Method for preparing nano material by electrodeposition based on corrosion of amorphous alloy anode material
A technology of amorphous alloys and anode materials, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for materials and surface science, can solve the problem of poor electrical conductivity of electrode materials, unfavorable nanostructures, uneven corrosion elements, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of avoiding poor electrode conductivity, stable reaction system, and easy control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] (1) According to the Zr:Al:Co atomic ratio of 56:16:28, a total of 40 g of Zr, Al, and Co pure metals (purity 99.99%) were taken, and ultrasonic cleaning was performed with acetone and deionized water respectively to remove surface pollutants. The cleaned Zr, Al and Co pure metals are mixed in the crucible in the electric arc melting furnace, and smelted under an argon atmosphere, and the smelting current is about 180A. During smelting, both sides of the alloy ingot are smelted twice, each time for about 3 minutes.
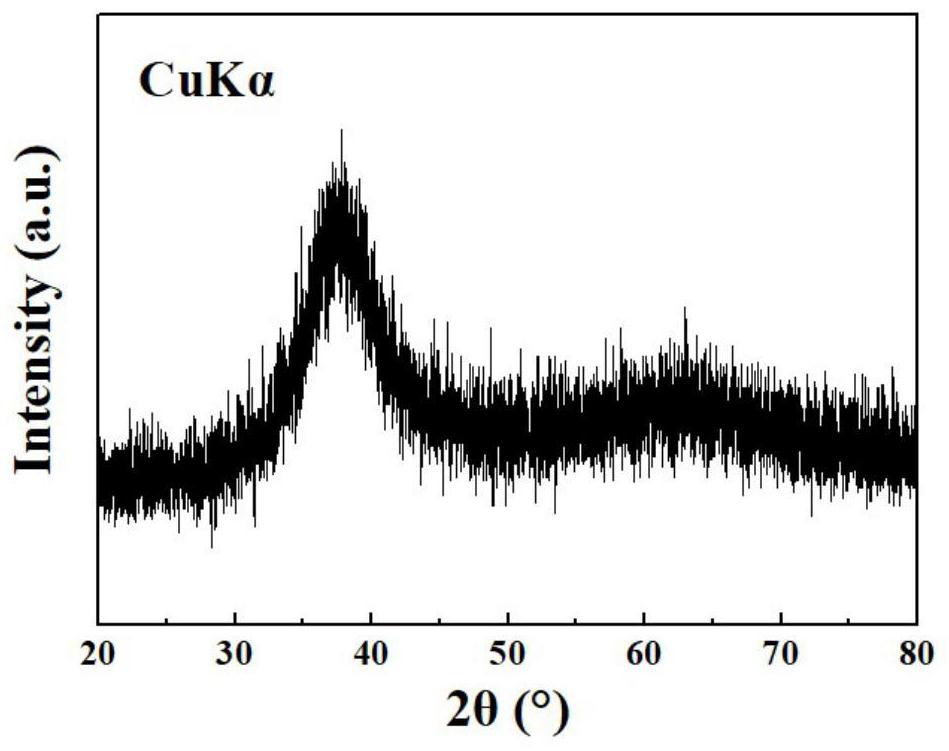
[0036] (2) Take Zr after smelting 56 Al 16 co 28 About 10g of the master alloy is placed at the bottom of a special quartz tube (diameter of the quartz tube is 16mm, and the bottom opening is 5mm). In an argon atmosphere, the ZrAlCo amorphous alloy strip is obtained by a single copper roll strip quenching method. The number of roll rotations is 2500 rpm, and the alloy is smelted to a molten state by induction heating for injection, and finally a Zr alloy...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Step (1) and step (2) are the same as the first embodiment, the polarization potential in step (3) is adjusted to 2.5V vs. SCE, and other conditions remain unchanged.
