Method for screening SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) sites and application thereof
A locus and candidate locus technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as small target range, uneven genome distribution, and inability to obtain heterozygous loci.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] A method for screening multi-purpose SNP sites, which includes the following steps.
[0079] (1) Obtain SNP candidate sites:
[0080] Select the sites that appear frequently in databases such as Thousand Genomes, ExAC, and gnomAD, that is, select points with an allele frequency (AF) of 40% to 60% as candidate sites, so that the selected sites can be used in different populations. The utilization rate is large and stable (that is, there are more loci showing heterozygosity in the population cases and the fluctuation between different people is small).
[0081] Then, according to the repetitive sequence information recorded in the human rmsk database, the mutation sites located in the repetitive sequence were removed to form a pre-set of SNP candidate sites.
[0082] (2) Formulate the primary selection panel: design a 120nt probe based on the 60 bp sequence information before and after the above SNP candidate site, remove the probe sequence that can be compared to more t...
Embodiment 2
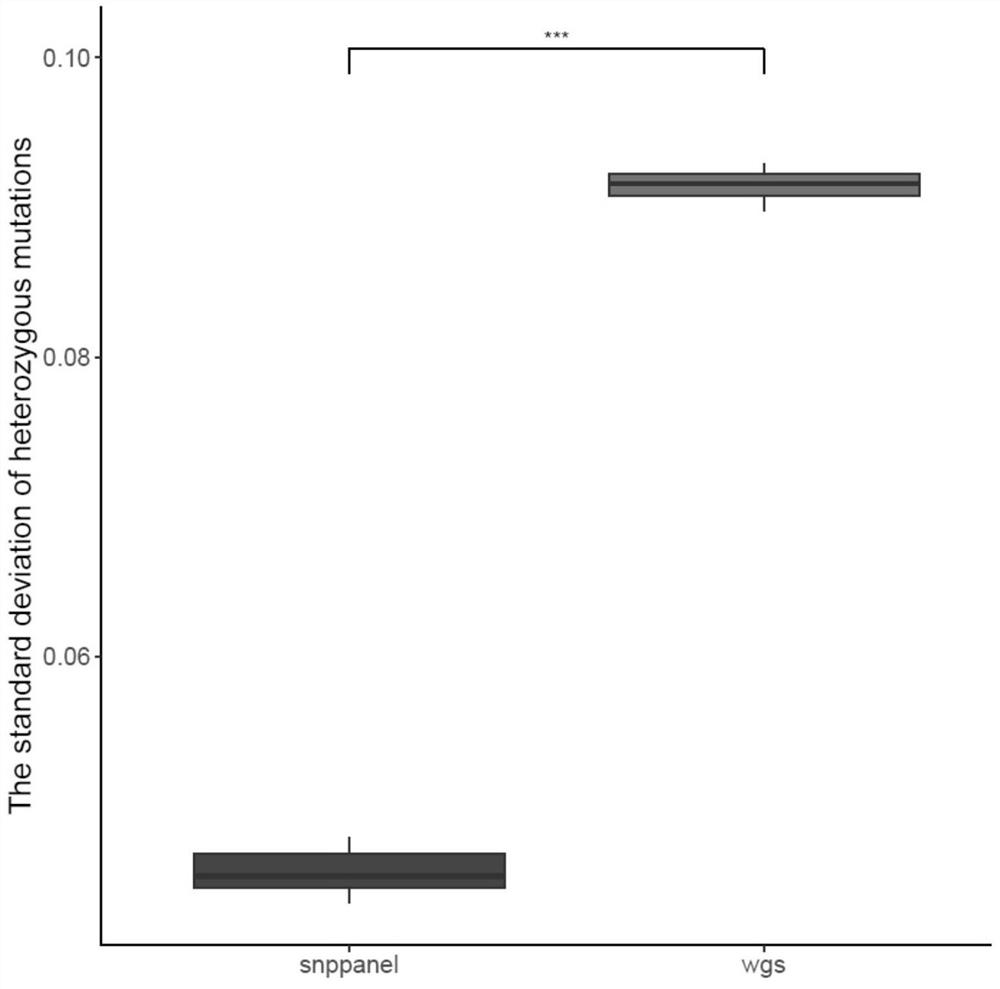
[0116] Detect the difference in the standard deviation of the mutation abundance of all heterozygous mutation sites in the SNP panel and the whole genome sequencing in 36 samples, the results are as follows figure 1 shown.
[0117] The present invention tests the SNP panel screened out by the present invention, the standard deviation of the heterozygous mutation frequency is 0.05957, the general panel gene region is 0.1247, and the WGS data is 0.0710. combine figure 1 It can be seen that the standard deviation of the mutation frequency of the SNP panel screened by the present invention is significantly lower than that of the whole genome sequencing, reflecting that the method of using the SNP panel can make the mutation frequency of the mutation site more stable.
