Application of NADPH oxidase 2 as therapeutic target in preparation of medicine for treating vascular dysfunction
A technology for dysfunctional and oxidative enzymes, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as functional impairment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
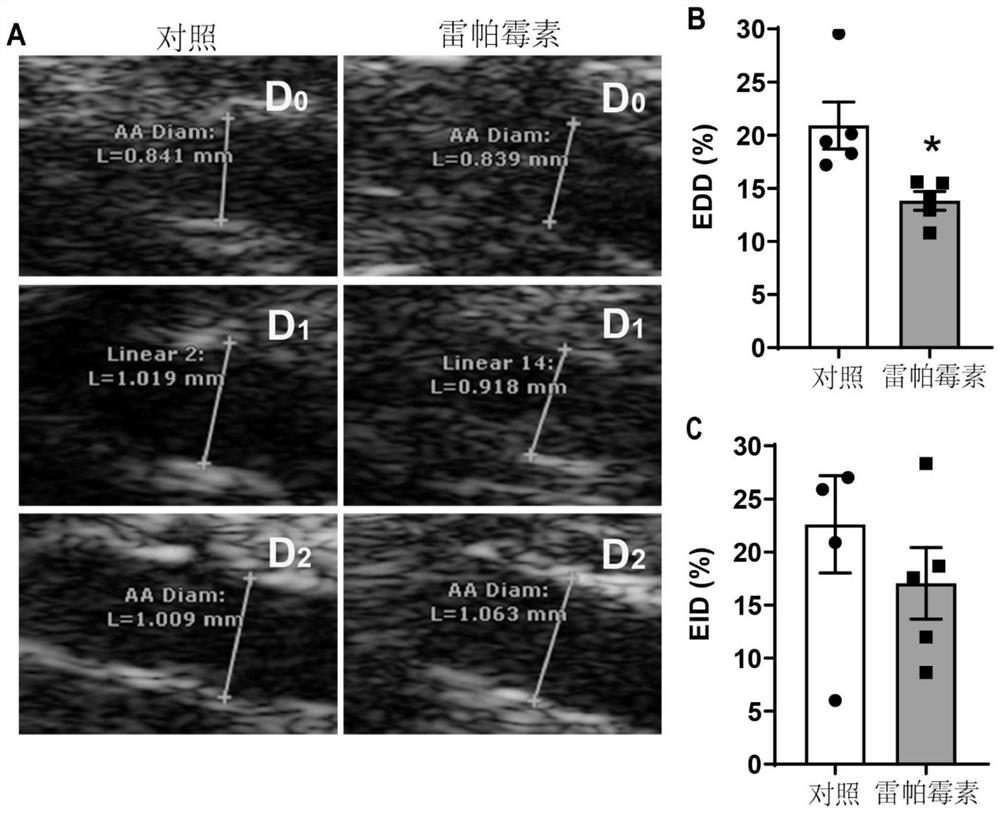
[0037] Example 1, intraperitoneal injection of rapamycin damages mouse aortic EDD function
[0038] C57BL / 6 background mice were randomly divided into control group and treatment group. The mice in the control group were intraperitoneally injected with corn oil, and the mice in the treatment group were injected intraperitoneally with 2 mg / kg body weight of rapamycin, which was similar to the blood concentration achieved by clinical use of rapamycin. After the mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 1% pentobarbital sodium (60 mg / kg), they were placed in a supine position, their abdomen was shaved, and couplant was applied. The end-diastolic diameter of the abdominal aorta was detected with an ultrasound instrument (Vevo 770). During the measurement, the ultrasound probe remained at the same position, and the average values of the three cardiac cycles were taken. First, measure the inner diameter of the abdominal aorta (denoted as D 0 ), and then tied the rig...
