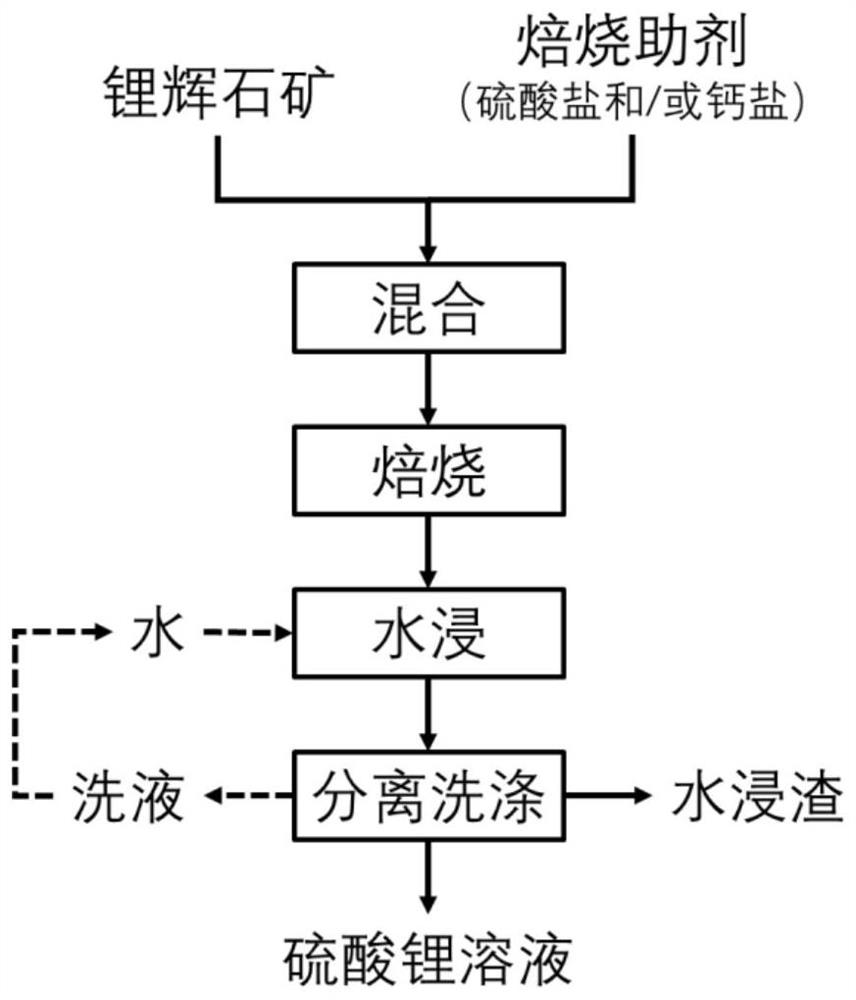
Method for producing lithium sulfate solution by spodumene sulfate roasting method
A sulfate and lithium sulfate technology, applied in the field of lithium extraction from ores, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, large by-products, and complicated impurity removal in high-temperature calcination, and achieve the effect of simplifying subsequent impurity removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Will Li 2 Spodumene ore with an O content of 6.1% (mass fraction) and sodium sulfate were mixed evenly by dry ball milling at a mass ratio of 1:0.9, and placed in a muffle furnace for constant temperature roasting at 980 ° C for 30 min. After cooling to room temperature, the roasted material was crushed and ball-milled, leached with water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 0.05 g / mL at 35°C for 120 min, and filtered to obtain a lithium sulfate solution.
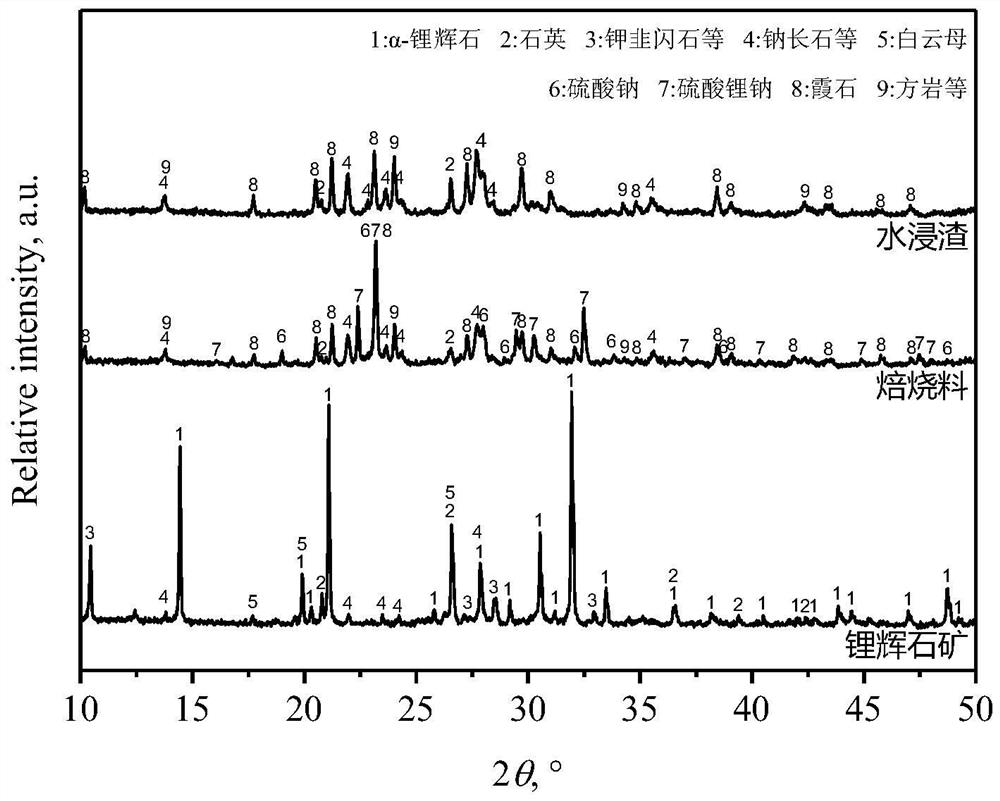
[0036] according to figure 2 , when spodumene ore and sodium sulfate are mixed and roasted under the above conditions, α-spodumene reacts with sodium sulfate to generate lithium sodium sulfate. After water immersion, lithium sodium sulfate is dissolved and leached by water. After water immersion, the impurity ion content of the solution is K 18.8mg / L, Ca27.5mg / L, Mg 10.1mg / L, Si 18.3mg / L, Al 6.4mg / L, of which about 92% of the lithium in α-spodumene is transformed into a water-soluble lithium salt.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Will Li 2 Spodumene ore with an O content of 6.1% (mass fraction) and sodium sulfate were mixed evenly by dry ball milling at a mass ratio of 1:0.1, and placed in a muffle furnace for constant temperature roasting at 1050°C for 120min. After cooling to room temperature, the roasted material was crushed and ball milled, leached with water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 0.05 g / mL at 35°C for 60 min, and filtered to obtain a lithium sulfate solution.
