CD7-CAR-T cell as well as preparation method and application thereof
A cell and antigen technology, applied in the field of CD7-CAR-T cells and their preparation, can solve the problems of knocking out CD7 molecules, weakened antigen-antibody binding force and stability, and long-term existence, achieving significant killing effect and avoiding self-contrast. The effect of killing and ensuring safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0090] The present invention provides the preparation method of the immune effector cells, which includes infecting the immune effector cells with the isolated nucleic acid or the vector of the present invention. Preferably, the present invention produces genetically engineered immune effector cells by introducing chimeric antigen receptors into immune effector cells, such as T cells.
[0091] It should be noted that methods for introducing nucleic acid or vector into mammalian cells are known in the art, and the vector can be transferred into immune effector cells by physical, chemical or biological methods. Physical methods for introducing vectors into immune effector cells include calcium phosphate precipitation, lipofection, particle bombardment, microinjection, electroporation, and the like. Chemical means for introducing nucleic acids or vectors into immune effector cells include colloidal dispersion systems such as macromolecular complexes, nanocapsules, microspheres, b...
Embodiment 1
[0107] This example is for the preparation of mouse monoclonal antibody against CD7 antigen.
[0108] In this example, 5 polypeptides were designed and synthesized for the CD7 antigen to immunize BALB / c mice respectively. After cell fusion, primary screening, and secondary screening, a positive clone was obtained that simultaneously recognized the polypeptide BST001-2 and CD7 recombinant protein. The clone number of the positive hybridoma cell line is 5B5.
[0109] The amino acid sequence of the CD7 antigen precursor protein is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein amino acid residues 26-180 are the extracellular domain of the CD7 antigen. The CD7 recombinant protein is a recombinant human CD7 protein (with a his tag, a product of Biopsies, the article number is 11028-H08H), and its amino acid sequence is the sequence of the extracellular domain of the CD7 antigen, as shown in SEQ ID NO:2.
[0110] The amino acid sequences of the five synthetic antigen polypeptides used to immunize ...
Embodiment 2
[0153] This example is for the construction of CD7-Blocker and CD7-CAR lentiviral expression vectors.
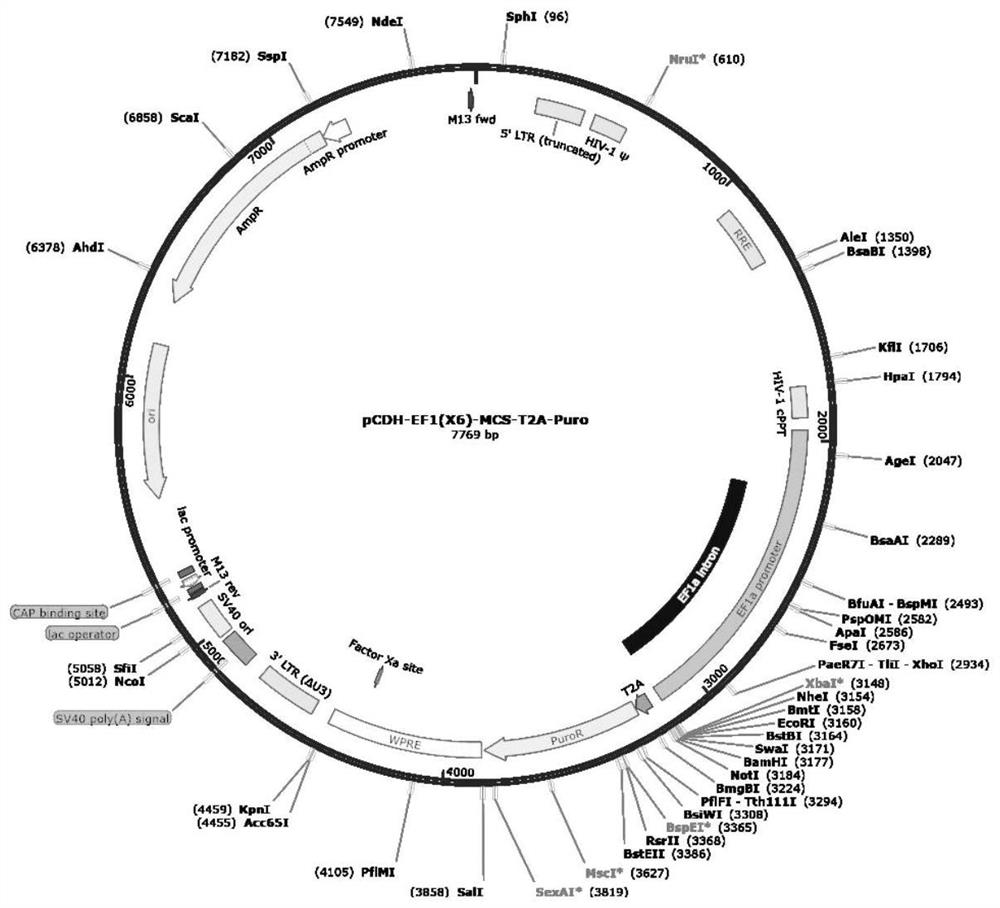
[0154] The CD7 blocking molecules CD7-Blocker and CD7-CAR were respectively constructed into the third-generation lentiviral expression plasmids by conventional technical means in the field. The plasmid is pCDH-EF1(X6)-MCS-T2A-Puro, and its map is as follows figure 1 As shown, the vector linearization restriction sites are XbaI and SalI, and the DNA sequences of CD7-Blocker and CD7-CAR (including the N-terminal KOZAC sequence) are inserted between the two restriction sites. The molecular structure of CD7-Blocker is as follows figure 2As shown, the CD7-Blocker molecule is composed of CD8a signal peptide SP, anti-CD7 scFv composed of (G4S)3 linker connecting VL and VH, and ER Retention Domain (endoplasmic reticulum localization domain). The front end of SP is inserted to promote expression The KOZAK sequence. Its full-length amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 18, a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com