Embodiment 2
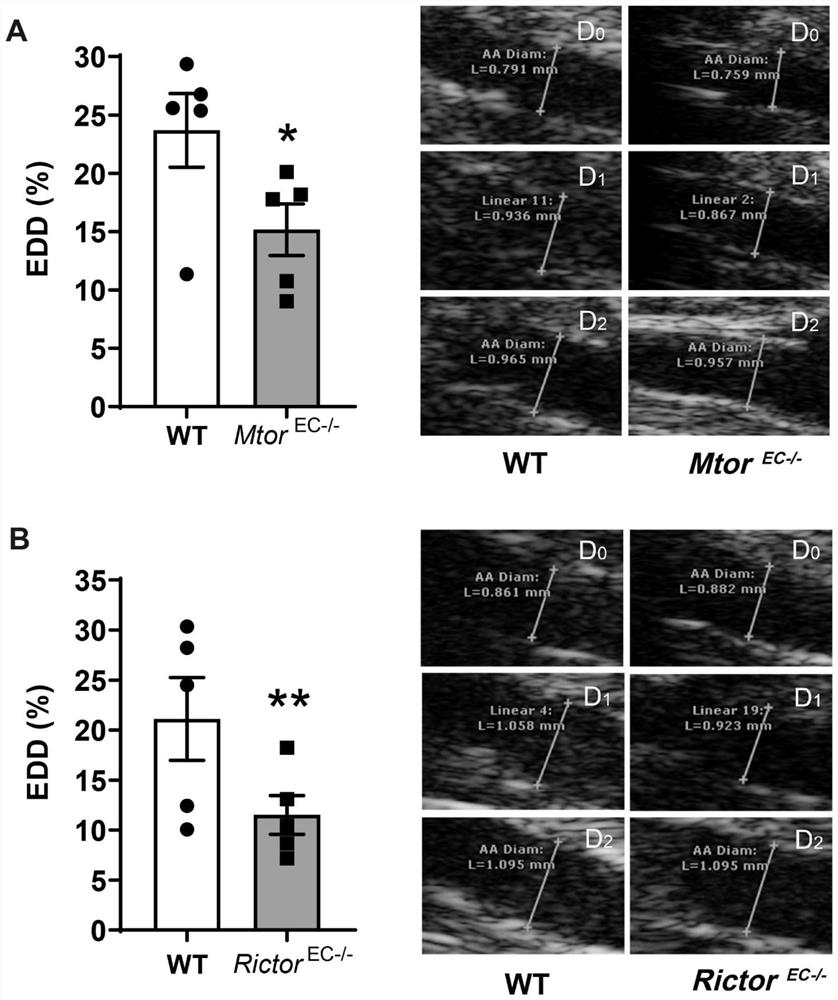
[0039] Example 2. Knocking out the Mtor gene in EC to inhibit mTOR, or the Rictor gene to inhibit mTORC2, both damage the mouse aortic EDD function
[0040] Mtor flox / flox and Cdh5Cre ERT2 After the mice were crossed, the EC-specific Mtor gene knockout mice (Mtor EC- / - ) and its control (WT) mice. Likewise, Rictor flox / flox and Cdh5Cre ERT2 After the mice were crossed, the EC-specific Rictor gene knockout mice (Rictor EC- / - ) and their control mice. Select about 6 weeks Mtor EC- / - and Rictor EC- / - and wild-type mice of the same age and sex, and induced EC-specific gene knockout by intraperitoneal injection of tamoxifen for a week. Transcutaneous ultrasound examination of vasomotor function was the same as above.
[0041] result( figure 2 ) shows that knocking out the Mtor gene in EC to inhibit mTOR, or knocking out Rictor in EC to inhibit mTORC2, both damage the mouse aortic EDD function. %. This suggests that mTORC2 is involved in maintaining normal arterial EDD ...
Embodiment 3
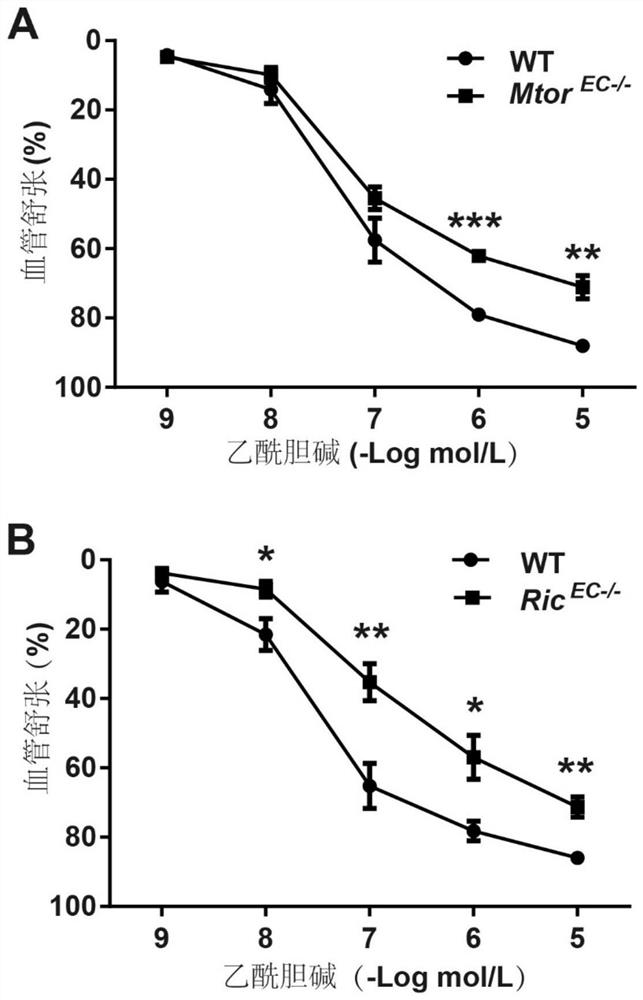
[0042] Example 3. Inhibition of mTOR or mTORC2 significantly reduces the EDD function of isolated vascular rings
[0043] Mtor processed from Example 2 EC- / - or Rictor EC- / - and its control mice to isolate the aortic vascular ring, with 10 -9 ~10 -5 Acetylcholine (Ach) with a mol / L concentration of 10 times as a gradient induced EDD respectively, and was detected by an isolated blood vessel tonometry (Myograph). result( image 3 ) showed that the deletion of mTOR or Rictor in EC significantly reduced the degree of EDD in the aortic vascular ring, which was consistent with the above in vivo experimental results, and further supported the conclusion that the above mTOR-inhibiting drugs inhibited the function of EDD by inhibiting mTORC2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com