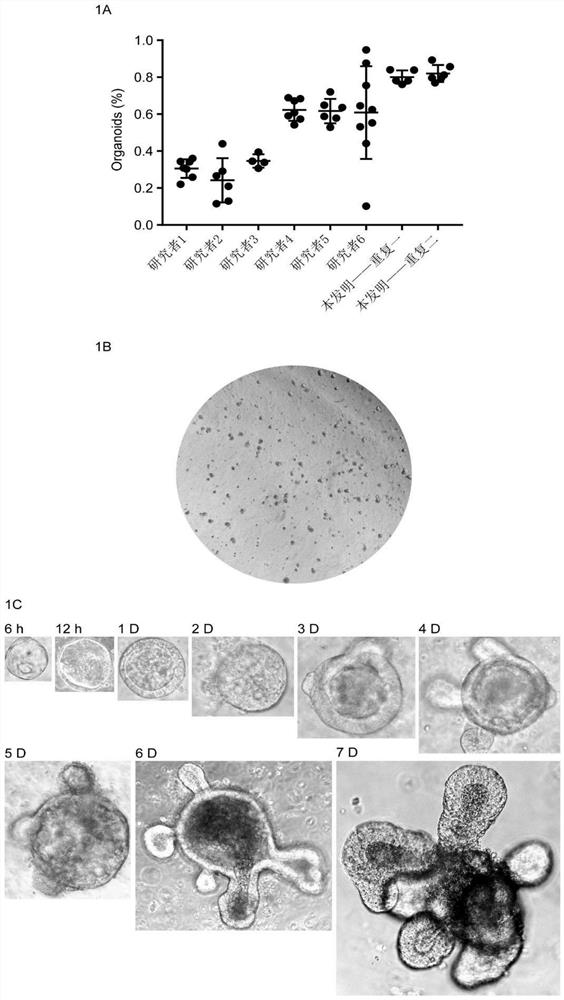
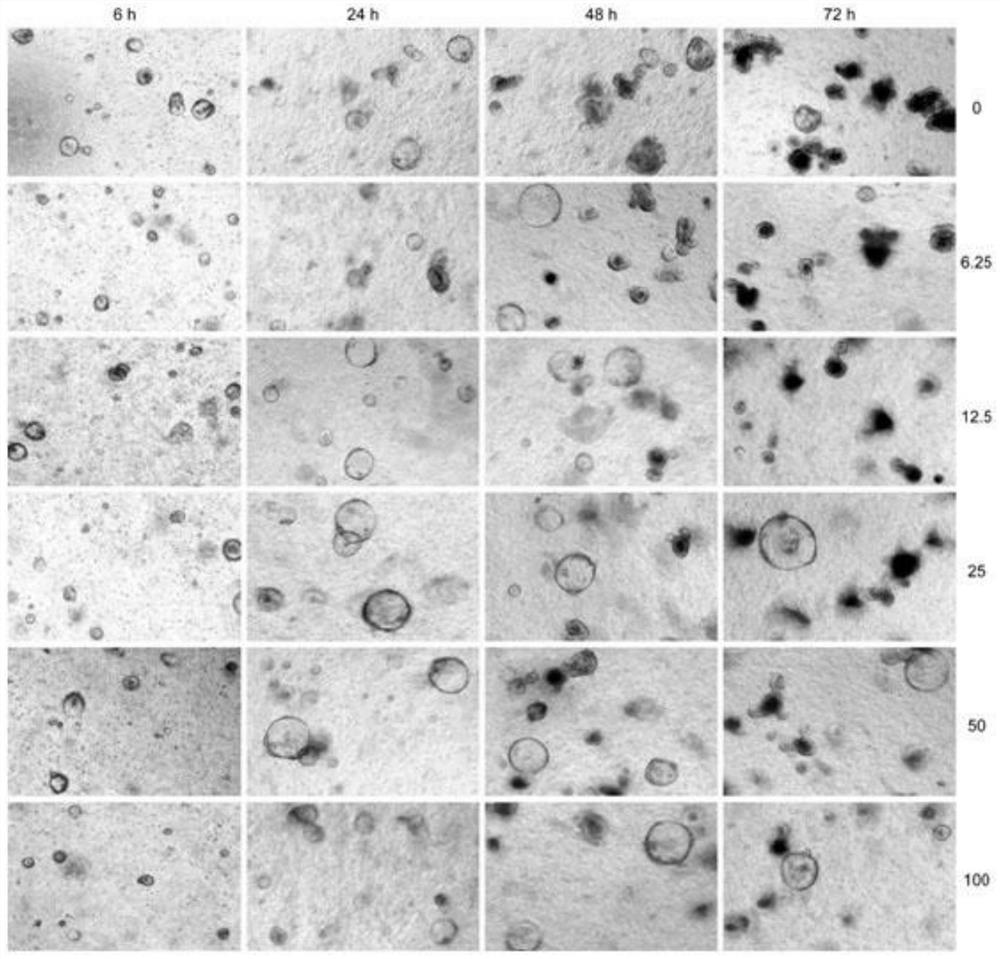
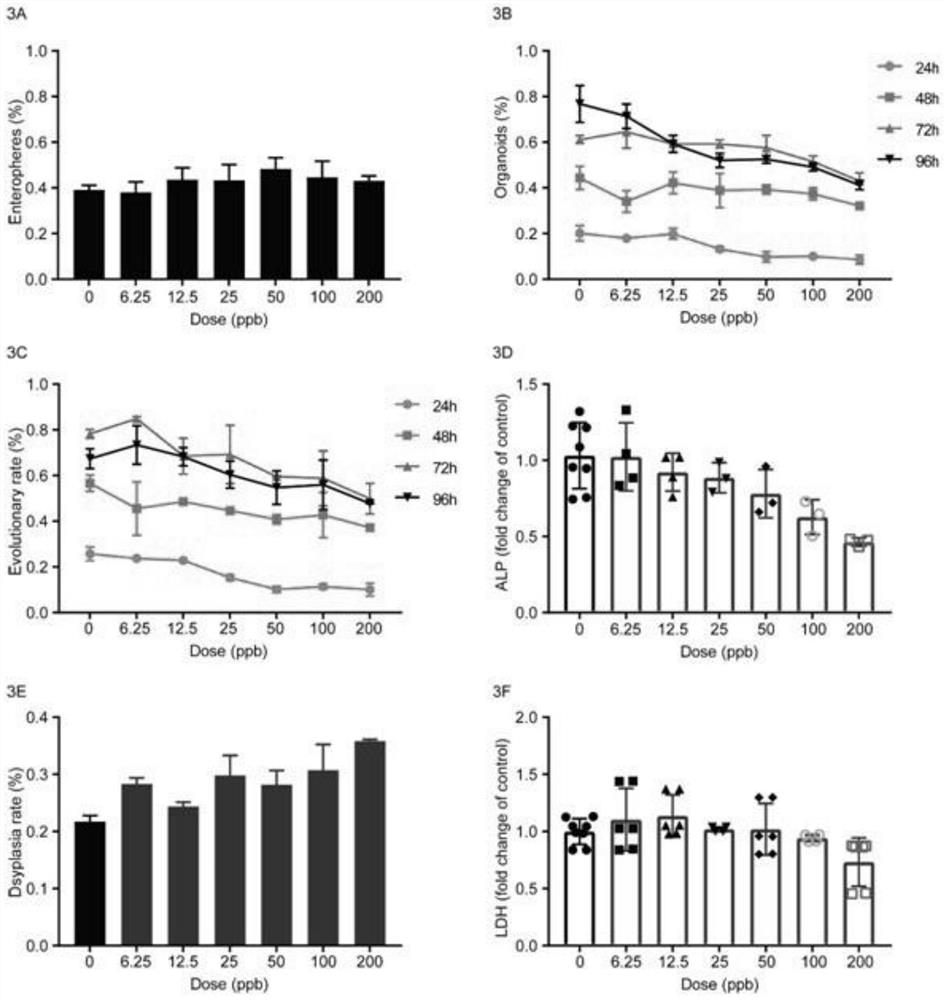
Culture method of intestinal organoids and application of intestinal organoids in intestinal toxicity test
A culture method and organoid technology, which is applied in the field of biosafety detection and evaluation, can solve problems such as the difference in the formation rate of intestinal organoids, and achieve the effects of sensitive toxicity response, expanded application range, and improved repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Culture method of mouse intestinal organoids
[0038] This embodiment provides a method for culturing mouse intestinal organoids, comprising the following steps:
[0039] 1) Separation of intestinal crypts in mice: after 6-10 weeks of mice were sacrificed, a jejunum section with a length of 10 cm was taken from the end near the stomach, and after the mesentery and fat were removed, the intestinal tissue was dissected longitudinally, rinsed and scraped off For intestinal villi, cut the intestinal tissue into 2-5mm long tissue fragments and transfer them to a centrifuge tube, wash them with cold PBS solution, add cold PBS solution containing 2mM EDTA to dissociate the tissue, and discard the supernatant after incubation on a shaker; Add cold PBS solution containing 0.1% BSA, shake vigorously to fully release the crypts from the tissue, take the supernatant and filter it through a filter with a pore size of 70 μm, collect the filtrate, and add cold PBS solution c...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 The method of using intestinal organoids to test the intestinal toxicity of heavy metals
[0043] This example provides a method for testing the intestinal toxicity of heavy metals using intestinal organoids, including the following steps:
