Electroplating heavy metal ion back-bath sodium removing process
A technology of heavy metal ions and electroplating process, which is applied in the direction of ion exchange water/sewage treatment, electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc. It can solve the problems of poor corrosion resistance, loose coating, affecting the quality of electroplating coating, etc., and achieve low free acid content , the effect of low sodium ion content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
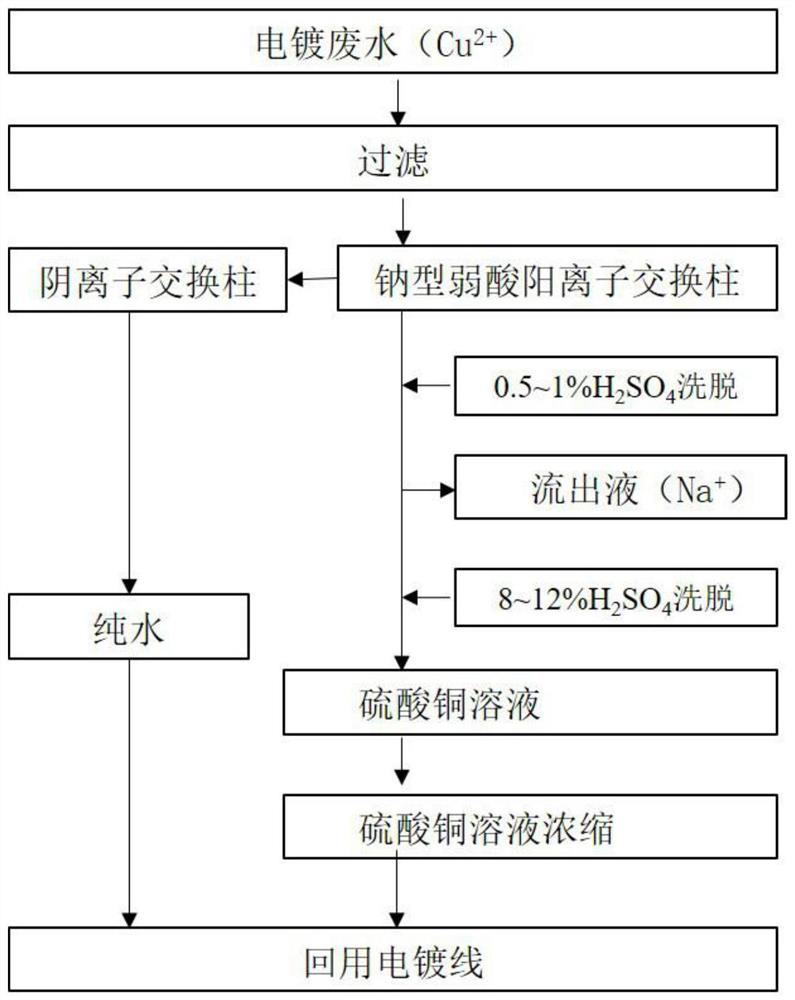
[0012] This embodiment relates to a process for removing sodium from electroplating heavy metal ions back into the tank, comprising the following steps: collecting copper-containing rinsing wastewater from the electroplating production line, Cu 2+ Concentration 102mg / L, after filtration, Cu 2+ The wastewater ions enter the 110 sodium type weakly acidic cation exchange resin column for ion exchange, and the sodium type weakly acidic cation exchange resin column is saturated to adsorb Cu 2+ After ions are cleaned, first dilute with 0.75% H 2 SO 4 Countercurrent elution was performed as the eluent, the elution volume was 1.75 times the column volume, and the elution rate was 0.65 times the column volume / h; after that, 10% H 2 SO 4 For the countercurrent elution of the eluent, the elution flow rate volume is 2.5 times the column volume / h, and the Cu-containing 2+ The ion effluent is concentrated and returned to the electroplating process line for use.
[0013] Cu in this exam...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The present embodiment specifically comprises the following steps: collecting nickel-containing rinsing waste water from the electroplating production line, Ni 2+ Concentration 118mg / L, after filtration, Ni 2+ The waste water enters the 116 sodium type weakly acidic cation exchange resin column for ion exchange, and the 116 sodium type weakly acidic cation exchange resin column is saturated to adsorb Ni 2+ After ions are cleaned, first dilute with 0.5% H 2 SO 4 Countercurrent elution was performed as the eluent, the elution volume was 1.5 times the column volume, and the elution rate was 0.5 times the column volume / h; after that, 10% H 2 SO 4 For the countercurrent elution of the eluent, the elution flow rate volume is 2 times the column volume / h, and the Ni-containing 2+ The ion effluent is concentrated and returned to the electroplating process line for use.
[0025] Ni in this example 2+ Ionic effluent, Ni 2+ Concentration 30g / L, Na + <1mg / L, pH 6.5.
Embodiment 3
[0033] This embodiment specifically includes the following steps: collecting zinc-containing rinsing wastewater from the electroplating production line, Zn 2+ Concentration 121mg / L, after filtration, Zn 2+ The ionic wastewater enters the D152 sodium type weakly acidic cation exchange resin column for ion exchange, and the D152 sodium type weakly acidic cation exchange resin column is saturated to adsorb Zn 2+ After ion cleaning, first dilute with 1% H 2 SO 4 Countercurrent elution was performed as the eluent, the elution volume was 2 times the column volume, and the elution rate was 0.75 times the column volume / h; after that, 10% H 2 SO 4 For the countercurrent elution of the eluent, the elution flow rate volume is 3 times the column volume / h, and the collected Zn-containing 2+ The ion effluent is concentrated and returned to the electroplating process line for use.
[0034] In this example Zn 2+ Ionic effluent, Zn 2+ Concentration 31g / L, Na + <1mg / L, pH 6.5.
[0035]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com