Method for constructing immune repertoire high-throughput sequencing library for removing chimera sequence in sample, group of primers and kit
A technology of immune repertoire and sequencing library, applied in primers and kits and its application in next-generation sequencing, and in the field of preparation of high-throughput sequencing library of immune repertoire, which can solve the problem that the antibody sequence cannot be clearly quantified and removed, and cannot be obtained from Distinguish issues such as chimeric antibody sequences on the sequence, to achieve the effect of correcting bias and accurate immune repertoire information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Obtaining sample RNA
[0040] 1. Human peripheral blood was collected using EDTA anticoagulant tubes, and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were separated by density gradient centrifugation;
[0041] 2. Use human naive B cell sorting kit (Stemcell, 17254) to sort and obtain human naive B cells
[0042] 3. Count human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and naive B cells and extract total RNA (Qiagen, 74106). The concentration is shown in Table 7.
[0043] Table 7
[0044]
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Human BCR repertoire library construction
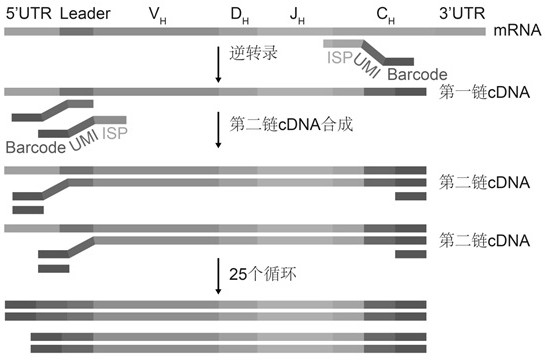
[0046] Using the total RNA obtained in Example 1 as a template, use the BCR subtype-specific primers with downstream Barcode and UMI to synthesize the first strand of cDNA by reverse transcription, and then use the leader region and V gene-specific primers with upstream Barcode and UMI The mixture is subjected to 1 cycle of PCR to realize UMI that is specifically paired with each template molecular marker in the sample, and then the upstream and downstream Barcode primers are used for unbiased amplification, as shown in the schematic diagram figure 1 , the specific process is as follows:
[0047] 1. cDNA synthesis by reverse transcription
[0048] Reverse transcription was performed using BCR subtype-specific primers (SEQ ID NO: 11-15, 23 and 35) with downstream Barcode and UMI, as follows:
[0049] a. Configure the mixed system according to Table 8, and carry out the reaction on the PCR machine. The reaction prog...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Example 3: Removing chimeric sequences in human naive B cell antibody repertoire sequencing data
[0086]The chimera sequence in the human naive B cell antibody library sequencing data in Example 2 was removed through the bioinformatics analysis process, specifically as follows Figure 4 .
[0087] 1. The off-machine data is identified and removed from the chimeric antibody sequences between samples by pairing Barcode;
[0088] 2. Based on the abundance distribution of UMI pairs, remove the chimeric antibody sequences in the samples that obey the poisson distribution;
[0089] 3. Re-cluster and establish consensus sequences based on CDR3s and UMI pairs, eliminate base errors introduced in PCR and high-throughput sequencing, and obtain real antibody sequences.
[0090] The amount of sequencing data before and after removing chimeras and constructing consensus sequences is shown in Table 15.
[0091] Table 15
[0092]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com