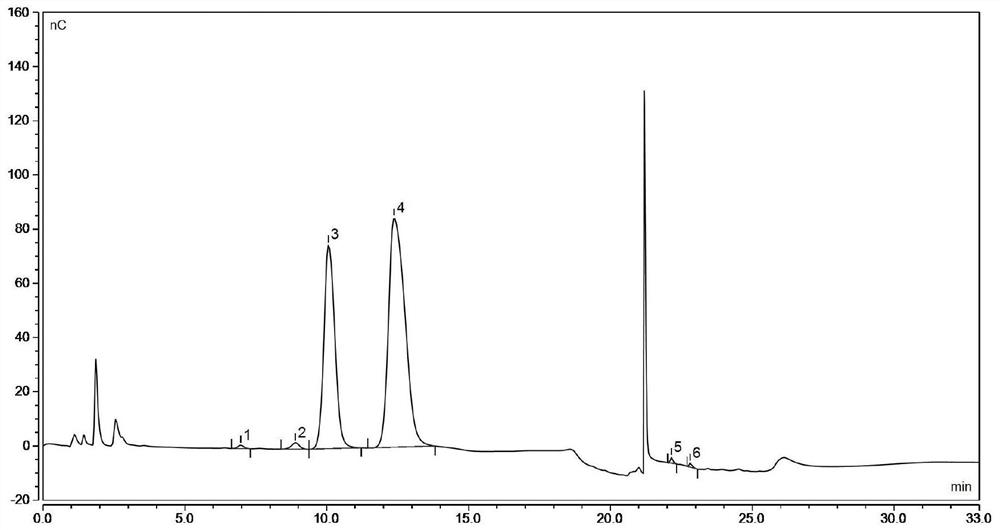
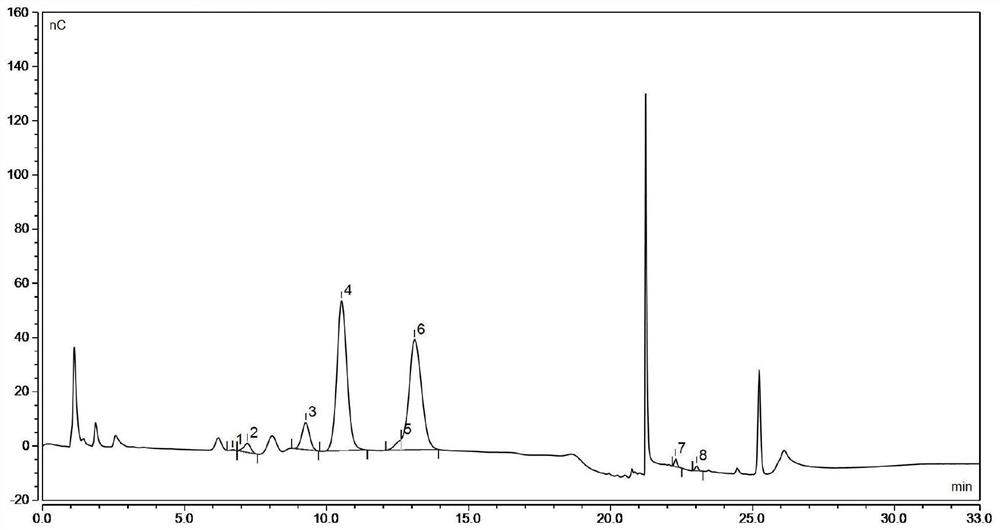
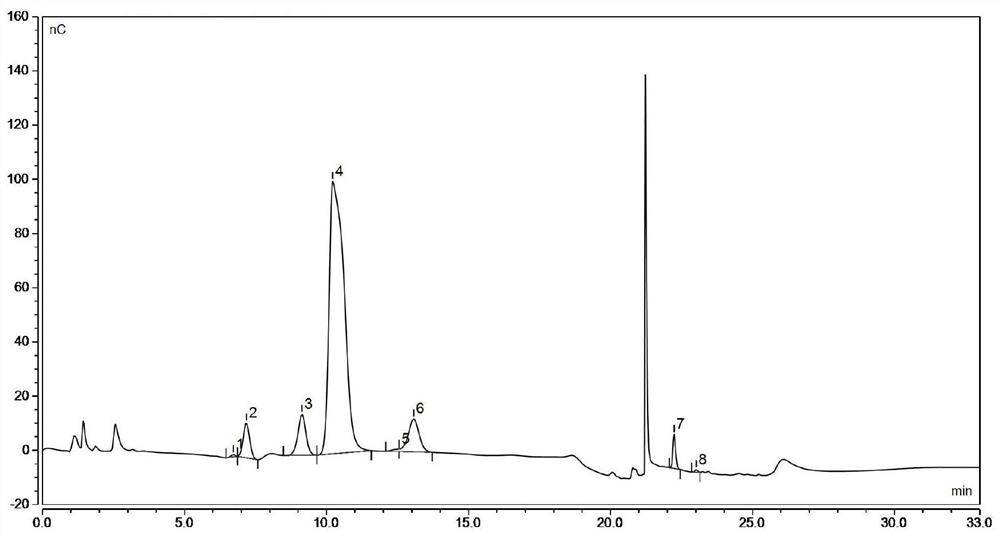
Bacillus subtilis for improving yield of traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharide and regulating skin barrier and immunity
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and traditional Chinese medicine, applied in the direction of skin diseases, bacteria, drug combination, etc., to reduce NO content and improve cell survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Embodiment 1: Screening and identification of strains
[0065] Specific steps are as follows:
[0066] 1. Screening
[0067] The sample comes from kimchi in Lijiang, Yunnan. After pretreatment, the sample is stored in 20% glycerol in a -80°C refrigerator. After taking out and thawing, mix well and add 0.5mL sample to 4.5mL normal saline to contain 9g / L normal saline for gradient dilution, select the appropriate gradient dilution and spread it on the LB solid medium, culture at 37°C for 48 hours, pick the typical colony of Bacillus subtilis to streak and purify on the LB solid medium, and pick a single colony Transferred to LB liquid medium for enrichment and preserved in 30% glycerol to obtain a strain named CCFM1162; wherein, the typical colony of Bacillus subtilis presents a rough and opaque surface, stained white or yellowish.
[0068] 2. Identification
[0069] The genome of the bacterial strain CCFM1162 was extracted, the 16S rDNA of the bacterial strain CCFM11...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The extraction of embodiment 2 dendrobium crude polysaccharides
[0071] Specific steps are as follows:
[0072] (1) Preparation of Dendrobium raw material fermentation medium: Mix 40g / L Dendrobium raw material, 10g / L yeast extract powder and 10g / L NaCl evenly, add purified water to make up the volume, adjust the pH value to 7.0, and heat at 115°C for 20min to extinguish bacteria;