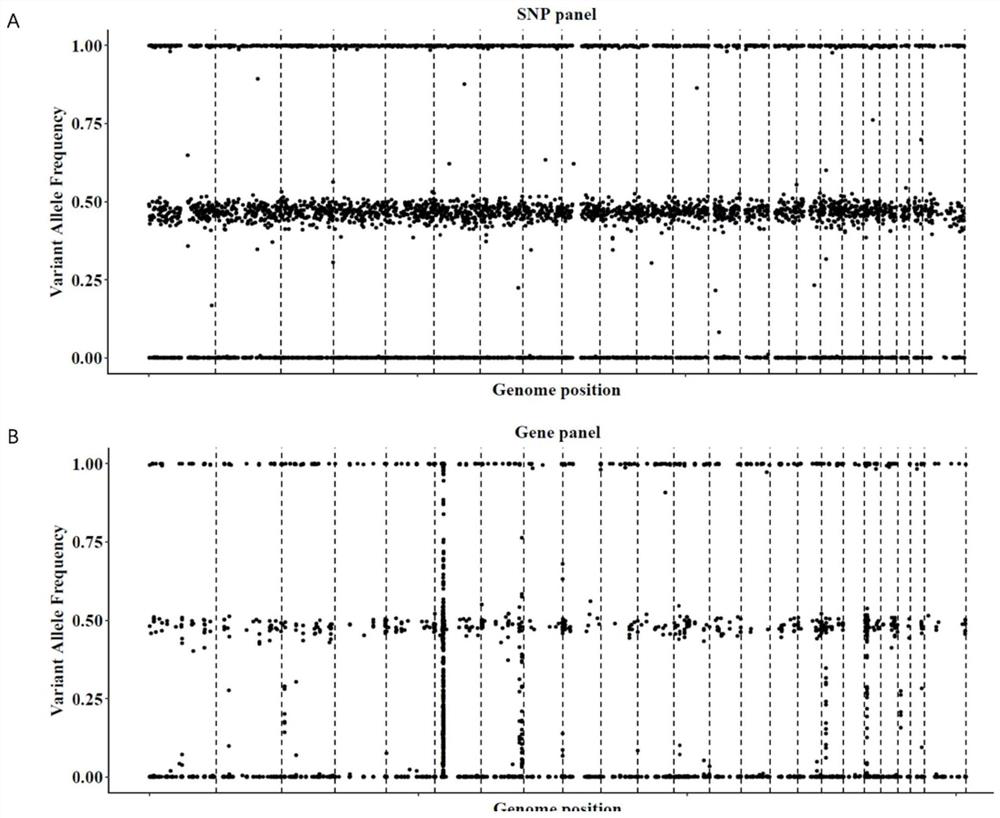
[0118] figure 2is the distribution of mutation sites in SNP panel and traditional Gene panel, where, figure 2 A is the result of SNPpanel, figure 2 Middle B is the result of the traditional Gene panel. From ...
Embodiment 3
[0120] Use the third-party software Conpair (Bergmann E A, Bo-Juen C, Kanika A, et al. Concordance and contamination estimator for matched tumor–normal pairs [J]. Bioinformatics (20): 3196-3198.) for contamination assessment, The evaluation samples were 88 contaminated samples with contamination levels from 0.6% to 27% and 95 non-contaminated samples. All sample data were target capture sequencing data containing our SNP panel sites.
[0121] Use the conpair software to perform contamination detection on these samples, set the markers parameter as the default or the SNP panel provided in Example 1 of the present invention to generate two sets of evaluation results.
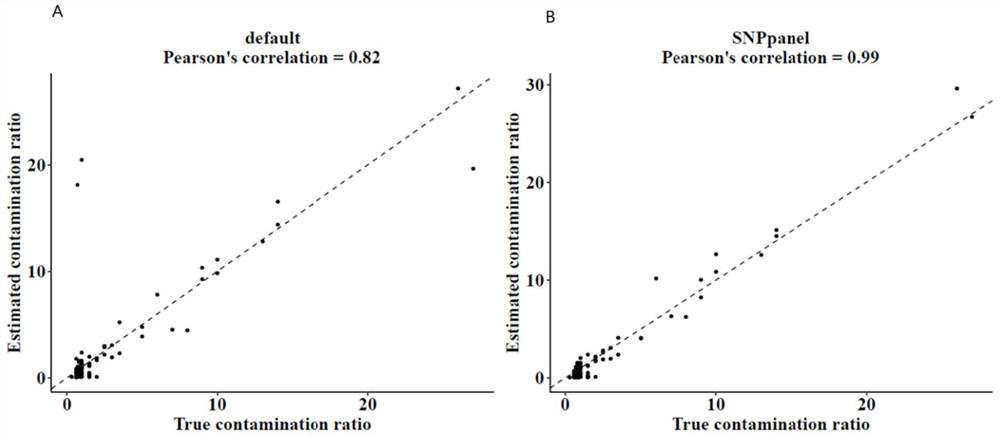
[0122] image 3 is the correlation analysis between two groups of evaluation results and real results of contaminated samples, where, image 3 A is the correlation analysis result of Compair, image 3 Middle B is the correlation analysis result of SNP panel. The result shows that the correlation between the res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com