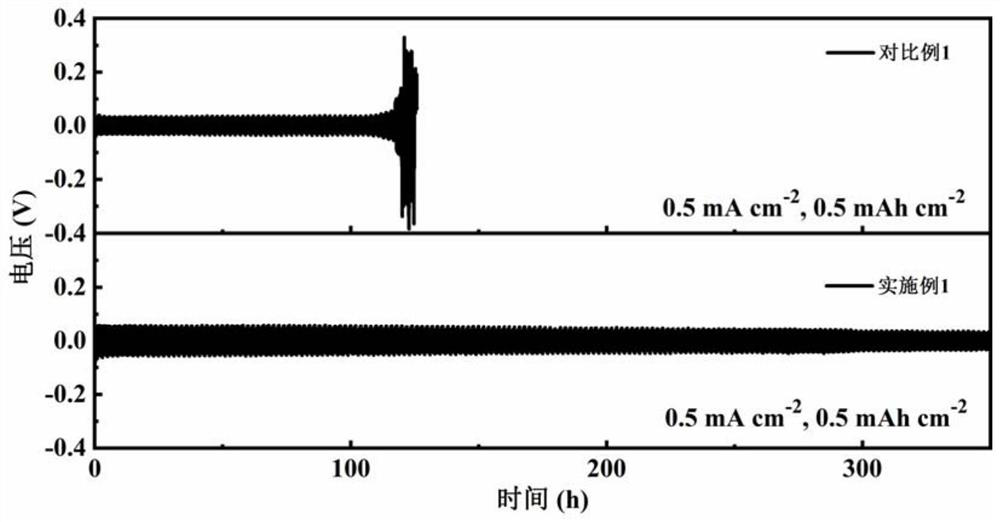
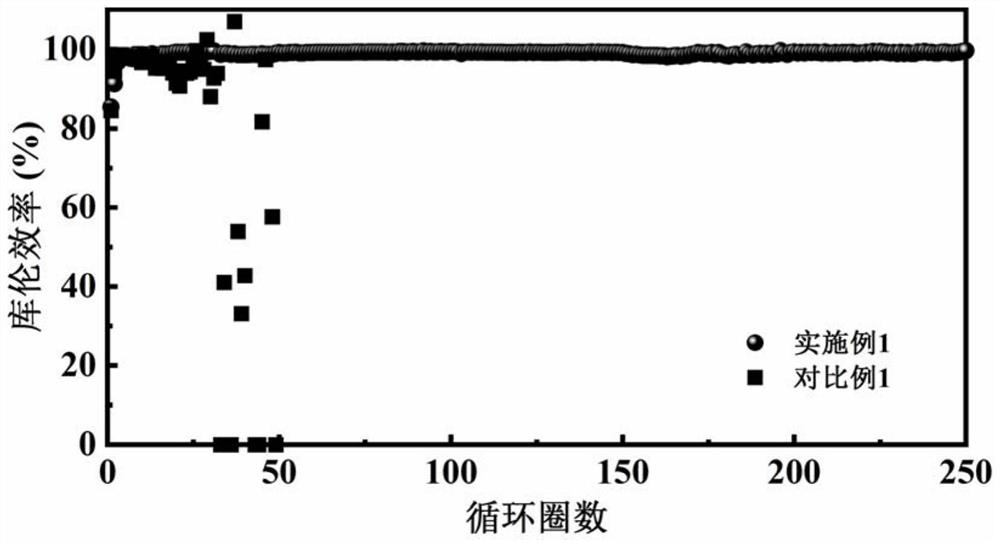
Polyanion zinc salt hydrogel electrolyte and zinc battery system
A gel electrolyte, polyanion technology, applied in aqueous electrolyte batteries, electrolyte immobilization/gelation, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as inhibition, zinc dendrites and side reactions, and achieve low cost and easy raw materials. the effect of high ionic conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] In this embodiment, a polyanionic zinc hydrogel electrolyte is prepared as follows:
[0025] Under the condition of 30°C, 13.6g AMPS was completely dissolved in 80mL deionized water. Then add 5g of zinc carbonate, dissolve evenly, and set aside. Dissolve 0.5g of divinylbenzene and diisocyanate, 0.1g of ketoglutaric acid in 80mL of deionized water, and irradiate with gamma rays for 1 hour to obtain polyanionic zinc hydrogel electrolyte.
[0026] In the present embodiment, adopt AMPS as organic monomer, AMPS (structural formula ) in the sulfonic acid group is substituted by the zinc ion in the zinc carbonate, and the organic acid zinc salt monomer with double bond is prepared, and its structural formula is as follows:
[0027] The polymer formed after the polymerization of the organic acid zinc salt monomer with a double bond has an anionic chain on the polymer skeleton, which plays a confinement effect on zinc ions, and at the same time restricts the free movement o...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is:
[0032] At 80°C, 10 g of AMPS was completely dissolved in 100 mL of deionized water. Then add 5.26g of zinc chloride, dissolve evenly, and set aside. Dissolve 5 g of boric acid, 5.26 g of zinc chloride, and 0.1 g of azobisisobutyronitrile in 100 mL of deionized water, and heat at 100° C. for 2 h to obtain a polyanionic zinc hydrogel electrolyte.
[0033] A zinc-air battery was assembled by combining the polyanionic zinc hydrogel electrolyte of this example with zinc foil and an air positive electrode. The resulting zinc-air battery can achieve 1000 charge-discharge cycles, and the discharge platform is maintained at about 1.5V.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is:
[0036] At 70°C, 7.6g of AMPS was completely dissolved in 20mL of deionized water. Then add 3g of zinc sulfate, dissolve evenly, and set aside. 1 g of divinylbenzene was dissolved in 20 mL of deionized water, and reacted under ultraviolet light for 0.5 h to obtain a polyanionic zinc hydrogel electrolyte.
[0037] A zinc-manganese dioxide battery was assembled by combining the polyanionic zinc hydrogel electrolyte of this example with zinc foil and manganese dioxide positive electrode, and the obtained zinc-manganese dioxide battery could cycle 200 cycles at a current density of 0.1A / g, and the capacity The retention rate was 92.3%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com