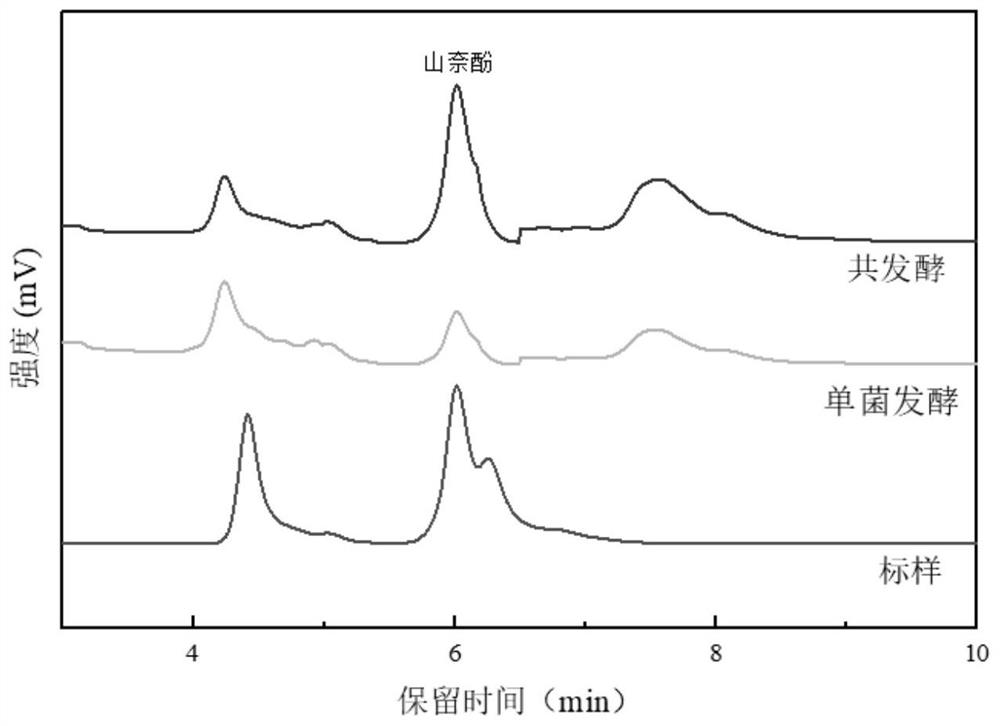
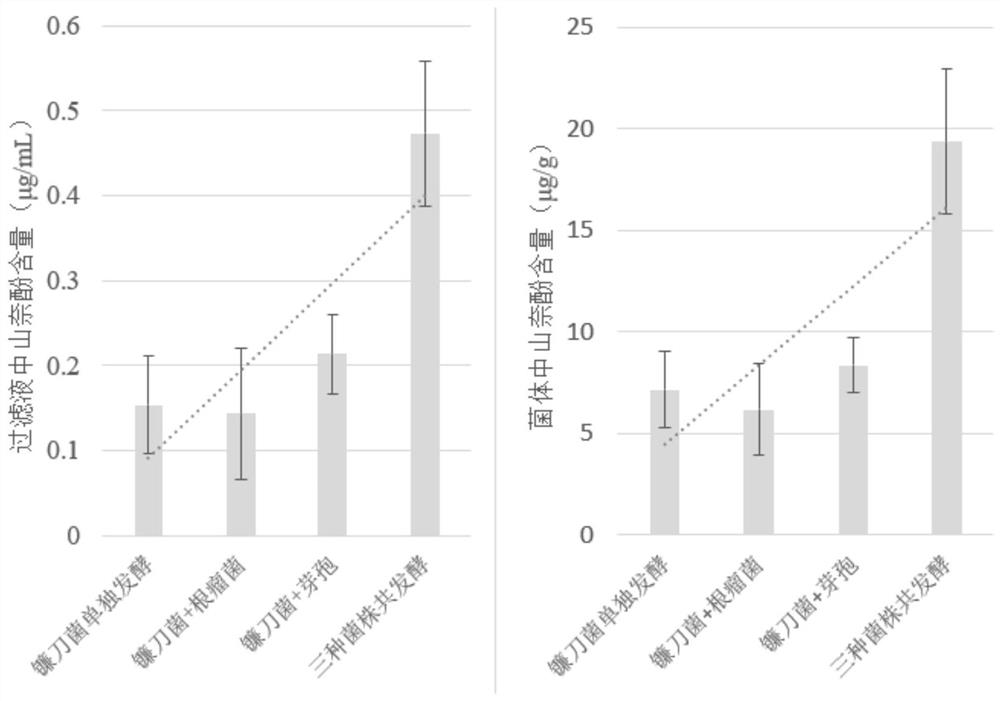
Functional flora for producing kaempferol as well as preparation and application of functional flora
A technology of functional bacteria and kaempferol, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, fungi, etc., can solve the problems of inability to directly utilize natural raw materials, high application cost, and high complexity of fermentation process, and achieve the promotion of industrialization development and cost. The effect of low and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Preliminary screening of functional microorganisms
[0027] In order to solve the problems of serious pollution and high cost in the production process of kaempferol, it is first necessary to select a suitable strain. According to the existing research basis, the Fusarium spp. producing kaempferol was determined as the main fermentation strain. The co-fermentation strain mainly considers that it has the ability to hydrolyze the cell wall, change the permeability of the cell membrane, and withstand pressure (adapt to harsh fermentation conditions), can antagonize chloramphenicol, can produce a large amount of biofilm, and can coexist with Fusarium. And the growth and metabolism are strong. The main focus has been on various Bacillus species and Rhizobium species. Further, to reduce the antagonism between strains and exert their synergistic effect, mainly select Bacillus and Rhizobium to co-ferment together. The co-fermentation effects of different combinati...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: Composition and source of functional microorganism
[0038] The microorganisms involved in the present invention are all purchased from various bacterial species preservation banks, respectively Fusarium solani ATCC 36031, Bacillus velezensis DSM 28326, Bacillus pumilus ATCC 7061, Bacillus subtilis Bacillus subtilis ATCC6051, Rhizobium alamii LMG 24466 and Rhizobium mesosinicum LMG 24135.
[0039] The strains purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) in May 2018 include: Fusarium solani ATCC 36031, Bacillus pumilus ATCC 7061, and Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051.
[0040] The strains purchased from the German Microorganism and Cell Collection (DSM) in October 2017 include: Bacillus velezensis DSM 28326.
[0041] Purchased from the National Type Culture Collection (NTCC) in October 2017, including: Rhizobium alamii LMG 24466 and Rhizobium mesosinicum LMG 24135.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: the cultivation method of each microbial strain
[0043] Bacillus Velez and Rhizobium sinensis were inoculated into the culture medium to obtain seed solution. The culture conditions were: temperature 26°C, rotation speed 160rpm, initial pH value 7.0, dark culture to logarithmic phase. For the entire fermentation process of the Fusarium, the separate culture conditions in the early stage are that the temperature is 26°C, the rotation speed is 160rpm, the initial pH value is 6.5, and the dark culture time is 3 days; The medium used was all potato dextrose medium supplemented with 0.12g / L chloramphenicol.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com