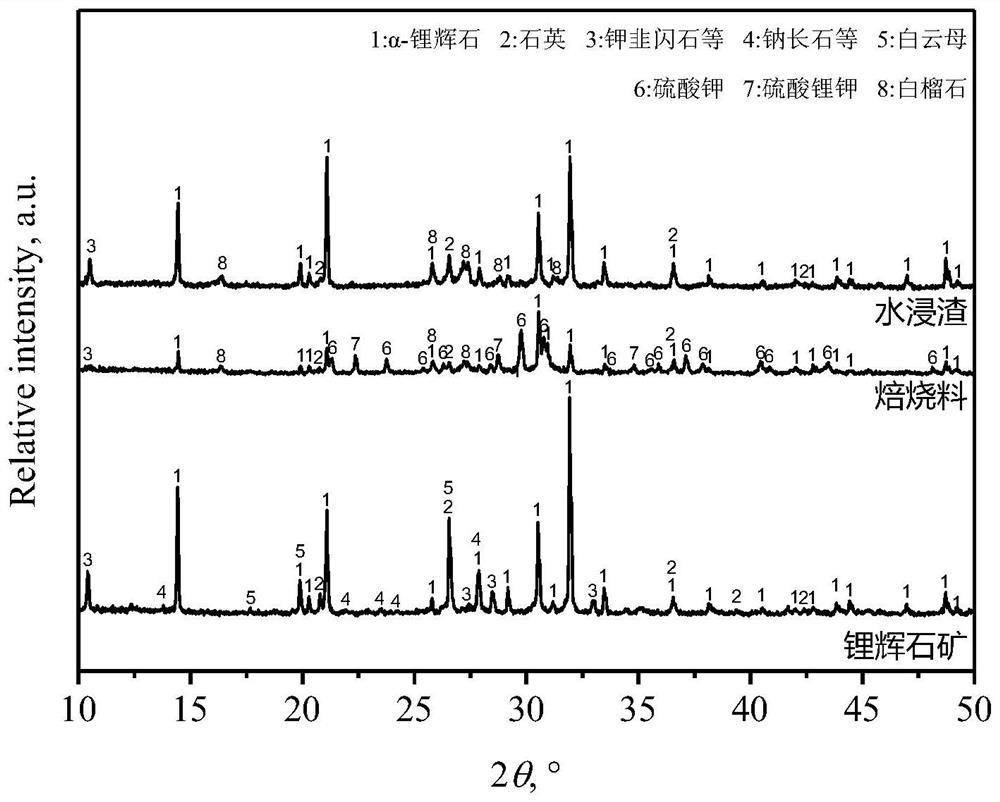
[0039] The XRD pattern of roasted material and water leaching residue and figure 2 Similarly, when spodumene ore and sodium sulfate are mixed and roasted under the above conditions, α-spodumene reacts with sodium sulfate to form lithium sodium sulfate. After water immersion, lithium sodium sulfate is dissolved and leached by water, of which about 80% α- The lithium in the spodumene is transformed into a water-soluble lithium salt.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Will Li 2 Spodumene ore with an O content of 5.3% (mass fraction) and sodium sulfate were mixed evenly by dry ball milling at a mass ratio of 1:3, and placed in a muffle furnace for constant temperature roasting at 700 °C for 50 min. After cooling to room temperature, the roasted material was crushed and ball-milled, leached with water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 0.05 g / mL at 35°C for 120 min, and filtered to obtain a lithium sulfate solution.
[0042] The XRD pattern of roasted material and water leaching residue and figure 2 Similarly, when spodumene ore and sodium sulfate are mixed and roasted under the above conditions, α-spodumene reacts with sodium sulfate to form lithium sodium sulfate. After water immersion, lithium sodium sulfate is dissolved and leached by water, of which about 78% α- The lithium in the spodumene is transformed into a water-soluble lithium salt.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com