Single-base editing tool TaC9-ABE and application thereof
A single-base, tac9-abe technology, applied in the field of gene editing, can solve the problems of limited selection of target sites, reduced deaminase efficiency, and narrowed targeting range, so as to reduce DNA off-target problems and increase recognition specificity Sexuality, the effect of increasing operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
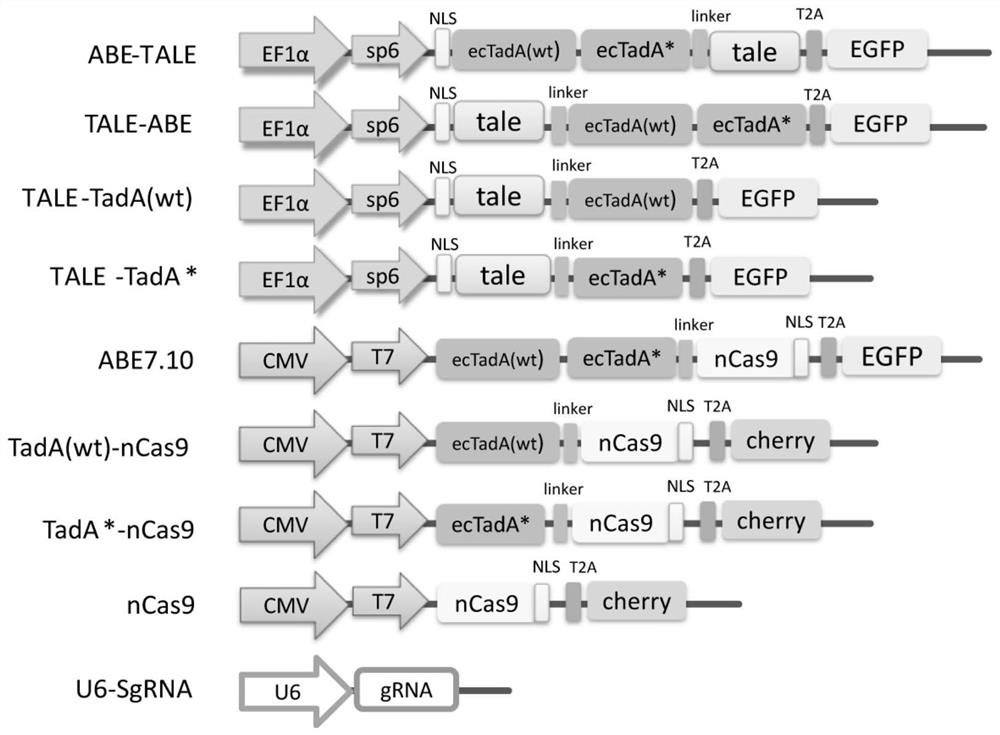
[0070] Example 1 TaC9-ABE plasmid design and construction
[0071] (1) Design two-component plasmids
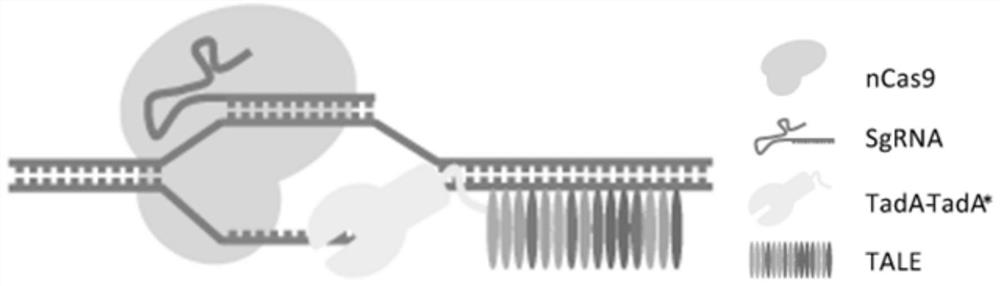
[0072] In this example, the combination of sgRNA and TALE system for site-specific recognition, nCas9 opening double strands and repairing after single strand cutting, and adenosine deaminase converting A to G was used for single-base genome editing.
[0073] Such as figure 1 As shown, the adenosine deaminase is designed at the N-terminus of the TALE recognition region, leading the adenosine deaminase close to the target editing site while the specific recognition protein binds to the target sequence located downstream of the target site, while sgRNA and nCas9 The formed riboprotein complex binds to the target site to open the DNA double helix, which facilitates the function of the single-stranded base editing protein adenosine deaminase, and completes the sgRNA targeting range 4-8 under the combination of two-component gene editing tools The base A within the position is c...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Example 2 examines the effects of different combination types on editing efficiency.
[0102] In order to compare the effects of different combinations and spatial positions of deaminase components connecting TALE and nCas9 on the editing effect, in this example, plasmids with different combinations were transfected to test the AAVS1 site.
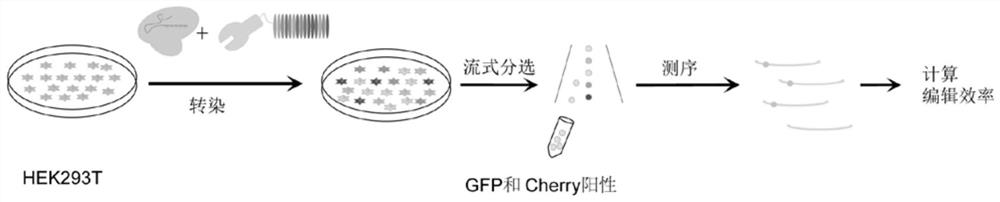
[0103] The specific operation steps are as image 3 shown, including:
[0104] Transfect the plasmid into HEK 293T cells with a density of about 70%-80% using liposome transfection reagent, change the medium for 12 hours after transfection, and perform flow sorting after three days of culture;
[0105] Cells expressing the green fluorescent protein EGFP and the red fluorescent protein cherry at the same time were collected, and the genome of the sorted cells was used as a template to perform PCR amplification and sequencing of the targeted site, and the single-base editing efficiency of the edited site was calculated.
[0106] Suc...
Embodiment 3
[0111] Example 3 Test the influence of the distance between the two-component recognition sites on the editing efficiency
[0112] In this example, an optimization test was performed on the distance of the two components at different gene loci.
[0113] from Figure 6A It can be seen that the efficient editing range of the AAVS1 site is between +6bp and +12bp in the tested editing distance of +4bp to +14bp, and the editing efficiency of the A6 site is as high as 87% when the distance is +6bp , followed by A5 efficiency of about 88% at +10bp.
[0114]When the distance is far away, such as +10bp, +11bp, +12bp, the editing efficiency of A5 is higher, and when the distance is closer, such as +6bp, +8bp, the editing efficiency of A6 is higher; the reason for this analysis is mainly because A5 is closer to the side of the TALE protein , the deaminase is closer to A5 when the distance is longer, resulting in higher editing efficiency than the A6 site. Similarly, only A4 was edited...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com