[0044] 1) Intestinal organoids were obtained by culturing as described in Example 1;
[0045] 2) performing toxicity tests on the intestinal organoids treated with substances containing different concentrations of heavy metals, and measuring the change curve of the intestinal organoid model toxicity damage index with the concentration of heavy metals;
[0046] 3) Based on the dose-response relationship data obtained from the change curve, a Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation algorithm is used to establish a dose-response relationship curve, and the baseline dose corresponding to a 10% change in toxic effects is estimated.
[0047] In step 2) of this embodiment, the toxic damage of the cell model includes: clone formation...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3 Application of Intestinal Organoids to Evaluate the Enterotoxicity of Hexavalent Chromium at Environmental Exposure Levels
[0056] Hexavalent chromium (Cr-VI) is a typical environmental pollutant, and non-occupational people are often exposed to Cr-VI through ingestion and drinking. Acute exposure to large doses of Cr-VI will cause adverse health effects of the gastrointestinal tract such as irritation, diarrhea, and acute bleeding. Long-term low-dose exposure to Cr-VI will significantly increase the risk of gastrointestinal tumors. Cr-VI has been listed as one of the priority water pollutants by many countries. At present, as the current health standard in China, the maximum allowable pollution level of Cr-VI in drinking water is 50 μg / L. However, due to fluctuations in seasonal precipitation and industrial production, the concentration of hexavalent chromium in drinking water in many regions often exceeds the standard. Therefore, the environmental polluti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com