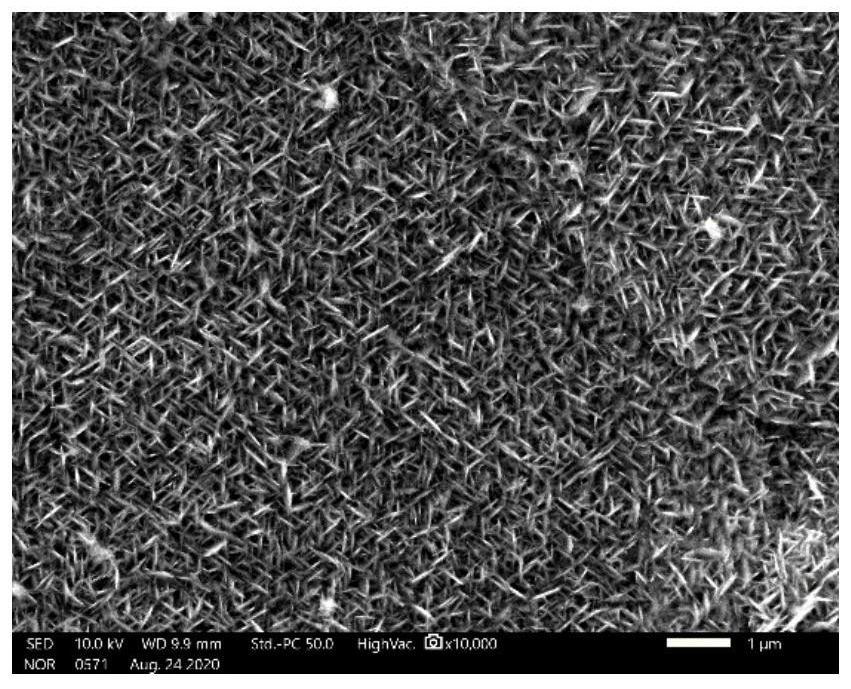
[0045] When the potential is raised to 2.5V vs. SCE, the deposition potential of Zr and Co elements is reached at the same time, and finally a nanosheet structure containing Zr and Co elements is obtained, which is also consistent with Zr 56 Al 16 co 28 At 2.5V vs. SCE potential, the amorphous alloy can achieve the expected deposition of Zr and Co elements, and the composition deposition is controllable. It looks like image 3 The content of each element is shown in Table 2.
[0046] The EDS data of table 2 embodiment two
[0047] Elements Wt% At% O 11.68 34.66 co 73.25 58.14 Zr 15.07 7.72 Total 100.00 100.00
Embodiment 3
[0049] Step (1) and step (2) are the same as in Example 1. In step (3), the working electrode is adjusted to Co simple substance with the same area, and the polarization time is 1 h.
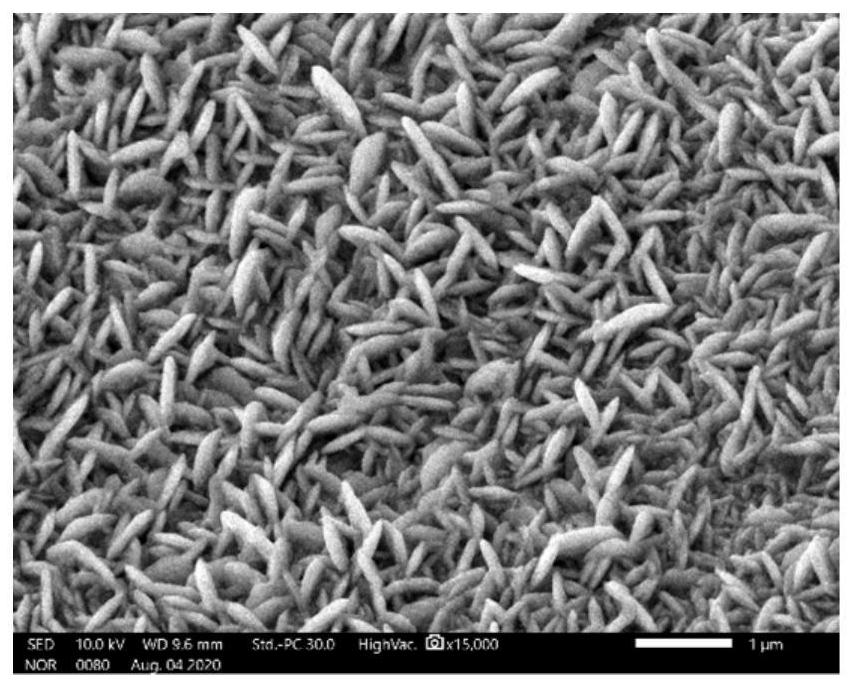
[0050] At this potential, the Co elemental working electrode corrodes very violently, and the reaction current is too large. Due to the excessively fast reaction rate, a large number of dendrites are formed on the foamed nickel substrate, and nanostructures cannot be obtained. The morphology is as follows Figure 4 The content of each element is shown in Table 3.
[0051] The EDS data of table 3 embodiment three
[0052] Elements Wt% At% O 8.54 25.59 co 91.46 74.41 Total 100.00 100.00
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com