Method for separating and recovering diethyl phosphate sodium salt from fluorescent whitening agent synthesis liquid
A technology of fluorescent whitening agent and diethyl phosphate, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, compounds of Group 5/15 elements of the periodic table, etc., can solve the problem of large-scale processing and recovery of diethyl phosphate in enterprises Diethyl phosphate sodium salt, restricting the sustainable, healthy and stable development of fluorescent whitening agent enterprises, and the low recovery rate and purity of diethyl phosphate sodium salt, so as to increase the economic benefits of the enterprise, solve the recycling difficulties, and achieve the effect of simple recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
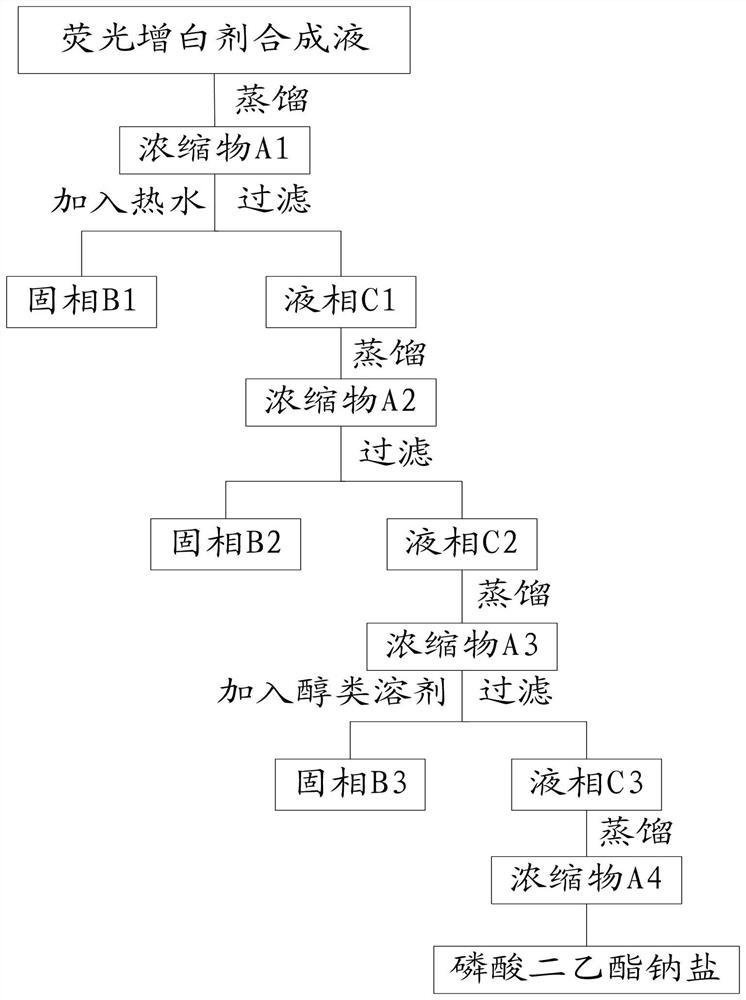
[0035] A method for separating and recovering diethyl phosphate sodium salt from fluorescent whitening agent synthetic liquid, comprising the following steps:
[0036] S1. Add 1000g of fluorescent whitening agent CBW synthetic solution into a 2L three-necked flask, which contains 180g of whitening agent CBW, 112.7g of diethyl phosphate sodium salt, 673g of organic solvents such as methanol, 34.3g of sodium chloride and other substances. Under a vacuum of 0.095MPa, distill under reduced pressure to a residual volume of 347g, and the residual solvent content is <5%.
[0037] S2. Add 680 g of deionized water at about 60°C to 347 g of the concentrate while it is hot, stir to dissolve completely, transfer it to a beaker, cool down, and filter under reduced pressure to obtain 250 g of filter cake and 777 g of filtrate. The filter cake is refined, washed and dried to obtain CBW semi-finished products.
[0038] S3. Distill 777g of the crude filtrate to a residual mass of 260g in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A method for separating and recovering diethyl phosphate sodium salt from fluorescent whitening agent synthetic liquid, comprising the following steps:
[0043] S1. Add 1500g of fluorescent whitening agent CBW synthetic solution into a 2L three-necked flask, which contains 270g of whitening agent CBW, 169.05g of diethyl phosphate sodium salt, 1009.5g of organic solvents such as methanol, 51.45g of sodium chloride and other substances. Under a vacuum of 0.096MPa, distill under reduced pressure to a residue of 520.5g, and the residue of solvent is <5%.
[0044] S2. Add 1040 g of deionized water at about 70°C to 520.5 g of the concentrate while it is hot, stir to dissolve completely, transfer it to a beaker, cool down, and filter under reduced pressure to obtain 380 g of filter cake and 1180.5 g of filtrate. The filter cake is refined, washed and dried to obtain CBW semi-finished products.
[0045] S3. Distill 1180.5 g of the crude filtrate to a residual mass of 260 g, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] A method for separating and recovering diethyl phosphate sodium salt from fluorescent whitening agent synthetic liquid, comprising the following steps:
[0050] S1. Add 1500kg of fluorescent whitening agent CBW synthetic solution to the 3000L reaction kettle, which contains 270kg of whitening agent CBW, 169.05kg of diethyl phosphate sodium salt, 1009.5kg of organic solvents such as methanol, 51.45kg of sodium chloride and other substances. Under a vacuum of 0.096MPa, distill under reduced pressure to a residual mass of 510kg, and the residual solvent content is <5%.
[0051] S2. Add 1000kg of deionized water at about 78°C to the 510kg concentrate while it is hot, stir to dissolve completely, transfer to a cooling kettle, cool down and crystallize, and filter through plate and frame to obtain 350kg of filter cake and 1160kg of filtrate. The filter cake is refined, washed and dried to obtain CBW semi-finished products.
[0052] S3. Distill 1160kg of the crude product fil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com