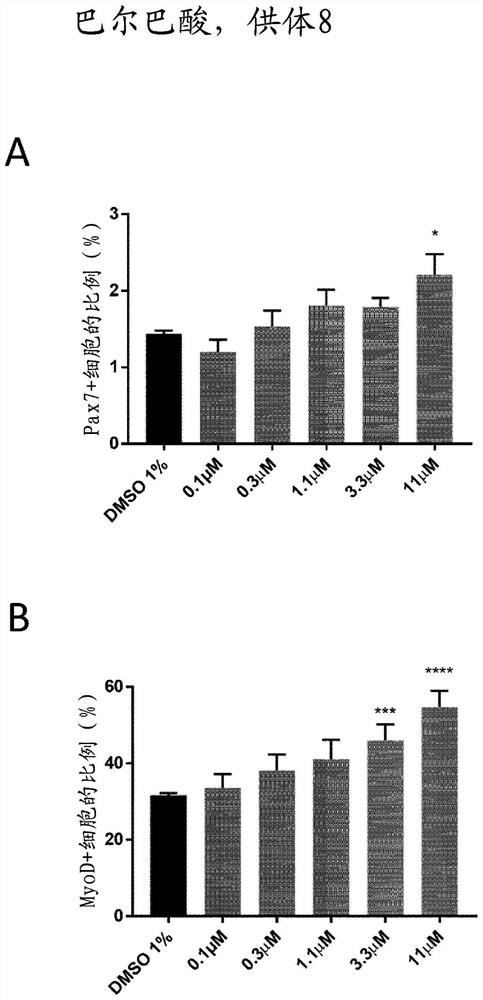
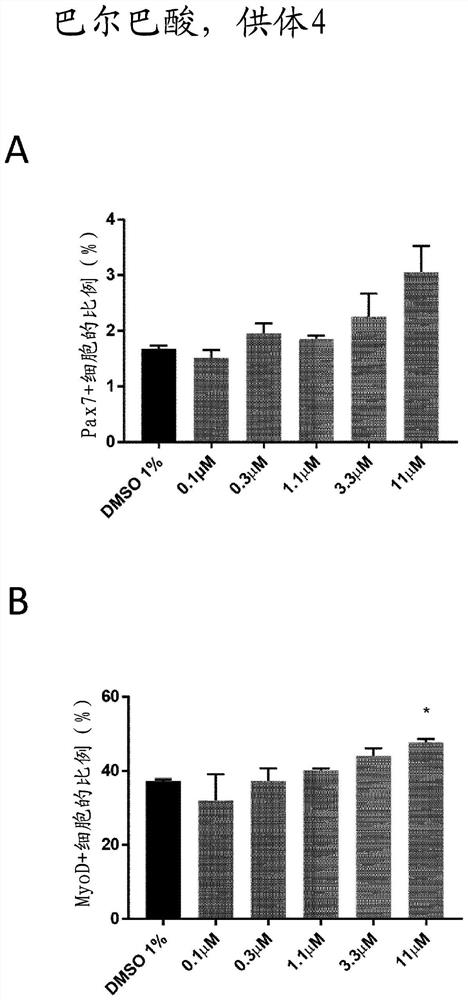
[0249] The inventors developed a high content screen to test compounds on primary human adult muscle cells in vitro. Human skeletal muscle myoblasts (HSMM) were purchased from Lonza ( https: / / bioscience.lonza.com ). These cells were isolated from normal donor upper arm or leg muscle tissue and used after a second passage. Several donors were tested to ensure cell viability and purity before selecting the final donors who were a 36-year-old Caucasian female (Donor 8) and a 20-year-old Caucasian female (Donor 4).
[0250] Muscle Stem Cell Commitment Assay
[0251] The primary screening assay was based on the detection of high levels of two important myogenic regulators (Pax7 and MyoD) by immunofluorescence. Pax7 and MyoD are major markers of stemness and commitment of muscle stem cells and can be used to monitor muscle stem ce...
Embodiment 2
[0254] Example 2: Myoblast Differentiation Assay
[0255] Human primary myoblasts from two different donors (Donor 8 and Donor 4) were seeded at a density of 3'000 cells per well in 384-well plates in Skeletal Muscle Growth Medium (SKM-M , AMSbio). One day later, differentiation was induced by medium exchange. For treatment, compounds were added directly to myoblast cultures for 96 hours. Myotubes were stained with an antibody against Troponin T to determine Troponin T expression and counterstained with Hoechst 33342 to visualize nuclei. Image acquisition was performed using the ImageXpress (Molecular Devices) platform. Quantification was performed using a custom module analysis based on MetaXpress software for multiwavelength cytoscoring. For each condition, the number of cells was counted to control for compound toxicity, and myotubes were characterized by several readouts in order to assess the level of differentiation and their morphology.
[0256] image 3 - Saf...
Embodiment 4
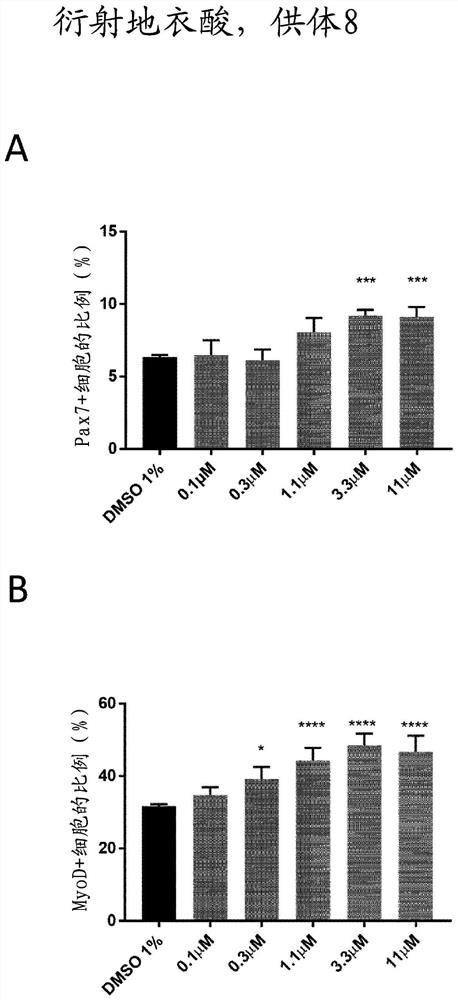
[0258] Example 4: Diffractive lichenic acid can promote muscle regeneration process in vivo
[0259] To recapitulate the physiological process of muscle regeneration in adult skeletal muscle in response to injury or disease, we injected cardiotoxin intramuscularly into mouse hindlimb muscles. One week before induction of muscle damage, diffracted lichenic acid (100 mg / kg body weight) was administered to mice by oral gavage relative to the water control group. Mice were handled once a day until the end of the experiment. To assess the efficiency of muscle regeneration, previously injured muscles were harvested 5 days after injury and cryosections were prepared. Several myogenic markers are then measured. Cryosections were stained with specific antibodies against Pax7, myogenin, laminin, and embryonic myosin heavy chain (eMHC) expression and counterstained with Hoechst33342 to visualize nuclei. Diffractive lichenic acid is able to promote the process of muscle regeneration ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com