[0073] (2) Preparation of dendrobium raw material fermentation broth: cool the dendrobium raw material fermentation medium in step (1) to below 40°C, and in a sterile environment, add 1 × 10 to the dendrobium raw material fermentation medium 6 The amount of cfu / mL was added to Bacillus subtilis CCFM1162, and fermented at a constant temperature and pH value of 7.0 at a temperature of 37°C and a pH value of 7.0 for 15-16 hours. At this time, the number of viable bacteria reached ≥10 9 cfu / mL; continue to ferment for 24 hours, reach the end of fermentation, and obtain the raw material ferment...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The extraction of embodiment 3 astragalus crude polysaccharides
[0078] Specific steps are as follows:
[0079] (1) Prepare astragalus raw material fermentation medium: mix 80g / L astragalus raw material, 10g / L yeast extract powder and 10g / LNaCl evenly, add purified water to constant volume, adjust pH value to 7.0, and heat at 115°C for 20min to kill bacteria;
[0080] (2) Preparation of astragalus raw material fermentation broth: cool the sterilized astragalus raw material fermentation medium in step (1) to below 40°C, and in a sterile environment, add 1×10 6 The amount of cfu / mL was added to Bacillus subtilis CCFM1162, and fermented at a constant temperature and pH value of 7.0 at a temperature of 37°C and a pH value of 7.0 for 15-16 hours. At this time, the number of viable bacteria reached ≥10 9 cfu / mL; continue to ferment for 24 hours, reach the end of fermentation, and obtain astragalus raw material fermentation liquid.
[0081] (3) Extracting astragalus polysa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com