Wireless miniature fluorescent microscopic imaging device and application thereof
A fluorescence imaging and wireless technology, applied in the fields of application, analysis using fluorescence emission, image communication, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in realizing free activities, not allowing researchers to observe experimental data in real time, wired connection, etc., to avoid deviations in research results Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1: Wireless Miniature Fluorescent Microscopic Imaging Device
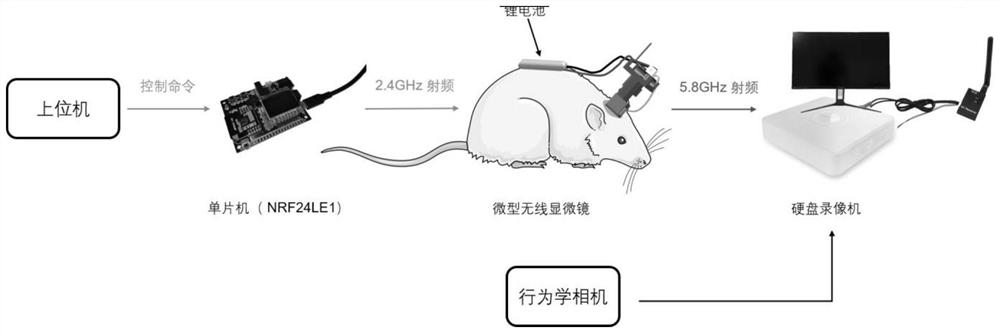
[0064] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a wireless miniature fluorescent microscopic imaging device, including a fluorescent imaging microscope, a wireless control unit, a wireless video transmission unit, a wireless video receiving unit and a video storage unit, wherein the wireless control unit includes a receiving control unit Components of end instruction and components of control fluorescence imaging microscope.
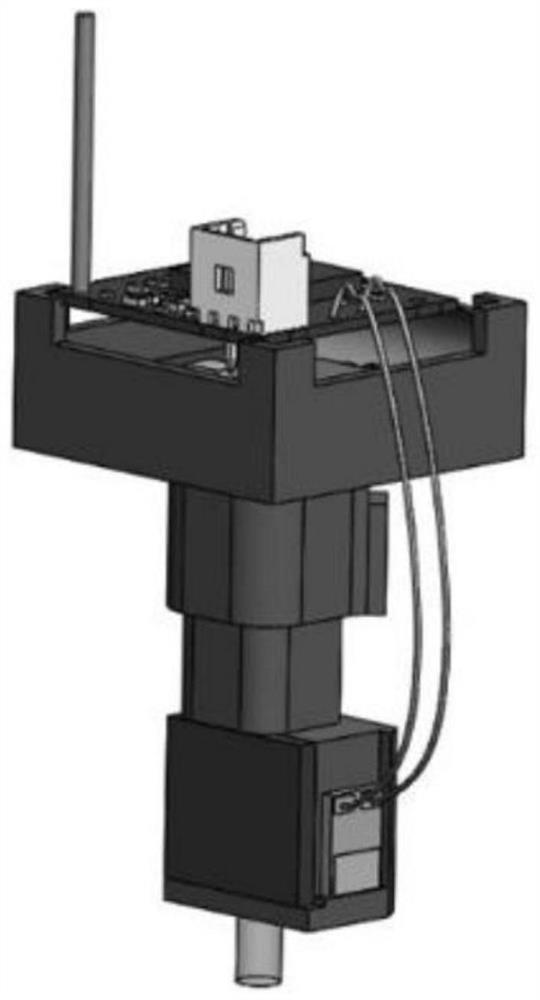
[0065] The miniature fluorescence microscope preferably includes a microscope illuminator, a number of independent optical components such as mirrors, micro-objective lenses, and filters, and an area array photodetector; the optical components are fixed together by a mechanical housing. Microscope illuminators are available with either monochromatic LEDs or fiber-coupled external lasers. By configuring different wavelength light sources and filter sets, fluorescenc...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Embodiment 2: the visual stimulation experiment of single mouse
[0078] The wireless miniature fluorescent microscopic imaging device in Example 1 was used to conduct a visual stimulation experiment of a single mouse.
[0079] The way the miniature microscope is fixed on the head of the mouse: All animal experiments were carried out in the animal center. Wild-type C57BL / 6 mice (male, 8-12 weeks old) were purchased from Vital River Laboratories (Beijing, China) and maintained on a 12 / 12-h reverse dark-light cycle. All experiments were performed during light cycling. Before surgery, mice were anesthetized with tribromoethanol (240 mg / kg, Sigma), and a craniotomy was performed on the primary visual cortex of the right hemisphere (Bregma coordinates: anteroposterior, -2.8 mm; middle, 2.5 mm; dorsoventral , 0.2 mm). After the craniotomy, a 1.8 mm diameter GRIN lens (Edmund Optics) was placed on the cortical surface without damaging the tissue. The gap between the GRIN l...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Embodiment 3: Photostimulation experiment of multiple mice
[0083] The light stimulation experiment of multiple mice was carried out using the wireless miniature fluorescent microscopic imaging device in Example 1.
[0084] Referring to the method in Example 2, the wireless miniature fluorescent microscopic imaging device in Example 1 was fixed on the heads of two mice.
[0085] Use a 50cm*50cm open field made of black acrylic, and paste black matte velvet to reduce the reflection on the inner wall, and install a circle of LED light strips at the bottom of the open field as a light stimulus. Since it is inconvenient to control the sight direction of the two mice in the free state, it is chosen to control the on and off of the LED light strip as the light stimulus. During the experiment, the LED light strip was turned on for 2 seconds and turned off for 18 seconds, and cycled sequentially. Each cycle time was 20 seconds, and the cycle was 20 times in total. At the same...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com